We recruited 10 healthy volunteers (nine men and one woman; mean age=41.6 years, range=20–67) who had no history of any DSM-IV axis I disorder according to the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. None acknowledged a history of depression in a first-degree relative. All subjects had been free of psychotropic medication for at least 3 months and gave written informed consent for the study, which was approved by the local ethics committee.
Subjects were scanned (eyes open) on two occasions (mean test interval=12.2 days, range=4–37) after receiving either intravenous citalopram (10 mg) or saline over 30 minutes in a randomized, double-blind, crossover design. MRS spectra were acquired from subjects between 40 and 65 minutes after completion of the infusion. The 10-mg dose of citalopram was chosen on the basis of a previous dose-response study that showed reliable 5-HT neuroendocrine responses in the absence of significant subjective side effects
(5).
To measure occipital total GABA (GABA and the GABA dipeptide homocarnosine), we applied a proton MR spectral editing technique based on a spatially localized (point-resolved spectroscopy
[6]) double-quantum filter
(7). This single-shot technique (256 averages, TR=3 seconds) allowed us to detect the GABA-CH
2 resonance (3 ppm) with suppression of uncoupled resonances from choline, creatine, and
N-acetylaspartate. The localized double-quantum filter method was implemented on a 3-T Varian-Inova spectrometer with a standard birdcage head coil; 27 cm
3 (3×3×3 cm
3) voxels were placed in the occipital lobe region guided by T
1-weighted axial images. We studied the occipital lobe because it offers clear landmarks for consistent placement of the spectroscopic voxel and is removed from major sources of static magnetic field inhomogeneities in the head, allowing narrower spectroscopic line widths to be achieved. We also acquired a standard point-resolved spectroscopy spectrum (TE=68 msec, TR=3 seconds) in order to measure signal intensities from choline, creatine, and
N-acetylaspartate. Three-dimensional structural images (T
1-weighted, gradient echo imaging providing 32 32-mm slices) were used for voxel segmentation to estimate gray matter content in the MRS voxel.
Spectra were analyzed by using Magnetic Resonance User Interface software (MRUI project: http://carbon.uab.es/mrui/) with frequency-selective, time domain-fitting VARPRO
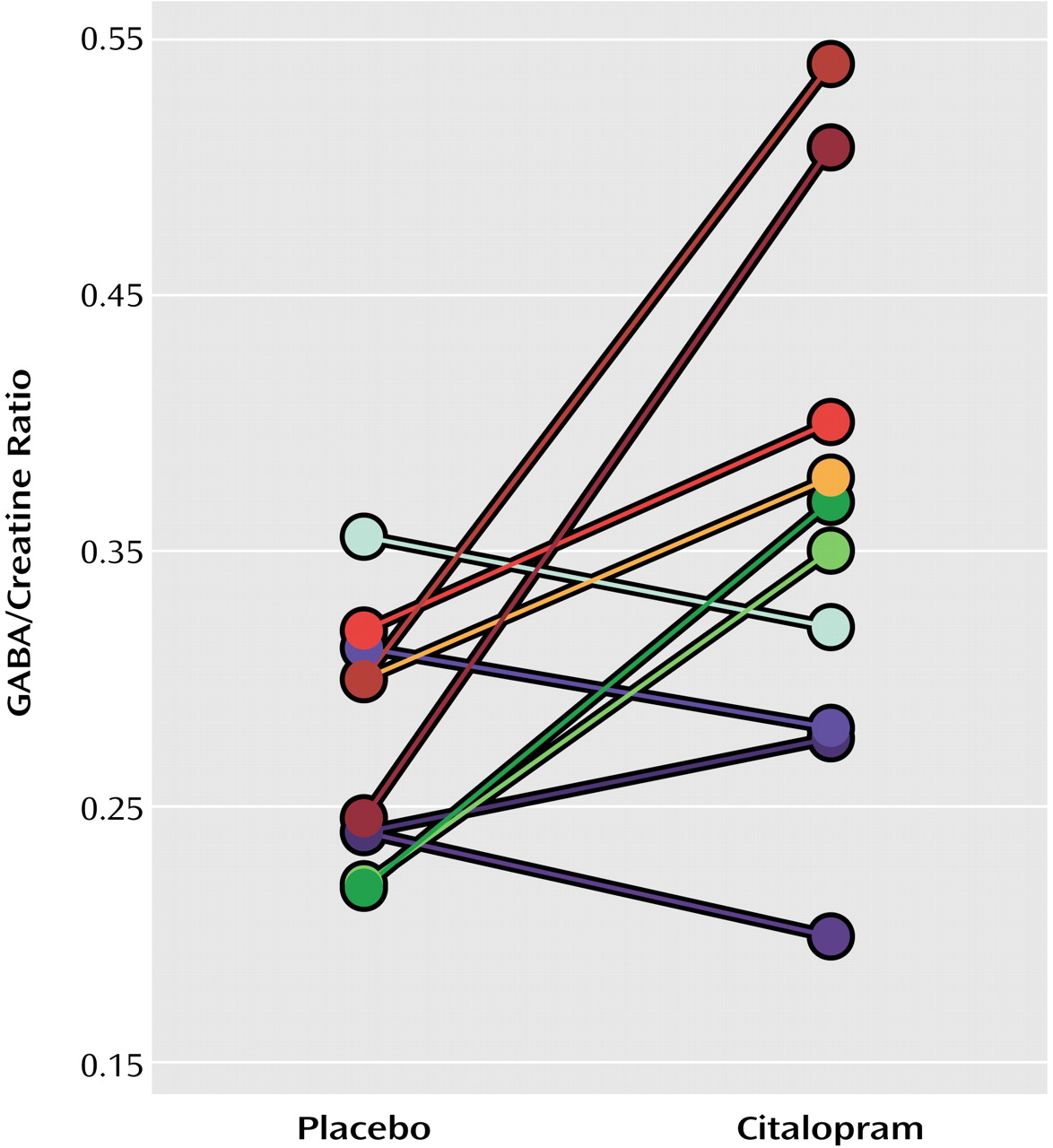
(8). We calculated GABA/creatine ratios after correcting for editing efficiency and number of equivalent protons in GABA and creatine; we assumed that the saturations of GABA and creatine resonances were similar. These GABA/creatine ratios can be converted to absolute concentrations of GABA, given known concentrations of creatine in the brain (assumed to be 7 mM, based on measured, approximately equal voxel concentrations of gray and white matter). Differences in GABA levels after pretreatment with saline and citalopram were compared by using a paired t test, and Pearson’s product-moment correlation analyses were performed. Scan/rescan reliability, calculated as twice the standard deviation of the difference in measurements on two occasions without drug administration, was 26.7%.