Schizophrenia is generally considered to be a brain disease resulting from disturbed neurodevelopment
(1). One manifestation of this maldevelopment may be the neurological abnormalities, identified on clinical neurological examination, that are so frequently observed among both patients with schizophrenia and their nonpsychotic relatives
(2–
6). Neurological abnormalities could represent an important early biological marker for schizophrenia risk
(7), as a higher rate of neurological abnormalities early in life has been found among individuals who later develop schizophrenia
(8–
11), and the individual’s level of neurological abnormalities correlates positively between patients and siblings in the same family
(6). However, for neurological abnormalities to function optimally as a biological marker for schizophrenia risk, we need to know the specific form of neurological abnormality related to schizophrenia risk, its distribution among high-risk and normal-risk individuals, its personal stability over different ages, and its specificity for risk for schizophrenia versus other psychoses. Current knowledge is incomplete concerning all of these topics.
Both schizophrenia patients and their relatives have thus far shown considerable diversity in form and frequency of neurological abnormalities, although the abnormalities have primarily been in the functional domains representing sensory integration, motor coordination, and sequencing of complex motor acts
(2–
6). This diversity is perhaps partly due to methodological differences across studies
(2). Our study using a comprehensive method showed that schizophrenia patients are more differentially characterized by neurological abnormalities representing “hard signs,” while siblings of schizophrenia patients are more characterized by “soft signs”
(6).
Studies of the high-risk offspring of parents with schizophrenia at different ages have detected a subgroup with an especially high frequency of neurological abnormalities and with a higher risk for later development of schizophrenia-related psychopathology
(11–
17). The size of the subgroup (25%–50%) has varied across studies, possibly because of differences in methods and definitions.
The extent to which high-risk individuals have stable schizophrenia-related neurological abnormalities over time also remains unclear. In the Swedish High-Risk Study, we found no personal stability of neurological abnormalities between the neonatal period and 6 years of age
(13,
14). Similarly, the Jerusalem Infant Development Study
(10–
12) showed only modest stability between infancy and adolescence (14–21 years of age) but strong stability between school age (8–13 years) and adolescence.
It is also unclear whether neurological abnormalities related to schizophrenia are associated primarily with risk for schizophrenia or even affective psychosis. Patients with affective disorders and their relatives generally show more neurological abnormalities than healthy comparison subjects but lower rates of neurological abnormalities than patients with schizophrenia and their relatives
(13–
16), but results vary across both high-risk and prepatient groups
(15,
17–19). This question is related to unresolved issues concerning whether schizophrenia and affective psychosis belong to the same biological continuum and what the definitional limits for each of these disorders are somatically
(20).
The type, frequency, personal stability, and specificity of neurological abnormalities for offspring of women with different psychotic disorders were investigated in the Swedish High-Risk Study, which is a prospective, longitudinal investigation of high-risk offspring of women with a history of psychosis and women without such a history
(21). The project was begun in 1973 during the mothers’ pregnancies, and the first adult follow-up of this sample was completed when the offspring were about 22 years of age
(22). In the current study we investigated 1) whether young adult offspring of mothers with a history of schizophrenia or affective psychosis, as compared with normal-risk comparison offspring, have significantly higher levels of neurological abnormalities in total, in particular functional neurological domains, and in hard versus soft signs, 2) whether such neurological abnormalities are especially prominent among a distinct subgroup, and 3) whether the level of neurological abnormalities is personally stable from birth to adulthood. We also investigated 4) whether extending the groups of mothers with “core” schizophrenia and affective psychosis to include those with broader, “spectrum-type” psychoses affects the offspring’s pattern of neurological abnormalities in adulthood.
Method
Subjects
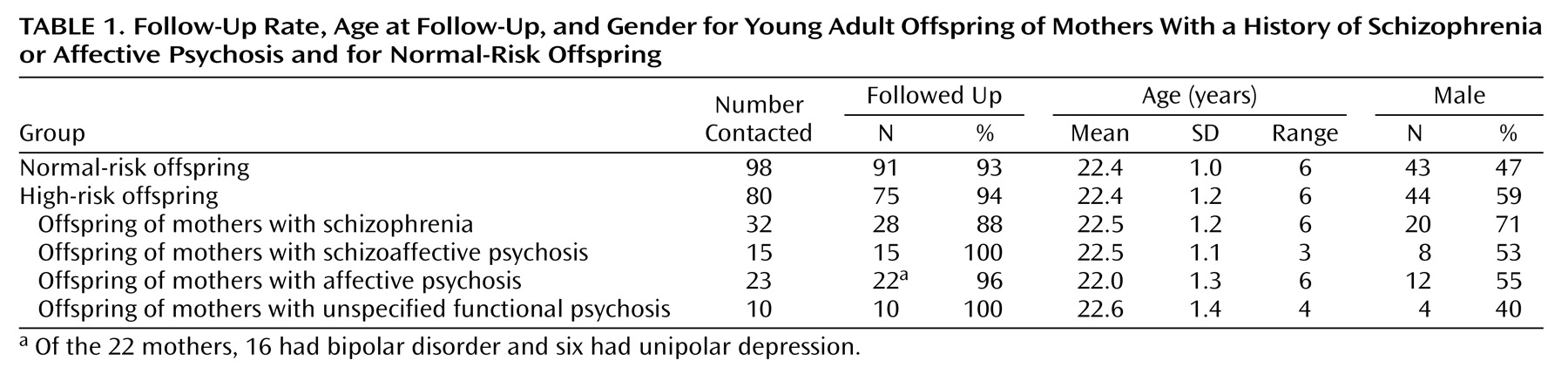
The current sample was taken from the first adult follow-up (93% effective) of this longitudinal study at a mean age of 22.37 years (SD=1.12)
(22). Heightened offspring risk for psychopathology was defined as a history of psychosis in the (index) mother, diagnosed by senior project diagnosticians on the basis of all known psychiatric records for the woman and, where relevant, her biological relatives. Normal offspring risk was defined as the absence of a psychosis history in both the (comparison) mother and biological father, determined through medical records. Further, the index and comparison mothers were systematically interviewed (by T.F.M.) during pregnancy concerning psychiatric symptoms
(23).
Both the index and comparison mothers were selected from women registered at the local prenatal clinics in a large geographical area in southwest Sweden during 1973–1977. Comparison subjects were chosen to have the same prenatal clinic, maternal age (±1 year in 75% of the cases, ±2 years in the remaining cases), parity (0 versus 1 versus ≥2), social class (upper, middle, lower), and formal marital status during pregnancy as the index subjects. The offspring and their environment were studied extensively from before birth until 2 years of age
(24), with follow-up and investigation at 6 years of age
(25).
Beginning in 1996, the 178 offspring (80 with high risk, 98 with normal risk) potentially participating in the project were traced through the Swedish population registers and invited to participate in the young adult follow-up. The sample was contacted over a 4-year period, in order to standardize the age at this follow-up examination. Contact was made first by letter, which was followed by a telephone call. In total, 166 (93.3%) of the 178 offspring were followed up (
Table 1)
(22). The 162 subjects with data on neurological abnormalities comprised 74 high-risk offspring and 88 normal-risk offspring of comparison mothers. Four other subjects included in the general follow-up could not be assessed neurologically because of poor current mental health (one high-risk, one normal-risk offspring), problematic examination situation (one normal-risk offspring), or recent death (one normal-risk offspring).
The final group of high-risk subjects with data on neurological abnormalities consisted of 28 offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, 22 offspring of mothers with affective psychosis (16 mothers with bipolar disorder and six with unipolar depression), 15 offspring of mothers with schizoaffective psychosis, and nine offspring of mothers with unspecified functional psychosis, all defined by Research Diagnostic Criteria
(26).
Because of the small subgroup sizes, the offspring of mothers with schizoaffective psychosis and offspring of mothers with unspecified functional psychosis were not analyzed separately. Instead they were individually reassigned to “mainly schizophrenic” (N=10) or “mainly affective” (N=14) maternal disorder groups, on the basis of the mother’s psychiatric history
(22). This reclassification was used to investigate the effect of extending the groups of mothers with schizophrenia and affective psychosis to include additional “spectrum” cases.
After complete description of the study to the subjects, written informed consent was obtained.
Neurological Examination in Adulthood
The subjects were followed up during a full day of assessment at their local general practitioners’ offices. The standardized procedure during the morning session included a neurological examination
(22) based on a comprehensive, standardized assessment scale
(6) previously used by us to study adult schizophrenia patients and their siblings. The scale consists of 44 items (26 items permitted bilateral assessment) and comprises 21 items from Woods et al.
(4), all 19 items from an instrument of Rossi et al.
(5), two items (right-left confusion and finger-thumb opposition) from Quitkin et al.
(3), and two items (finger-nose test, crossing body midline) from a study by us
(14). Neurological soft signs were operationally defined as the items used by Rossi et al.
(5), while the remaining items were defined as hard signs
(6). The neurological assessment scale includes the following functional domains and items:
Motor functions
Motor functions were represented by the following subdomains: 1) motor coordination (hard signs: finger-nose test, finger-thumb opposition, crossing body midline, Romberg test, gait deviation, whole body clumsiness, dysarthria; soft signs: dysdiadochokinesia, complex motor acts, tapping rhythm), 2) involuntary movements (hard signs: choreiform movements, athetotic movements, intention tremor, postural tremor, resting tremor), 3) mirror movements (hard signs: mirror movements on finger-thumb opposition and on diadochokinesia), 4) deviant muscle power (hard sign: unilateral weakness), 5) deviant muscle tone (hard signs: unilateral cogwheel rigidity, spastic rigidity, hypotonia, pes cavus), and 6) cranial nerve deviations (hard sign: unilateral facial weakness; soft signs: ocular vergence, gaze nystagmus, oral apraxia). (Muscle power and muscle tone were included in the total deviation score but not in the statistical analysis of specific subdomains, because of the low frequency of abnormality in the total sample.)
Sensory functions
Sensory functions were represented by one hard sign, unilateral sensory loss, and four soft signs: astereognosis, graphesthesia, blunt/sharp discrimination, and simultaneous bilateral extinction.
Reflexes
Reflexes were represented by one hard sign, unilateral reflex hyperactivity, and the following soft signs: snout reflex, suck reflex, blink reflex, palmomental test, grasp reflex, and Babinski reflex.
Cognitive functions
Cognitive functions were represented by two hard signs, right-left confusion regarding self and regarding examiner, and four soft signs: imaginary acts, the two-object test, motor perseveration, and gaze impersistence.
Scoring
The total score for neurological abnormalities was the sum of the scores on all 44 items (potentially ranging from 0 to 124), while the score for each domain or subdomain was the sum of the scores on the respective items. On the basis of previous research
(14,
22), a score on the total scale that was above the 90th percentile for the normal-risk offspring (i.e., a score higher than 7) was operationally defined as “high” and was used to investigate the possible existence and relative size of a high-scoring subgroup among the high-risk subjects.
One physician (E.W.S.) examined all subjects. During data collection and analysis the examiner was blind to the subject’s high-risk versus normal-risk offspring status and all previous project data. The interrater reliability for the neurological assessment was determined by testing agreement with an experienced physician
(6) on the total scores of 20 subjects (10 patients with psychosis and 10 hospital personnel). The interrater coefficient (intraclass correlation) was 0.97 (F=65.44, df=9, 10, p<0.001).
Neurological Examinations Earlier in Life
Neonatal examination
Standardized neurological examinations were blindly performed by one assessor at the delivery hospitals on the third to fourth day after birth
(13). The examination was based primarily on the methods of Hagberg
(27) and of Prechtl and Beintema
(28,
29) and included evaluation of muscle tone, motor movements, simple and complex reflexes, activity level, and sensitivity to stimulation. A summary score composed of deviation points compiled across 19 different items represented the subject’s degree of total neonatal neurological abnormalities. As in our previous study
(13), a subject was classified as having a high score if the total neurological abnormality score was greater than 5.
Six-year examination
In the follow-up investigation at 6 years of age, neuromotor assessment was blindly conducted in the subjects’ homes by a different examiner. The neuromotor assessment was primarily based on Touwen and Prechtl’s neurological examination of children
(30) and included 26 test items
(14). A subject with a total neurological abnormality score higher than 7 was classified as high scoring at that age. The total scores in infancy and at 6 years of age were used for comparison with the total score in the current follow-up at 22 years of age.
Statistical Methods
Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance was used to compare the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, offspring of mothers with affective psychosis, and normal-risk offspring groups on the quantitative scores for total neurological abnormalities and each neurological domain and subdomain. When Kruskal-Wallis analysis showed a significant across-group difference or a strong trend, secondary comparisons of pairs among these three groups were done by Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney tests. The Fisher exact test, with odds ratio and 95% confidence interval (CI), was used for analysis of category data regarding rates of high-scoring subjects and confounder effects. Spearman rank correlations were used to study the stability of the quantitative neurological abnormality scores over time. Statistical significance was defined as p≤0.05 two-tailed, with 0.10≥p>0.05 denoting nonsignificant trends.
The effect of adding additional “mainly schizophrenic” or “mainly affective” cases to the core groups of mothers with schizophrenia and affective psychosis, to form extended offspring groups with “schizophrenia risk” and “affective psychosis risk” spectra, was evaluated visually but not submitted to formal statistical analysis.
Results
Neurological Abnormalities in Young Adulthood
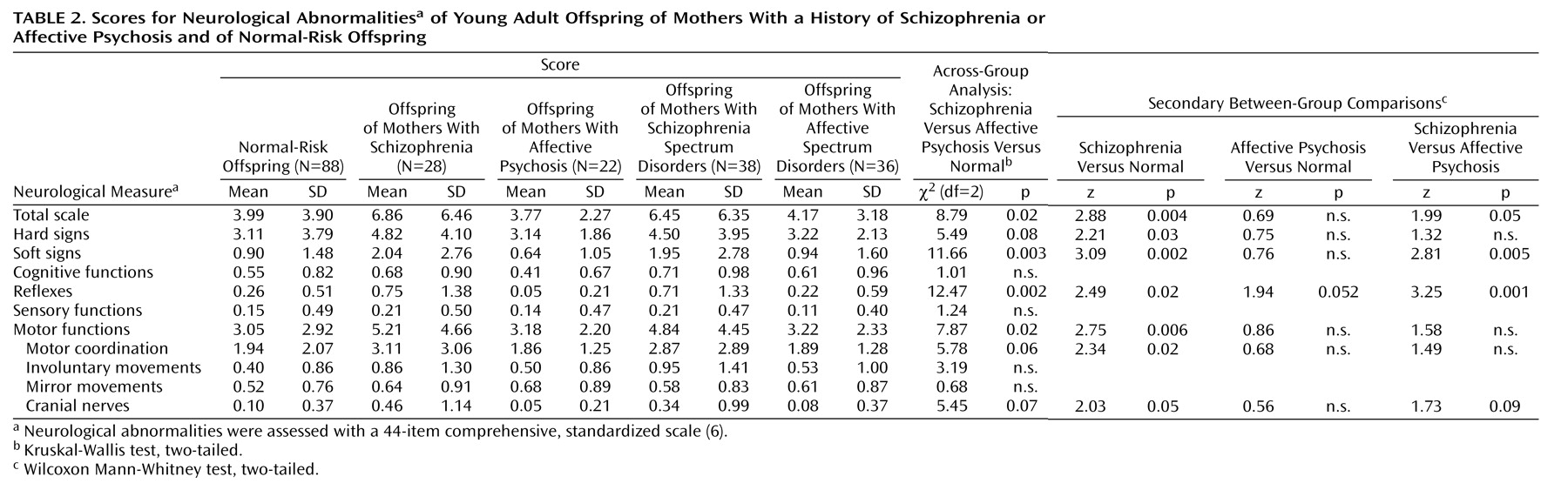
Significant differences were found across the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, offspring of mothers with affective psychosis, and normal-risk offspring for total neurological abnormality score, soft signs, reflexes, and motor functions, with nonsignificant trends for hard signs, motor coordination, and cranial nerves (
Table 2). Secondary analyses among these groups showed that the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia had significantly higher scores than the normal-risk offspring on total neurological abnormalities, hard signs, soft signs, reflexes, motor functions, motor coordination, and cranial nerves. The offspring of mothers with schizophrenia also had significantly higher scores than the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis on total neurological abnormalities, soft signs, and reflexes, with a nonsignificant difference in cranial nerves. The offspring of mothers with affective psychosis showed no significant difference from the normal-risk offspring on any neurological abnormality, but they had a trend toward
lower scores for deviant reflexes. Furthermore, among the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis, no difference was seen on any scale between the offspring of mothers with bipolar versus unipolar affective psychosis. Receiver operating characteristic curves (not shown) demonstrated that the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia were more readily discriminated from the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis and the normal-risk offspring by soft signs than by hard signs.
Possible Confounders for Group Differences
Schizophrenia spectrum disorders (schizophrenia, schizoaffective psychosis, and cluster A personality disorders) were found in three offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, one offspring of mothers with affective psychosis, and two normal-risk offspring by the time of this follow-up
(22). With these six subjects removed, the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia still scored significantly higher on total neurological abnormalities than the normal-risk offspring (z=3.53, p<0.0001) and the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis (z=2.33, p=0.02). There was a somewhat higher rate of male offspring among the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia than among the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis and the normal-risk offspring (
Table 1) (χ
2=5.04, df=2, p=0.08), but no significant relationship was found between gender and a high score for neurological abnormalities (above the 90th percentile) among the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia (Fisher exact test, p=0.22; odds ratio=4.67, 95% CI=0.48–45.60). Offspring of mothers with schizophrenia have a high rate of substance use disorders
(22), but in this study substance use disorders were not significantly related to high scores for neurological abnormalities in the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia (Fisher exact test, p=1.00; odds ratio=0.93, 95% CI=0.14–6.37). At the time of assessment, no subject in any group was receiving neuroleptic medication, and only two subjects were taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (one offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, one offspring of mothers with schizoaffective psychosis).
Subgroup With High Scores on Neurological Abnormalities
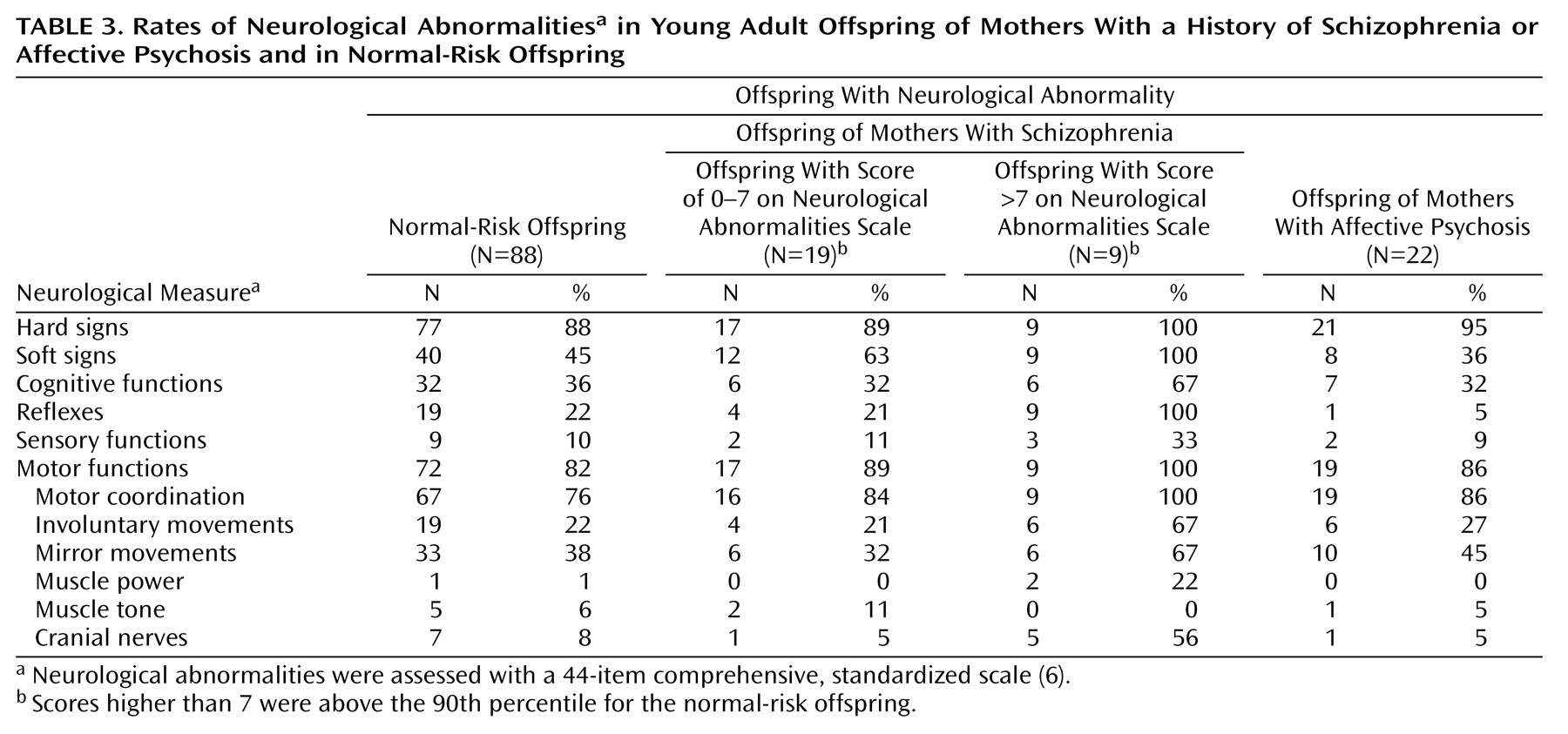
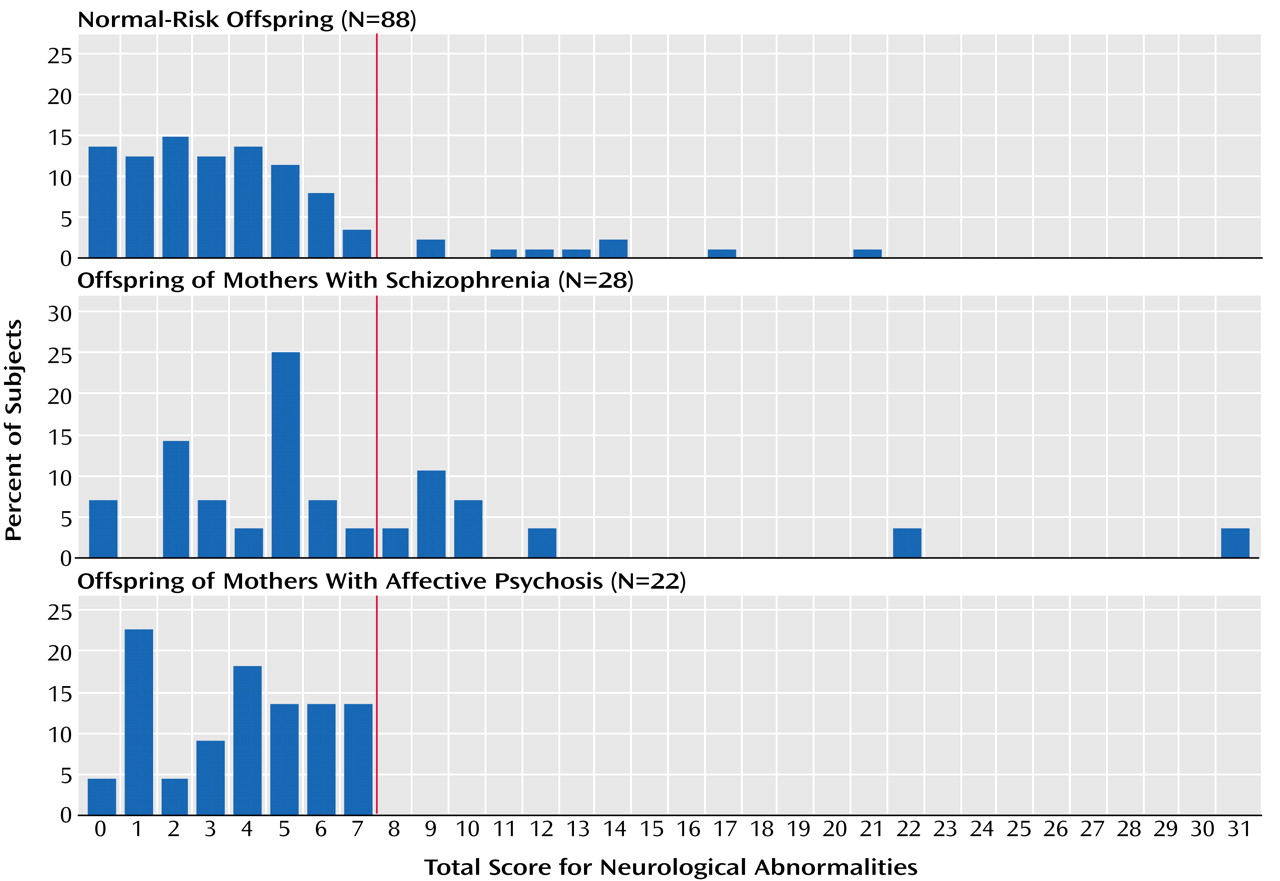
The distributions of total neurological abnormality scores for the three offspring groups demonstrate the existence of two subgroups among the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia (
Figure 1). Operationally defined, these offspring consisted of one subgroup (68%) with a total score of 7 or less (representing the normal-risk offspring’s 90th percentile cutoff level) and another substantial subgroup (32%) scoring above this level. The offspring of mothers with affective psychosis and the normal-risk offspring did not show such distributions. The proportion of individuals scoring above this cutoff level was significantly greater in the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia than in the normal-risk offspring (Fisher exact test, p=0.005; odds ratio=4.74, 95% CI=1.61–13.89) or in the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis (Fisher exact test, p=0.003; odds ratio=21.92, 95% CI=1.19–401.82). Compared with the normal-risk offspring and the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis (
Table 3), this high-scoring subgroup among the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia contained notably more subjects (odds ratio >7) with soft signs, deviant reflexes (especially primitive reflexes), involuntary movements, and cranial nerve deviations. All nine subjects in the high-scoring subgroup had some kind of disturbance in the eye region (glabellar reflex, N=8; gaze nystagmus, N=2; gaze impersistence, N=1).
Stability of Neurological Abnormalities From Infancy to Young Adulthood
The total score for neurological abnormalities at 22 years was significantly positively correlated with the total score at 6 years of age for the total high-risk group (rs=0.38, N=60, p=0.003), the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia (rs=0.46, N=20, p=0.05), and the normal-risk offspring (rs=0.26, N=85, p=0.02) but not for the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis (rs=0.07, N=20, p=0.76). In contrast, the total score at 22 years was not significantly correlated with the score in infancy for any group (rs values ranged from –0.21 to 0.11 across the four groups; the numbers of subjects were 47, 16, 17, and 65 for the total high-risk group, offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, offspring of mothers with affective psychosis, and normal-risk offspring, respectively).
Spectra of Schizophrenia Risk and Affective Psychosis Risk
The addition of mothers with “mainly schizophrenic” and those with “mainly affective” disorders to the original core schizophrenia and affective psychosis groups, to form extended spectra of schizophrenia risk and affective psychosis risk, generally resulted in only minor changes in mean neurological abnormality scores among the offspring (
Table 2), with slightly smaller differences between each spectrum group and the normal-risk offspring. Both the pattern of neurological abnormalities and the individual stability over time remained very similar to those for the original offspring of mothers with schizophrenia and offspring of mothers with affective psychosis. The size and characteristics of the neurological abnormalities among the high-scoring subgroup in the schizophrenia risk spectrum offspring (29%) were also similar to those for the high-scoring subgroup among the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia (32%).
Discussion
In this prospective, longitudinal study, personal stability of the level of neurological abnormalities was found in both high-risk and comparison offspring between middle childhood and adulthood but not between infancy and adulthood. This finding is congruent with results in the Jerusalem Infant Development Study
(12). At all three ages in the current study, the offspring of women with schizophrenia demonstrated high levels of neurological abnormalities, while the offspring of women with affective psychosis were not different from, or had even lower levels of neurological abnormalities than, comparison subjects
(13,
14). This strongly suggests that schizophrenia and affective psychosis belong to different biological continua and, further, that this neurodevelopmental disturbance is already manifest and detectable in childhood. The extension of the core schizophrenia and affective psychosis risk groups to include additional offspring of mothers with spectrum disorders had little effect on the rate and pattern of neurological abnormalities in the respective risk groups, indicating that the factors influencing rates of neurological abnormalities are as present in the additional offspring in the risk spectra as in the core offspring.
In young adulthood, the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia had a wide range of neurological abnormalities, consisting of hard signs, soft signs, deviant reflexes, and disturbances in motor functions, motor coordination, and cranial nerves. The total score for neurological abnormalities of these offspring (mean=6.86) was approximately halfway between the scores of schizophrenia patients (mean=10.13)
(6) and normal-risk offspring (mean=3.99). In congruence with findings for siblings
(6), the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia were best discriminated from normal-risk offspring by soft signs, rather than hard signs. Higher levels of neurological abnormalities (total score higher than 90th percentile of normal-risk offspring) were present in a substantial proportion (32%) of offspring of mothers with schizophrenia, and this subgroup had high rates of soft signs, primitive reflexes, involuntary movements, and cranial nerve deviations. In total, 18% of the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia had high scores for neurological abnormalities at all three ages, compared with none of the offspring of mothers with affective psychosis or normal-risk offspring. The fact that a substantial proportion of the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia scored in the same range as most normal-risk offspring (
Figure 1 and
Table 3) may reflect the absence of the presumed number and type of genes or environmental influences that lie behind the high rate of neurological abnormalities in families with schizophrenia.
The existence of similar diverse neurological abnormalities in the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia and in schizophrenia patients is congruent with the findings, emerging from neuroimaging studies, of subtle abnormalities in a widespread area of the brain in schizophrenia patients
(31). Such findings speak for a similar etiological, probably genetic, basis for the disturbed neurodevelopmental process found at large in these families.
The high-scoring subgroup of offspring of mothers with schizophrenia had high rates of both neurological disturbances in the eye region (reminiscent of findings in the siblings of schizophrenia patients
[6] and high-risk offspring developing psychotic symptoms
[31]) and involuntary movements (however, these differences were not significant in the group analyses). These observations are consistent with previous findings in preschizophrenia individuals as early as 2 years of age and in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia patients and patients’ siblings in childhood and adulthood
(7,
8,
14,
32).
The strengths of the study were the prospective design with previous neurological assessments; the high adult follow-up rate; the narrow age range at follow-up; the existence of different high-risk groups; the use of an extensive standardized examination routine with high interassessor reliability, previously tested with schizophrenia patients; and examination by one investigator who was blind with regard to the subject’s study group and previous project data.
The major limitation of this study lies in the small sample sizes of the specific high-risk groups. Given the observed means and variance for total neurological abnormalities, the study had only moderate power (62%) to identify a significant difference (p<0.05) between offspring of mothers with affective psychosis and normal-risk offspring that was of the same magnitude as the difference between offspring of mothers with schizophrenia and normal-risk offspring. The offspring of mothers with affective psychosis nevertheless had somewhat lower neurological abnormality scores than the normal-risk offspring and significantly lower scores than the offspring of mothers with schizophrenia.
In summary, a substantial subgroup of young adult offspring at risk for schizophrenia evidence a notable degree of diverse neurological abnormalities (in line with the neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia), which is not observed in offspring at risk for affective psychoses. Although other etiological factors cannot be excluded, the results support the role of genetic factors in neurological abnormalities related to parental schizophrenia. The question of whether the presence of neurological abnormalities in general or a specific type is associated with mental disturbance in adult high-risk offspring will be the focus of our future work.