During the past decade, a number of studies have demonstrated the importance of depressive disorder in suicide among elderly individuals
(1–
4). Major depressive disorder is more common among older people who commit suicide than among their younger counterparts
(4) and may affect as many as 83% of those who commit suicide late in life
(1). The importance of substance abuse in this age group is less clear, with figures ranging from 3%
(5) to 44%
(6).
Many older adults commit suicide in connection with their first depressive episode
(7). The relationship between different types of depressive disorder and suicide remains unclear, however. Depressive symptoms are common in the elderly
(8), and studies that employ representative control groups are lacking. The aim of the current study was to examine the relationship between different psychiatric disorders and suicide in individuals 65 years old or older. We hypothesized that single-episode major depressive disorder would be the diagnosis associated with the highest risk and tested this hypothesis by comparing the cases of a group of elderly subjects who had committed suicide with living population comparison subjects. Treatment history was also compared in the two groups.
Method
Subjects
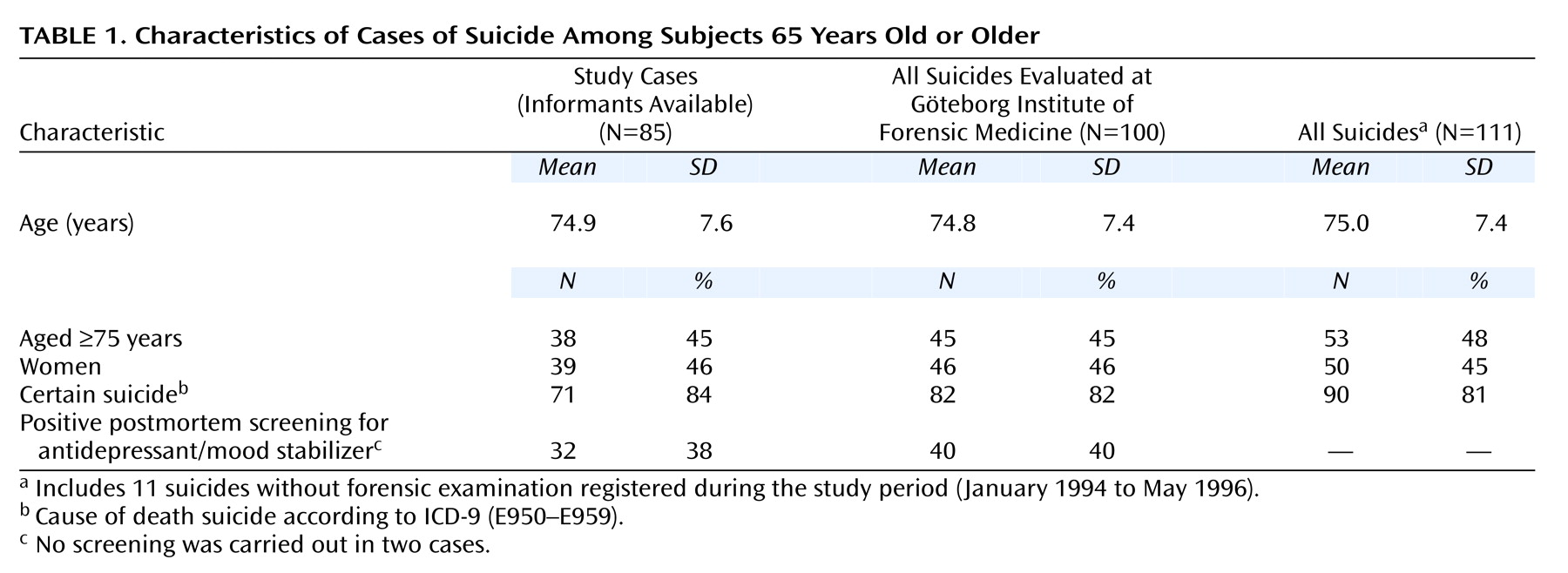
The cases of 100 elderly Scandinavian-born individuals who had committed suicide and were autopsied at the Göteborg Institute of Forensic Medicine were examined. Informants for 85 of these cases agreed to participate in the study; the cases were 46 men and 39 women whose median age was 73 years (range=65–97). The comparison group comprised 153 living subjects in the general population; these subjects were 84 men and 69 women whose median age was 77 (range=67–100). The catchment area included the city of Göteborg and two adjacent counties; the elderly population of the catchment area at the start of the study was 210,703.
Potential study cases were selected from deaths that the forensic examiner classified as certain suicide (ICD-9 E950–E959) or undetermined cause of death (ICD-9 E980–E989). After review of the police report and forensic data, two of us (M.W. and J.B.) made an estimate of the certainty of suicide (on a scale of 0–5) according to the Rating Scale for Determining the Degree of Certainty of Suicide
(9). We chose to include the first two categories, certain suicide (N=83) and almost certain suicide (N=17).
Death certificates for all suicides and undetermined deaths in the study area were obtained from Statistics Sweden. The forensic cases represented 90% of all suicides registered among Scandinavian-born elderly subjects during the study period (January 1994 to May 1996).
Next of kin or another person who knew the deceased well were identified from the police reports. They were informed about the study by telephone and then sent a letter containing more information. Primary informants (23 spouses, 27 adult children, seven siblings, nine other relatives, nine close friends, five home care assistants, and five visiting nurses/health care providers) for 85 cases of suicide agreed to participate. Eight of the 13 potential informants who declined to participate expressed concern that the subject matter was too difficult or too personal. Two others said they were too busy, and one was in poor health. Two declined without expressing a motive. No informant could be identified in two cases. Seventy-seven interviews with the primary informant were carried out in person; in eight instances, the primary informant declined a face-to-face interview but consented to a telephone interview. Twenty-eight of the 85 primary interviews were augmented by secondary interviews (26 telephone interviews, two face-to-face). All interviews with informants for the cases of suicide were conducted by a psychiatrist (M.W.).
Population Comparison Subjects
Two individuals living in the same area of residence and with the same sex and birth year (within 2 years) as the suicide case were randomly chosen from the tax roster. The selected individuals received a letter of information about the study and were then contacted by telephone. When an individual declined participation, a new person was invited to take part in the study (maximum of eight per case). Six potential comparison subjects could not be traced, and 87 declined participation (49 men with a mean age of 77.7, SD=7.3, and 38 women with a mean age of 77.9, SD=5.9). Reasons for nonparticipation included poor health (N=13), social reasons (N=8), and lack of interest (N=60). In all, 240 individuals were invited to take part in the study and 153 (64%) accepted.
Interviews with comparison subjects usually took place in the subject’s home and were carried out by a geriatrician (K.W.), a psychiatric nurse, or a psychiatric occupational therapist, all of whom had extensive clinical and interview experience. To reduce the risk of dropouts because of poor health, proxy interviews with close informants were carried out for 11 of the comparison subjects whose active participation was precluded by dementia (N=10) or psychosis (N=1).
Assessment Measures
The semistructured interview included questions about the subject’s social situation, life events, past and current mental and physical health, suicidal behavior, use of alcohol and illicit drugs, contacts with health services, and use of prescription drugs. The interview included psychiatric signs and symptoms in the past month derived from the Comprehensive Psychiatric Rating Scale
(10) and questions about dementia symptoms
(11). The same questionnaire was used in both telephone and face-to-face interviews.
Records from psychiatric facilities, primary care facilities, and other relevant disciplines were reviewed for the suicide cases. The comparison subjects were asked about previous health care contacts, and their medical records were requested on the basis of this information. Seven comparison subjects did not consent to the release of their records.
One of us (M.W.) made retrospective axis I diagnoses based on the diagnostic algorithms of DSM-IV. For the suicide cases, a symptom was rated as present during the last month of life if acknowledged by any source. For the comparison subjects, the interview and the case records provided the basis for assessment of mental symptoms in the past month. Only symptoms that caused significant distress or impairment of function were included. Suicide per se was not considered sufficient for an endorsement of the suicidality criterion (see DSM-IV criterion 9 for major depressive disorder).
A person was considered to have recurrent major depressive disorder if there was an interval of at least 2 months between the current episode and a past episode that met DSM-IV criteria for major depressive disorder. A person who currently fulfilled criteria for major depressive disorder and who had a past history of treatment for depressive disorder was also considered to have recurrent major depressive disorder. Minor depressive disorder was defined in accordance with DSM-IV research criteria, that is, an episode with depressed mood or decreased interest, fulfilling at least two (but fewer than five) A criteria for major depressive disorder. Nondemented subjects who experienced their first depressive episode in connection with stroke were considered to have depression due to a medical condition.
The anxiety disorder category included generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder not otherwise specified. Results for simple phobias are not shown. Substance use disorder was used to designate dependence or abuse of alcohol, sedatives, analgesics, or a combination of these drugs. Interview data and information from case records were used to diagnose dementia according to DSM-IV. We could not accurately identify cases of mild cognitive impairment with this approach, nor could we ascertain the specific etiological background in dementia. Cases with symptom constellations that did not fit the DSM-IV algorithms were given best-estimate diagnoses after discussion (with B.S.R.).
Physical illness was rated according to the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale—Geriatrics
(12) after review of medical records and interview data. This scale provides operationalized ratings of disability in 13 somatic organ categories. Each category is assigned a score of 0–4 in accordance with the organ-specific guidelines. Subjects were considered to have serious physical illness if they received a rating above level 2 in any category.
Statistical Analysis
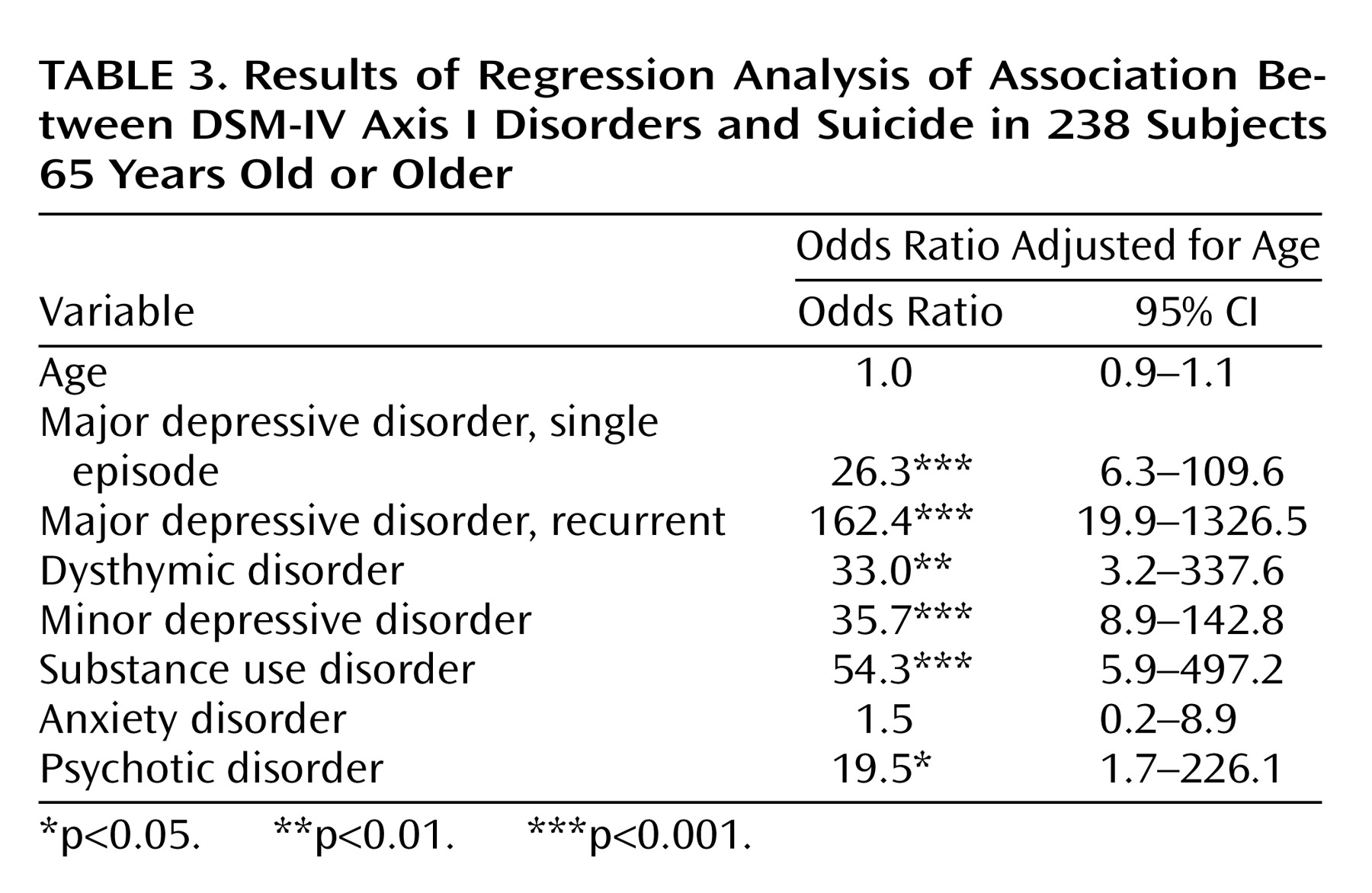
Odds ratios for suicide were calculated by applying logistic regression. Mental disorder variables that significantly affected odds ratios were analyzed in a multivariate logistic regression model (forward, conditional). All odds ratios were calculated with age as a covariate in the regression analyses because the comparison subjects were slightly older than the suicide cases as a result of a lag time between the suicide deaths and the interviews with comparison subjects. Fisher’s exact test was used to examine differences in proportions between subgroups when odds ratios could not be calculated. We performed all exploratory and formal statistical analyses with SPSS version 10.1 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago).
Ethics
Written informed consent was obtained from the informants and the comparison subjects after they had received oral and written information about the study, including an assurance that they could withdraw from the study at any time. For comparison subjects suffering from dementia, a close relative gave consent by proxy. The Research Ethics Committee at Göteborg University approved the study.
Discussion
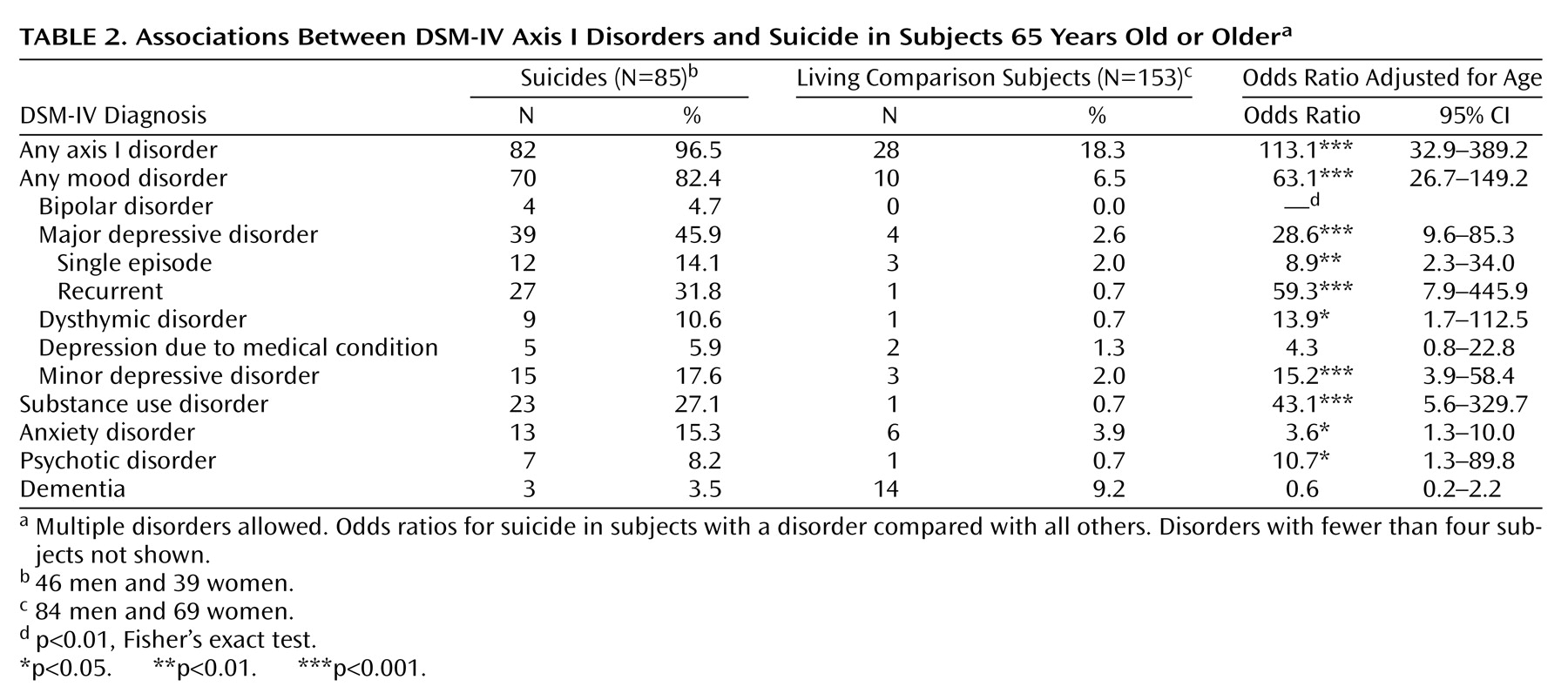
Most of the suicide victims in this study suffered from a depressive disorder at the time of their death, which is consistent with previous reports
(1–
5). We did not find support for the hypothesis that single-episode major depressive disorder would be associated with the highest risk of suicide, however. This was unexpected because earlier studies have stressed the importance of single-episode major depressive disorder
(5,
7). We thought that our conservative approach to the determination of depressive symptoms might explain the disparity, but recurrent major depressive disorder remained the mood disorder with the highest odds ratio even after data were reanalyzed with a more inclusive approach. A partial explanation for our disparate results might be the relative accessibility of records. Many of the suicide cases in the current study obtained psychiatric services in connection with previous episodes of illness; these episodes were documented in the records. Also, one can speculate that some vulnerable individuals might have committed suicide before they were old enough to be included in an elderly cohort.
We have demonstrated an elevated risk of suicide in subjects with dysthymic disorder and minor depressive disorder, which underlines the need for suicide risk evaluation even in elderly individuals who do not meet all criteria for major depressive disorder. The proportion of suicide victims with minor depressive disorder was similar to that reported for depressive disorder not otherwise specified in a study of elderly suicides in Finland (21%)
(3). Our inability to show an association between suicide and depressive disorder due to medical illness is probably attributable to small cell numbers.
We noted a strong association between substance use disorder and suicide. Although the role of substance abuse is well documented in mixed-age suicide cohorts
(13–
18), prevalence figures in elderly subjects who commit suicide vary widely. Several reports
(1,
3,
19) noted substance abuse in one-quarter to one-third of elderly suicide victims, which is similar to the proportion in our study.
In agreement with record-linkage studies of both mixed- age
(20) and elderly
(21) patients, we also observed that anxiety disorder was associated with suicide. However, none of the suicides in the current study had anxiety disorder as a sole diagnosis, and anxiety disorder was not independently associated with suicide in the regression model.
Depressive disorder, dementia, and delirium have been dubbed the three Ds of geriatric psychopathology. Although most of the suicide victims in our study suffered from symptoms of depressive disorder, few had dementia, and none of the suicides appeared to take place during an episode of delirium. Because of the proxy nature of the suicide interviews, we might have underdiagnosed dementia; however, the proportion of suicide cases with dementia in the current study is in line with several previous reports
(3,
4).
A high rate of comorbid disorders has been reported in elderly male suicides with major depressive disorder
(3). In the current study, comorbid disorders were relatively common in women as well. This was primarily attributed to superimposed depressive disorder in individuals with long-standing anxiety disorders.
Several uncontrolled studies have shown that elderly individuals who commit suicide tend to seek physicians for somatic complaints shortly before their deaths
(1,
2). A recent contact with a general practitioner or some other nonpsychiatric specialist was not associated with suicide in our study. However, psychiatric contact was more common than in previous studies
(1,
22), which may reflect differences in the availability of services and in help-seeking behavior
(23). We have previously reported that over two-thirds of the suicide cases had expressed suicidal feelings to their next of kin during their final year of life, but only 10% had communicated such feelings at their last doctor’s appointment
(24).
Half of the suicide cases had received treatment for depressive disorder during their final year of life. This finding, taken together with those of others
(25,
26), suggests that physicians have become more likely to recognize and treat depressive disorder in the elderly. However, not all suicidal elderly patients will respond to treatment, and even those who do respond may retain feelings of hopelessness
(27). Concomitant mental and physical disorders provide the clinician with a particular challenge.
Limitations and Strengths of the Study
One limitation of this study is that, although the participation rate for the suicide informants was high (85%) and the study cases appear to be fairly representative of all suicides among elderly subjects registered during the study period, the acceptance rate for the comparison subjects was only 64%. Individuals with mental disorders might be more likely to decline participation than others, resulting in inflated odds ratios for suicide.
A second limitation of the study is that proxy interviews were used for the suicide cases, which involves an inherent risk for false negatives attributable to memory effects, guilt feelings, and the stigma of mental illness
(28). Both the interviewer and the informant were aware of the suicide outcome, however, and certain associations might be anticipated that could lead to overreporting of psychiatric symptoms. Most of the comparison subjects were interviewed in person, which should reduce the risk of false negatives for current mental illness. However, some subjects may have declined to report previous episodes of mental illness.
Third, there was no formal test of measurement reliability; however, one psychiatrist made all diagnoses. There is evidence for the validity of psychological autopsy diagnoses
(29), but we stress that our results are not validated. The use of data from multiple sources, including psychiatric records, rendered our results less vulnerable to recall bias. Psychiatric records, which were available for 50 (59%) of the suicide cases, were authored by clinicians who were blind to the future suicide outcome.
Fourth, no adjustment was made for multiple comparisons; however, all analyses were based on plausible hypotheses regarding risk factors. Fifth, some of the diagnostic subgroups in our study were small, which is reflected in the very wide confidence intervals. There was a risk of false negative findings attributable to low statistical power. The number of individuals with mental disorder would have been greater had we chosen psychiatric patients as comparison subjects. However, such a highly selected comparison group would not reflect the distribution of mental and physical illness in the source population. A procedure involving deceased comparison subjects would pose similar problems.
Finally, survival effects influence the results in studies of the elderly, and some factors that were associated with suicide (i.e., psychiatric treatment) might actually increase survival. This limitation, however, is shared by all studies dealing with this age group.
To our knowledge, this is the first psychological autopsy study focusing specifically on elderly suicides to use population comparison subjects. The relative availability of medical records in a small country with a rather uniform health care system made it possible to trace episodes of mental illness that occurred decades before the suicide.
Divergent suicide rates, sex ratios, age distributions, culturally determined patterns of suicidal behavior, and health care delivery systems limit the generalizability of our results to other settings. The suicide rate for men 65 years old or older in the study area (38/100,000) was lower than the national rate (46/100,000) at the start of the study in 1994. The suicide rate for women 65 years old or older in the study area was identical to the national rate (19/100,000). On an international scale, Swedish suicide rates are at an intermediate level
(30).
Implications for Suicide Prevention
Our findings suggest that elderly individuals who commit suicide represent a heterogeneous group with regard to mental disorders, implying a need for differentiated prevention strategies. Detecting late-onset depressive disorder at the primary care level is one important approach to the prevention of suicide in late life. Interventions that target the needs of the elderly with other diagnoses such as substance abuse, recurrent depressive disorder, and comorbid anxiety disorder also require further development.