Adolescent anxiety is highly prevalent and predicts adverse outcomes such as adult anxiety and depression (
1–
3). Four sets of key findings guide questions on the precursors, mechanisms, and consequences of adolescent anxiety. First, adolescent anxiety disorders are often co-occurring, with particularly high comorbidity between social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder (
4). Second, some anxiety disorders share risk factors, which could explain their high comorbidity levels (
4–
6). Third, despite comorbidity and shared risks, evidence of specificity still emerges (e.g., adolescent social phobia predicts risk for adult social phobia but not adult generalized anxiety disorder) (
2). Similarly, behavioral inhibition is an early childhood temperament associated with heightened risk for social phobia (
6–
9) but not generalized anxiety disorder (
10). Finally, based on prior neuroimaging data on behavioral inhibition, a heightened neural response to anticipated incentives may be a marker that links early childhood behavioral inhibition specifically to later social phobia but not generalized anxiety disorder (
11). We used methods previously employed in a study of adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition (
11) to test this possibility and compared neural responses to anticipated incentives in adolescents with social phobia and adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder.
Amygdala and ventral prefrontal cortex responses to threat are altered in adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition (
12,
13) and in those with anxiety disorders (
14–
19). These findings are nonspecific, however, since they are seen in behavioral inhibition, social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, and to a degree, major depression (
12–
20). Altered neural response to potential incentives may occur in a more restricted, specific fashion given unique responses to anticipated incentives in behavioral inhibition (
11,
21,
22) that are distinct from responses in adolescent depression (
23). However, few studies have extended such research to clinically anxious and healthy adolescents, and none have compared social phobia with generalized anxiety disorder. Direct comparison of social phobia with generalized anxiety disorder in adolescents may reveal unique risk mechanisms shared between social phobia and early childhood behavioral inhibition.
Several findings link anxiety and incentive processing. An initial study found that high state anxiety correlates positively with a hypersensitive behavioral response to rewards (
24). Subsequent studies examined neural manifestations of incentive hypersensitivity in behavioral inhibition (
11,
21). Adolescents characterized by early childhood behavioral inhibition, relative to those characterized as noninhibited, showed greater striatal response modulation with increasing incentive magnitudes (
11). A later study showed striatal hyperactivation in behaviorally inhibited adolescents, specifically when anticipated incentives were contingent on participants' choices (
21). Consistent with these data, research in adult social phobia has found altered striatal dopamine function (
25,
26) and task-elicited striatal perturbations (
27); no such work has examined striatal function in adolescent social phobia. These findings suggest that striatal hyperactivation may manifest in adolescent social phobia and raise questions about the specificity of this functional alteration in social phobia relative to generalized anxiety disorder.
In the present study, we compared striatal function in healthy adolescents, adolescents with social phobia, and adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder on the same monetary incentive delay task used previously to show striatal hyperactivation in adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition (
11). Given data linking behavioral inhibition to adolescent social phobia (
10), we hypothesized that incentive magnitude would modulate striatal response more strongly in adolescents with social phobia than in healthy adolescents or adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder.
Method
Participants
Participants were 26 healthy adolescent volunteers, 18 adolescent patients diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder but not social phobia, and 14 adolescent patients diagnosed with social phobia (
Table 1). Three social phobia patients met criteria for generalized anxiety disorder as a secondary diagnosis. Three patients with generalized anxiety disorder and two with social phobia met criteria for depression; all five of these patients were included because anxiety was the primary reason for referral.
Patients sought treatment for anxiety symptoms (Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale [
28] score: ≥10; Child Global Assessment Scale score: <60). Diagnoses were determined using clinician-based interviews (
29). Anxiety severity was indexed by scores on the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders scale (
30) averaged from adolescent and parent reports. Exclusion criteria were current Tourette's syndrome, obsessive-compulsive disorder, conduct disorder, or suicidal ideation; history of mania, psychosis, or pervasive developmental disorder; traumatic exposure; an IQ <70; or psychoactive substance use in the past month (2 months for fluoxetine). The National Institute of Mental Health Institutional Review Board approved the study. After receiving complete description of the study, parents/legal guardians provided written informed consent, and participants provided written informed assent.
Groups were well matched on demographic characteristics (
Table 1). Both patient groups had similarly extreme elevations in their scores on the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders scale relative to healthy comparison subjects (p<0.001).
Task Paradigm
The monetary incentive delay task engages the striatum during anticipation of potential monetary gain or loss (
31,
32), with a parametric version varying the monetary amount at stake (
31). A cue indicates trial incentive magnitude. Participants respond as quickly as possible during target presentation. Successful performance leads to winning or avoiding loss. Based on our prior work (
11), we focused on the anticipatory phase, which is during the cue presentation before motor response. Participants practiced the task prescan to standardize performance and task difficulty by individually tailoring success on approximately 66% of trials (
31).
Participants completed two runs of 72 contiguous 6-second trials (see Figure 1 in the data supplement accompanying the online version of this article). Trials began with a cue presentation (250 msec) followed by cross-hair fixation points (2,000–2,500 msec) and target response cues (160–250 msec). Circle cues (N=64) indicated monetary gain (U.S. dollars) if the button press occurred quickly enough at target onset. Square cues (N=64) signified monetary loss if the button press did not occur quickly enough at target onset. Triangle “neutral” cues (N=16) indicated $0 at stake. Incentive magnitude was represented by a single line ($0.20; N=32), two lines ($1.00; N=32), or three lines ($5.00; N=32) within the cue. After the target's disappearance, feedback (1,650 msec) notified participants of a gain, a loss, or no change and of cumulative winnings. Trial-type order was fully randomized. Participants could win up to $50. Postscan, they rated their cue preferences from –5 (dislike very much) to +5 (like very much).
Behavioral Data Analysis
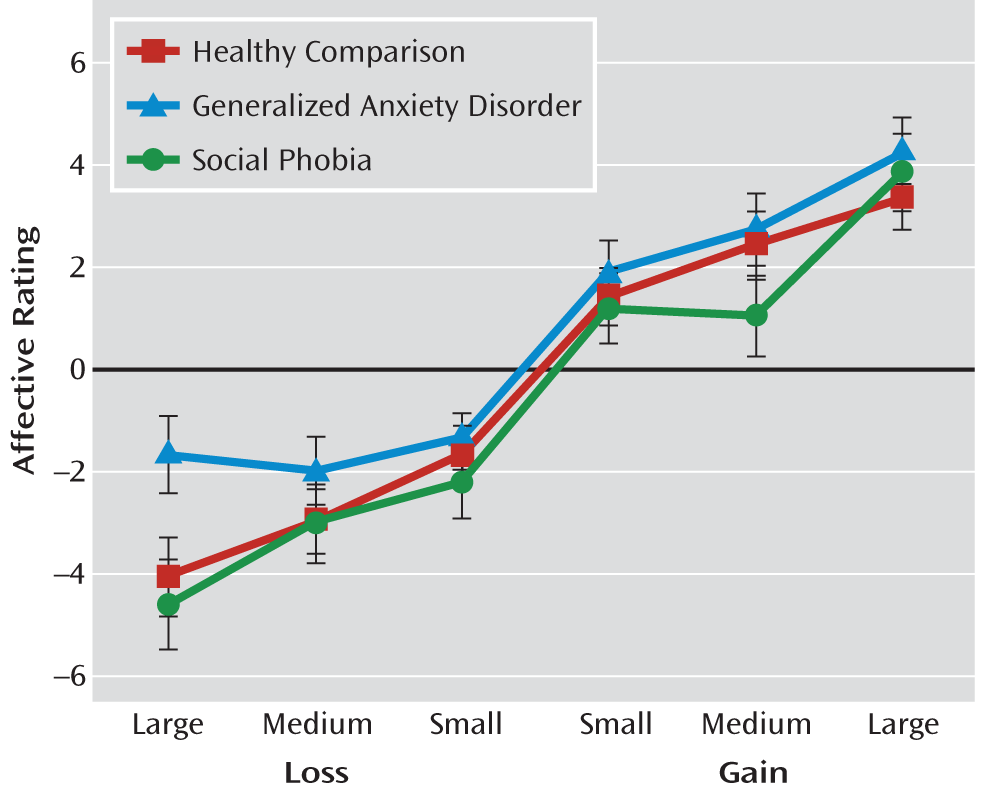
Dependent variables were accuracy (i.e., proportion of successful button presses during target presentation), reaction time for correct hits (i.e., time between target onset and successful button presses), and postscan affective ratings. Accuracy, reaction time, and affective ratings were examined with a group-by-magnitude-by-valence repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). To parallel imaging analyses, which used $0 trials as a baseline, response to $0 cues was a covariate (except for affective ratings).
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Data Acquisition
Scanning occurred on a General Electric Signa 3T magnet (General Electric Co., Waukesha, Wisc.), with a standard birdcage head-coil and Cedrus Lumina response box (Cedrus, San Pedro, Calif.). Stimuli were projected onto a screen at the foot of the scanner bed and viewed with mirrors. Functional imaging parameters were as follows: 30 interleaved 4-mm thick slices acquired in the sagittal plane using a T2-weighted gradient echo sequence; TR=2,500 msec, TE=23 msec, flip angle=90°, voxel dimension=3.75×3.75×4.0 mm, matrix size=64×64, and field of view=24 cm. Four acquisitions were obtained before task onset to stabilize the signal. A high-resolution structural image was acquired for spatial normalization (T1-weighted standardized magnetization-prepared spoiled gradient-recalled echo sequence with 124 1-mm slices; TR=8,100 msec, TE=32 msec, flip angle=15°, matrix size=256×256, field of view=24 cm).
fMRI Data Preprocessing
Analysis of Functional and Neural Images software (
33) was used. Preprocessing included slice time correction, motion correction, and spatial smoothing (6-mm full-width half-maximum kernel). A despiking algorithm applied on a voxelwise basis smoothed signal deviations >2.5 standard deviations from the mean. A band-pass filtering algorithm smoothed cyclical fluctuations in signals (either >0.011 second or <0.15 second) not temporally indicative of a hemodynamic response. Data for each participant were converted to percent signal change using each participant's voxelwise time-series mean as a baseline.
Time-series data for each participant were analyzed with multiple regression using a region-of-interest approach that followed past procedures (
11). The model included event-type regressors of interest (incentive cues, target cue, feedback), six regressors modeling effects as a result of residual motion (in the x, y, and z planes and yaw, pitch, and roll dimensions), and two regressors modeling baseline and linear trends per run. Regressors of interest were convolved with a gamma variate function that modeled a prototypical hemodynamic response (
34). Idealized signal time courses were estimated from the onset time of event type.
fMRI Data Analysis
Following past methods (
11), six contrasts of blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) activation were created individually for the three monetary gain cues and three monetary loss cues, each compared with no-monetary neutral cues. Activation was calculated as the net signal difference between each incentive magnitude and no incentive at the acquisition of the event-related hemodynamic response function during cue presentation. Mean contrast values were generated for all voxels located within each of the following three striatal structures: nucleus accumbens, caudate nucleus (encompassing the head and body), and putamen. Talairach anatomical boundaries, provided by Analysis of Functional and Neural Images software, defined voxels within each region after spatial normalization (
35). One contrast value was generated for each participant per region to minimize type I errors.
Contrast values were analyzed at the group level using SPSS software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago). Based on previous findings (
11), we hypothesized that the social phobia group would show increased striatal activation as a function of increased incentive magnitude. We tested this hypothesis using an omnibus repeated-measures ANOVA that included group (social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, healthy comparison), magnitude (small, medium, large), valence (gain, loss), and region (bilateral nucleus accumbens, caudate, putamen).
Although previous research on behavioral inhibition showed reactivity to incentive magnitudes across striatal regions, we retained specific striatal region as a factor for the following reasons. Because few studies examine reward function in clinical anxiety, it is important to generate initial data for specific regions. Moreover, because our prior study of adolescents with early-life behavioral inhibition was moderately sized (N=32), power on higher-order interaction tests was restricted. Similarly, a second, larger study of adolescents with early-life behavioral inhibition using a different task found region-specific striatal responses (
21). Finally, including region as a factor is consistent with documented functional specialization within the striatal structures examined in the present study (
31,
36,
37).
Dependent measures encompassed BOLD signal change values of each event-related contrast extracted from anatomically defined masks of a priori striatal regions. Based on past findings (
11), we expected to observe group-by-magnitude interactions, either within or across striatal regions. Least significant difference comparisons identified specific differences driving significant group main and interaction effects.
Discussion
The present study tested hypotheses about striatal circuitry alterations among healthy and clinically anxious adolescents. This work extends previous findings documenting striatal hypersensitivity to anticipated incentives in adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition (
11,
21). Because early childhood behavioral inhibition predicts risk for later anxiety disorders, particularly social phobia (
6–
10), we expected striatal circuitry hypersensitivity to be evident in adolescents with social phobia. Specifically, we expected incentive magnitude to modulate striatal activation more strongly in adolescents with social phobia than in healthy adolescents or adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder.
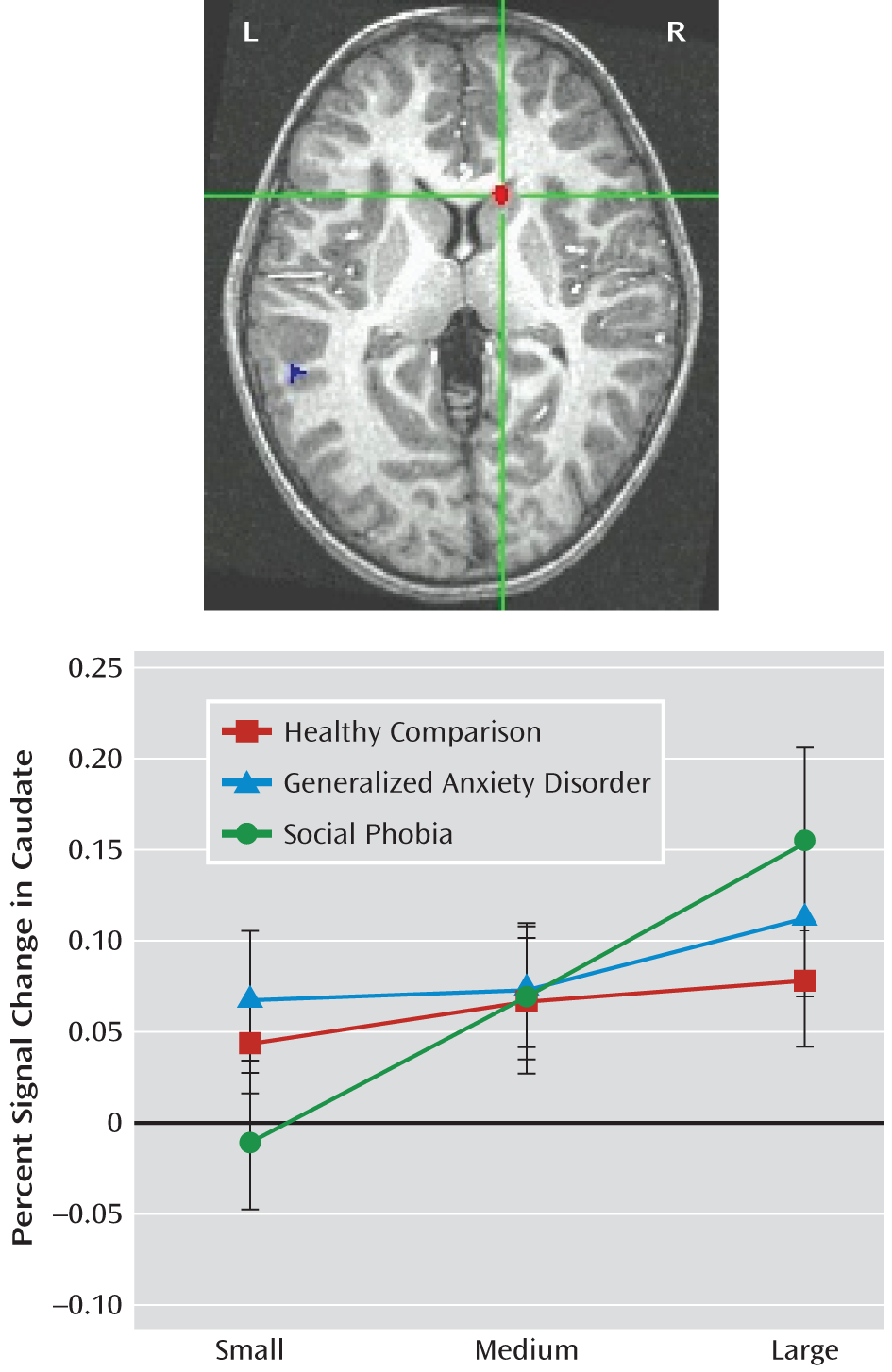
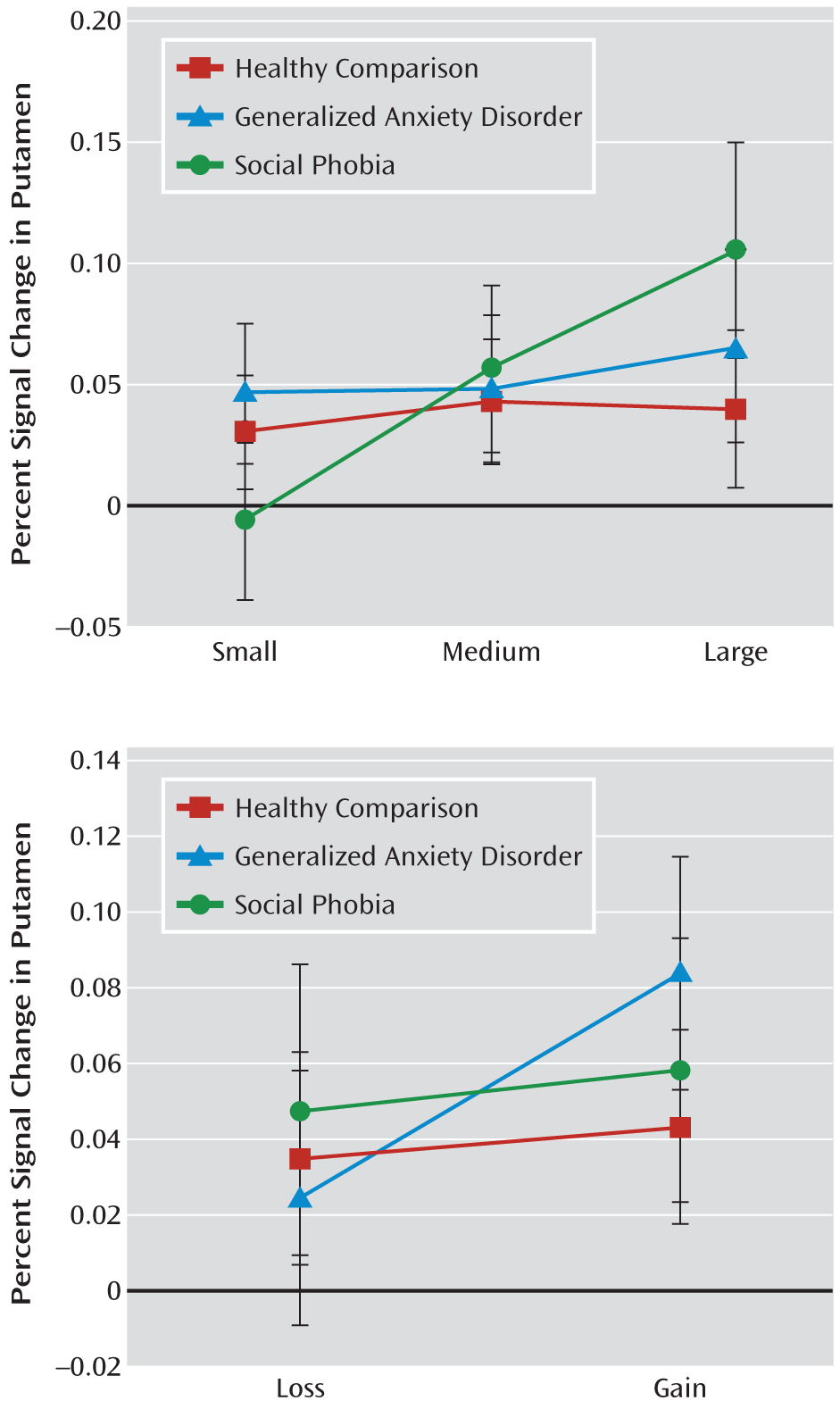
The caudate and putamen showed the expected pattern of increased activation as incentive magnitude increased in the social phobia group but not in the generalized anxiety disorder or healthy comparison group. This finding suggests a striatal circuitry functional profile shared by both a behaviorally inhibited temperament and social phobia in adolescence. Previous research has suggested that adolescents characterized by early childhood behavioral inhibition find cues indicating potential for reward or punishment to be highly salient because of performance-related concerns (
11). This interpretation was supported in work documenting striatal hyperactivity in adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition when anticipated reward outcomes resulted directly from the participants' actions (
21) and when anticipated rewards were not received (
22). In the present study, adolescents with social phobia also showed striatal sensitivity to stakes associated with performance, suggesting that rewards might engage similar psychological processes in adolescent social phobia and early-life behavioral inhibition.
Altered caudate and putamen function distinguished the social phobia group from the other two groups, but findings in the generalized anxiety disorder group did not quite mirror those in the healthy comparison group. Adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder showed putamen hyperactivation in response to valence (gain versus loss), findings not observed in those with social phobia or in healthy adolescents. Thus, while behavioral inhibition and social phobia are associated with one pattern of perturbed striatal response to incentives, adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder displayed a distinctly different perturbed neural response relative to healthy adolescents. In addition, adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder exhibited a different profile of cue preference that was sensitive to loss. It would be worthwhile for future research to test new hypotheses based on these results, which suggest that adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder may be more influenced by valence, particularly for anticipated losses, than their peers without generalized anxiety disorder. Collectively, these findings reflect reward-related perturbations in both generalized anxiety disorder and social phobia but with distinct patterns. Furthermore, in adolescents with early-life behavioral inhibition, similar to adolescents with social phobia, striatal sensitivity to valence or self-reported affective sensitivity to incentive magnitude was not seen (
11), supporting specificity in features of generalized anxiety disorder relative to social phobia or behavioral inhibition.
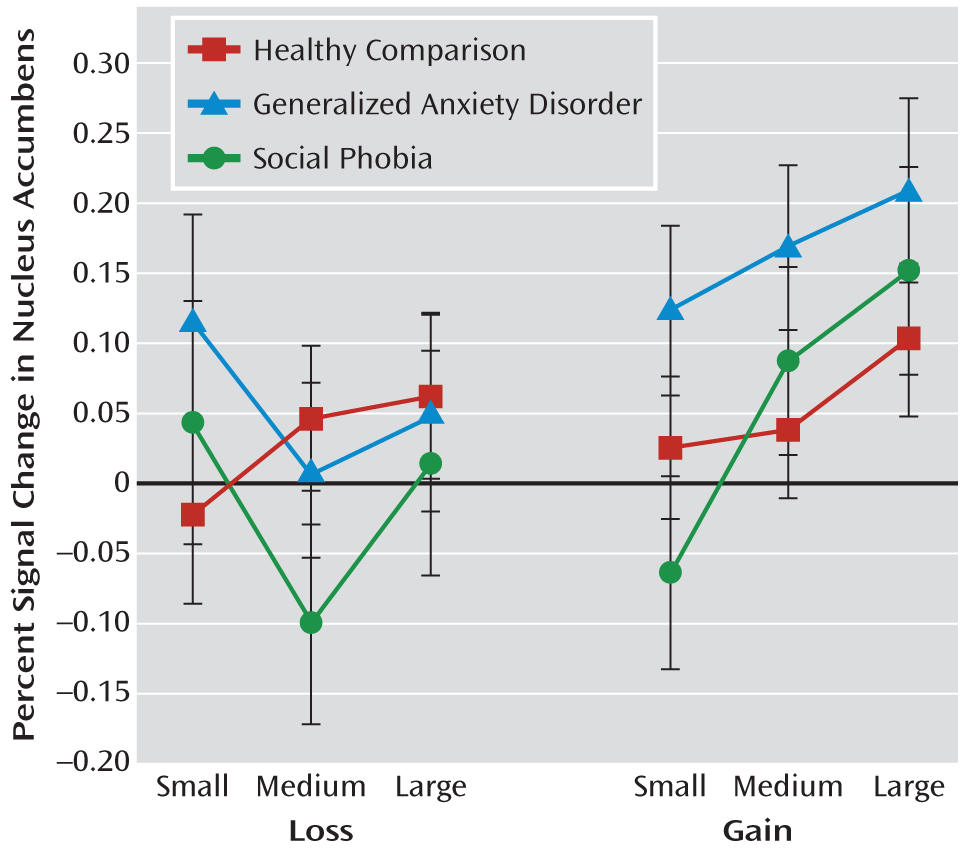
Distinct striatal subregion responses might provide clues about diagnostic specificity and the differential role of incentive processing in anxiety states. Relative to adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder, a more generalized pattern of striatal response was seen in adolescents with social phobia when compared with their healthy peers. This pattern emerged across the caudate, putamen, and nucleus accumbens. Similar to the pattern of magnitude-related hypersensitivity, this cross-region involvement echoes findings in behavioral inhibition (
11,
21). Widespread magnitude-related incentive activations may underlie psychological states common to behavioral inhibition and social phobia, such as performance monitoring or sensitivity to feedback (
22,
38). Finally, caudate hyperactivation in social phobia and behavioral inhibition suggests anomalies in goal-based processes (
39), which are more strongly modulated in the caudate than in the putamen or accumbens. By comparison, restriction of striatal abnormality to the putamen and nucleus accumbens in generalized anxiety disorder suggests more delimited incentive dysfunction.
Although early childhood behavioral inhibition is associated with risk for social phobia, longitudinal data suggest heterogeneous outcomes for behaviorally inhibited children. Some inhibited children develop social phobia, whereas others do not (
40). Similarly, only a subset of adolescents with social phobia likely exhibited early childhood behavioral inhibition. Such heterogeneity could explain why temperament-based group differences did not vary by striatal region in our previous work, whereas they did in the present study. Our inclusion of a generalized anxiety disorder group in the present study could further contribute to these differences. For example, we found previously that among adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition, striatal response did not differ by incentive valence. In contrast, in the present study we report heightened sensitivity to gains versus losses in the generalized anxiety disorder group but not in the social phobia or healthy comparison group. While these differences warrant further study, they suggest that risk for and expressions of adolescent anxiety disorders have different neural signatures. Collectively, adolescents with early childhood behavioral inhibition and those with current social phobia or generalized anxiety disorder show both commonalities and differences in striatal activation modulation by incentive magnitude and valence. Longitudinally tracking these patterns may elucidate processes that differentiate increased risk, as manifested in temperament (i.e., behavioral inhibition status), from overt expressions of psychopathology (i.e., anxiety disorder) and clarify neural mechanisms underlying shifts from nonpathological to pathological anxiety.
Our study has some limitations. First, because each group had a relatively small sample size, the results are vulnerable to type I errors. Thus, replication is important in larger samples. Additionally, sample size limited our ability to examine moderating factors such as sex or age/puberty. Future studies with larger samples should identify potential moderators of clinical anxiety and incentive-related striatal function. Second, the generalized anxiety disorder and social phobia groups included adolescents with comorbid depression. Analyses excluding these patients (data not reported) showed similar results. Thus, findings reported in the present study were related to the primary generalized anxiety disorder or social phobia diagnosis rather than the few comorbid depression cases. Because findings in depression typically reveal striatal hyposensitivity rather than hypersensitivity, comorbid depression would likely have muted our between-group differences. Again, studies of larger groups of adolescents with pure social phobia or generalized anxiety disorder need to replicate and extend the present findings. Finally, we focused specifically on striatal function using a model from prior work. Other brain regions may show differential incentive-modulated responses, particularly regions underlying executive function, and other neuroimaging paradigms should be used to probe interactions between incentive processing and executive function.
We found unique neural correlates of adolescent social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder and suggest that incentive-related brain hyperactivation may be an important target for the treatment of adolescent anxiety. Prospective longitudinal studies of incentive processing in adolescents at risk for anxiety disorders (e.g., by virtue of temperament or family history of anxiety) are needed. Such studies can help identify which subgroups of adolescents develop social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, or related disorders (e.g., depression) and, through repeated neuroimaging assays, what neural mechanisms predict the shift to psychopathology.