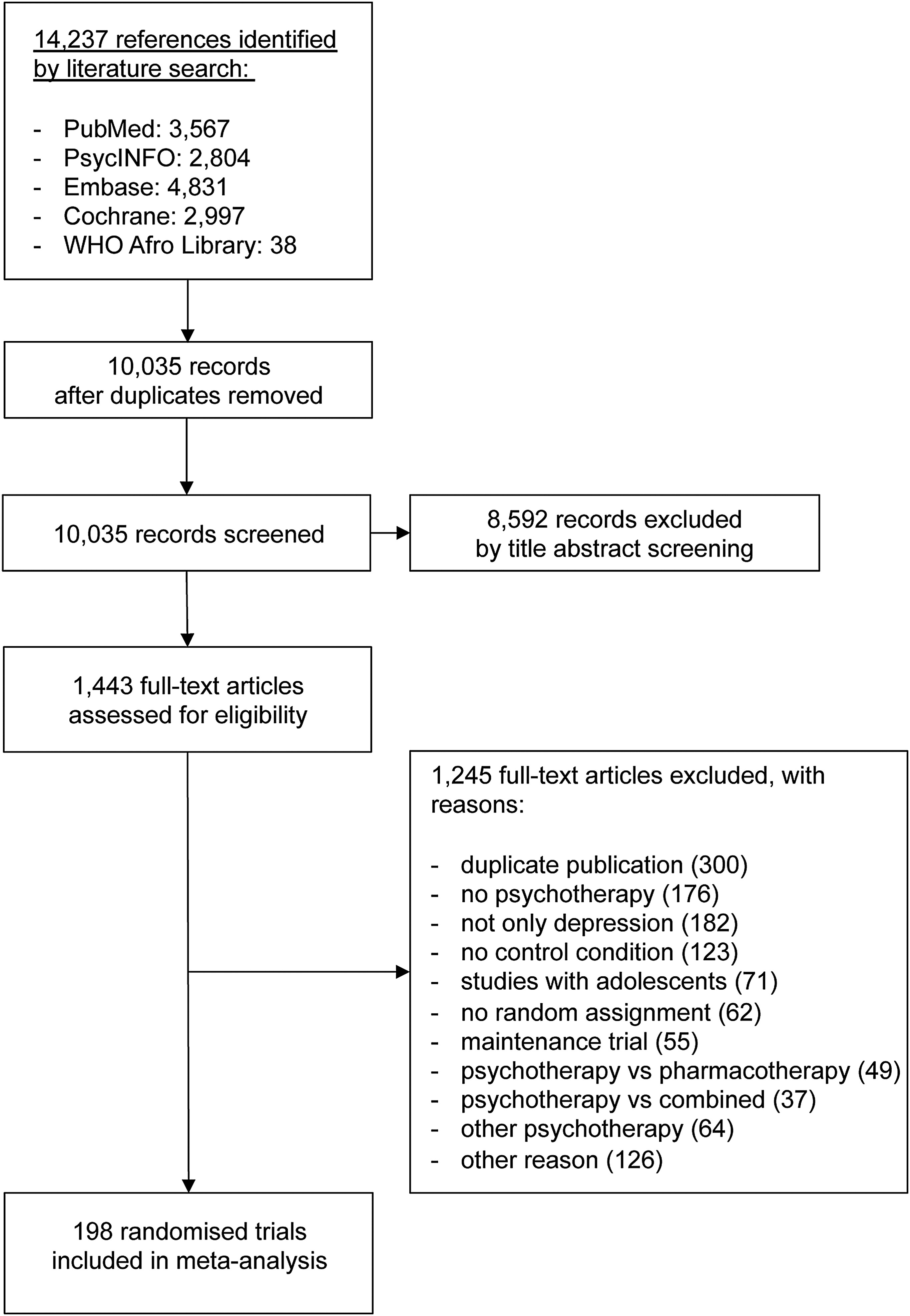
Comparative Efficacy of Seven Psychotherapeutic Interventions for Patients with Depression: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background:
Methods and Findings:
Conclusions:
Introduction
Methods
Study Selection and Inclusion Criteria
Psychotherapeutic Interventions
| Type of Psychotherapeutic Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) | IPT is a brief and highly structured manual-based psychotherapy that addresses interpersonal issues in depression to the exclusion of all other foci of clinical attention (http://www.interpersonalpsychotherapy.org). IPT has no specific theoretical origin, although its theoretical basis can be seen as coming from the work of Sullivan, Meyer, and Bowlby. The current form of the treatment was developed by the late Gerald Klerman and Myrna Weissman in the 1980s [50]. |
| Behavioural activation (ACT) | We considered an intervention to be activity scheduling when the registration of pleasant activities and the increase of positive interactions between a person and his or her environment were the core elements of the treatment. Social skills training could be a part of the intervention. Although this intervention was developed by Lewinsohn [51], we also included studies that used the principles of this intervention but did not refer directly to the work of Lewinsohn and colleagues [51]. Some studies referred to the behavioural activation component included in the manual for CBT by Beck et al. [52]. This component of CBT is based on similar principles. |
| Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) | In CBT, therapists focus on the impact a patient's present dysfunctional thoughts have on current behaviour and future functioning. CBT is aimed at evaluating, challenging, and modifying a patient's dysfunctional beliefs (cognitive restructuring). In this form of treatment, the therapist mostly emphasizes homework assignments and outside-of-session activities. Therapists exert an active influence over therapeutic interactions and topics of discussion, use a psychoeducational approach, and teach patients new ways of coping with stressful situations. |
| Problem-solving therapy (PST) | We defined PST as a psychological intervention in which the following elements had to be included: definition of personal problems, generation of multiple solutions to each problem, selection of the best solution, the working out of a systematic plan for this solution, and evaluation as to whether the solution has resolved the problem. There are several subtypes of PST, such as PST according to Nezu [53] and Mynors-Wallis et al. [54], but the number of studies for each of these subtypes was too small to include in this meta-analysis. |
| Psychodynamic therapy (DYN) | The primary objective in (short-term) psychodynamic therapy is to enhance the patient's understanding, awareness, and insight about repetitive conflicts (intrapsychic and intrapersonal). An assumption in DYN is that a patient's childhood experiences, past unresolved conflicts, and historical relationships significantly affect a person's present life situation. In this form of treatment, the therapist concentrates on the patient's past, unresolved conflicts, and historical relationships and the impact these have on a patient's present functioning. Furthermore, in DYN the therapists explore a patient's wishes, dreams, and fantasies. The time limitations and the focal explorations of the patient's life and emotions distinguish DYN from psychoanalytic psychotherapy |
| Social skills training (SST) | SST is a form of behavioural therapy in which clients are taught skills that help in the building and retainment of social and interpersonal relationships. In most versions of SST, patients are trained in assertiveness. This means that the client is taught to stand up for his or her rights by expressing feelings in an honest and respectful way that does not insult people |
| Supportive counselling (SUP) | We defined supportive counselling as any unstructured therapy without specific psychological techniques other than those common to all approaches, such as helping people to ventilate their experiences and emotions and offering empathy. It is not aimed at solutions or acquiring new skills. It is based on the assumption that relief from personal problems may be achieved through discussion with others. These nondirective therapies are commonly described in the literature as either counselling or supportive therapy. |
Study Characteristics.
Statistical Analysis
Results
| Descriptive Categories | Study Characteristic | Number of Studies | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient population | Regular depression | 94 | 47% |
| Geriatric depression | 26 | 13% | |
| Student populations | 8 | 4% | |
| Women with postpartum depression | 16 | 8% | |
| General medical patients with depression | 27 | 14% | |
| Miscellaneous | 27 | 14% | |
| Psychotherapeutic interventiona | Interpersonal therapy | 27 | 14% |
| Behavioural activation | 26 | 13% | |
| Cognitive-behavioural therapy | 139 | 70% | |
| Problem solving therapy | 19 | 10% | |
| Social skills training | 7 | 4% | |
| Psychodynamic therapy | 16 | 8% | |
| Supportive counselling | 37 | 19% | |
| Control conditionb | Placebo | 27 | 14% |
| Usual care | 60 | 30% | |
| Waitlist | 75 | 38% | |
| Intervention format and setting | Individual and face-to-face | 97 | 49% |
| Other | 98 | 50% | |
| Mixed | 2 | 1% | |
| Country | United States | 115 | 58% |
| United Kingdom | 23 | 11% | |
| Continental Europe | 27 | 13% | |
| Canada | 8 | 4% | |
| Australia | 13 | 6% | |
| Miscellaneous | 15 | 8% |
Meta-Analysis of Within-Study Comparisons
| Psychotherapeutic Intervention/Control Conditions | Waitlist | Usual Care | Placebo | Supportive Counselling | Psychodynamic Therapy | Social Skills Training | Problem Solving Therapy | Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy | Behavioural Activation | Interpersonal Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waitlist | - | - | –0.86 | –1.46 | –0.56 | –1.23 | –0.85 | –1.01 | –1.38 | |
| [–1.63 to –0.10]a | [–5.24 to 1.88] | [–1.06 to –0.10] | [–1.88 to –0.72] | [–0.99 to –0.72] | [–1.50 to –0.58] | [–4.55 to 1.34] | ||||
| τ2 = 0.241 | τ2 = 0.260 | τ2 = 0.056 | τ2 = 0.329 | τ2 = 0.147 | τ2 = 0.143 | τ2 = 0.215 | ||||
| k = 5 | k = 2 | k = 5 | k = 8 | k = 61 | k = 9 | k = 2 | ||||
| Usual care | –0.33 | - | –0.42 | –0.32 | - | –0.28 | –0.50 | –0.55 | –0.58 | |
| [–0.50 to –0.14] | [–0.61 to –0.24] | [–1.13 to 0.45] | [–0.68 to 0.09] | [–0.65 to –0.34] | [–6.90 to 5.34] | [–0.79 to –0.35] | ||||
| τ2 = 0.019 | τ2 = 0.122 | τ2 = 0.032 | τ2 = 0.142 | τ2 = 1.013 | τ2 = 0.078 | |||||
| k = 10 | k = 3 | k = 4 | k = 38 | k = 2 | k = 13 | |||||
| Placebo | –0.33 | –0.01 | –0.94 | –0.80 | - | –0.23 | –0.49 | –0.34 | –0.34 | |
| [–0.53 to –0.13] | [–0.20 to 0.19] | [n.e.]b | [–2.82 to 0.98] | [–1.09 to 0.55] | [–0.65 to –0.32] | [–0.88 to 0.14] | [–0.82 to 0.14] | |||
| τ2 = n.e. | τ2 = 0.736 | τ2 = 0.124 | τ2 = 0.033 | τ2 = 0.099 | τ2 = 0.050 | |||||
| k = 1 | k = 4 | k = 3 | k = 16 | k = 5 | k = 4 | |||||
| Supportive counselling | –0.62 | –0.29 | –0.29 | –0.18 | - | –0.58 | –0.13 | –0.38 | –0.42 | |
| [–0.82 to –0.40] | [–0.48 to –0.11] | [–0.51 to –0.06] | [–0.72 to 0.41] | [–1.44 to 0.09] | [–0.30 to 0.03] | [–1.05 to 0.27] | [–0.95 to 0.08] | |||
| τ2 = 0.046 | τ2 = 0.086 | τ2 = 0.064 | τ2 = 0.082 | τ2 = 0.054 | ||||||
| k = 3 | k = 3 | k = 23 | k = 4 | k = 4 | ||||||
| Psychodynamic therapy | –0.72 | –0.39 | –0.39 | –0.10 | –0.00 | - | –0.22 | –0.21 | - | |
| [–1.02 to –0.41] | [–0.68 to –0.11] | [–0.68 to –0.09] | [–0.41 to 0.20] | [–2.32 to 2.14] | [–0.59 to 0.06] | [–0.88 to 0.45] | ||||
| τ2 = 0.121 | τ2 = 0.063 | τ2 = 0.055 | ||||||||
| k = 2 | k = 9 | k = 3 | ||||||||
| Social skill training | –0.62 | –0.30 | –0.30 | –0.01 | 0.09 | –0.04 | 0.11 | 0.02 | - | |
| [–1.19 to –0.10] | [–0.88 to 0.25] | [–0.86 to 0.24] | [–0.60 to 0.54] | [–0.49 to 0.65] | [n.e.] | [–0.66 to 0.84] | [n.e.] | |||
| τ2 = n.e. | τ2 = 0.065 | τ2 = n.e. | ||||||||
| k= 1 | k = 3 | k =1 | ||||||||
| Problem solving therapy | –0.74 | –0.41 | –0.41 | –0.12 | –0.02 | –0.11 | –0.02 | 0.04 | - | |
| [–0.97 to –0.50] | [–0.63 to –0.18] | [–0.64 to –0.18] | [–0.36 to 0.13] | [–0.35 to 0.32] | [–0.68 to 0.49] | [–0.50 to 0.36] | [–2.53 to 2.51] | |||
| τ2 = 0.044 | τ2 = 0.156 | |||||||||
| k = 4 | k = 2 | |||||||||
| Cognitive-behavioural therapy | –0.78 | –0.45 | –0.45 | –0.16 | –0.06 | –0.15 | –0.04 | 0.12 | –0.05 | |
| [–0.91 to –0.64] | [–0.58 to –0.32] | [–0.61 to –0.28] | [–0.33 to 0.01] | [–0.33 to 0.22] | [–0.67 to 0.41] | [–0.25 to 0.17] | [–0.11 to 0.36] | [–0.31 to 0.20] | ||
| τ2 = 0.030 | τ2 = 0.031 | |||||||||
| k = 14 | k = 6 | |||||||||
| Behavioural activation | –0.80 | –0.47 | –0.46 | –0.18 | –0.08 | –0.17 | –0.06 | –0.02 | – | |
| [–1.08 to –0.51] | [–0.75 to –0.19] | [–0.76 to –0.18] | [–0.47 to 0.12] | [–0.43 to 0.26] | [–0.72 to 0.43] | [–0.38 to 0.26] | [–0.29 to 0.25] | |||
| Interpersonal therapy | –0.92 | –0.59 | –0.58 | –0.30 | –0.19 | –0.29 | –0.18 | –0.14 | –0.12 | |
| [–1.14 to –0.69] | [–0.78 to –0.39] | [–0.82 to –0.34] | [–0.54 to –0.05] | [–0.53 to 0.14] | [–0.85 to 0.31] | [–0.46 to 0.09] | [–0.33 to 0.07] | [–0.44 to 0.20] |
Network Meta-Analysis
Moderator Analyses.
| Characteristics | Number of Trials | Number of Patients | τ2 | Interpersonal Therapy | Behavioural Activation | Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy | Problem Solving Therapy | Social Skills Training | Psychodynamic Therapy | Supportive Counselling | d-Difference or p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All trials | 198 | 15,118 | 0.010 | –0.92 | –0.80 | –0.78 | –0.74 | –0.62 | –0.72 | –0.62 | – |
| [–1.14 to –0.69] | [–1.08 to –0.51] | [–0.91 to –0.64] | [–0.97 to –0.50] | [–1.19 to –0.10] | [–1.02 to –0.41] | [–0.82 to –0.40] | |||||
| Patient population | |||||||||||
| Regular depression | 94 | 6,992 | 0.015 | –0.92 | –0.91 | –0.82 | –0.70 | –0.76 | –0.77 | –0.70 | –0.08 [–0.34 to 0.18] |
| [–1.26 to –0.57] | (–1.31 to –0.51) | (–1.00 to –0.63) | (–1.05 to –0.37) | (–1.39 to –0.13) | (–1.20 to –0.33) | (–1.08 to –0.31) | |||||
| Specific population | 104 | 8,126 | 0.014 | –0.91 | –0.68 | –0.74 | –0.76 | –0.20 | –0.68 | –0.58 | p = 0.543 |
| [–1.24 to –0.59] | [–1.10 to –0.25] | [–0.93 to –0.56] | [–1.12 to –0.42] | [–1.55 to 1.13] | [–1.09 to –0.27] | [–0.87 to –0.29] | |||||
| Intervention format and setting | |||||||||||
| Individual and face-to-facea | 98 | 7,275 | 0.011 | –0.95 | –0.89 | –0.84 | –0.84 | –0.53 | –0.75 | –0.68 | –0.07 [–0.37 to 0.22] |
| [–1.29 to –0.60] | [–1.27 to –0.53] | [–1.10 to –0.58] | [–1.22 to –0.48] | [–1.39 to 0.25] | [–1.15 to –0.35] | [–1.04 to –0.31] | |||||
| Othera | 97 | 8,450 | 0.014 | –1.00 | –0.71 | –0.75 | –0.79 | –0.74 | –0.92 | –0.61 | p = 0.650 |
| [–1.39 to –0.59] | [–1.29 to –0.16] | [–0.90 to –0.60] | [–1.24 to –0.36] | [–1.46 to 0.03] | [–1.55 to –0.28] | [–0.91 to –0.30] | |||||
| Treatment dose | |||||||||||
| Low | 47 | 3,669 | 0.014 | –1.12 | –1.09 | –1.06 | –1.00 | –0.49 | –0.73 | –1.22 | 0.33 [–0.01 to 0.65] |
| [–1.77 to –0.47] | [–1.89 to –0.26] | [–1.36 to –0.76] | [–1.43 to –0.57] | [–1.52 to 0.54] | [–1.43 to –0.03] | [–1.77 to –0.66] | |||||
| High | 151 | 11,449 | 0.010 | –0.80 | –0.73 | –0.70 | –0.80 | –0.72 | –0.70 | –0.52 | p = 0.059 |
| [–1.06 to –0.55] | [–1.04 to –0.43] | [–0.84 to –0.55] | [–1.11 to –0.48] | [–1.38 to –0.09] | [–1.02 to –0.37] | [–0.76 to –0.29] | |||||
| Diagnosis | |||||||||||
| Formal diagnosis | 71 | 5,140 | 0.012 | –0.78 | –1.03 | –0.86 | –1.14 | –0.27 | –0.87 | –0.69 | –0.11 [–0.39 to 0.18] |
| [–1.14 to –0.45] | [–1.46 to –0.58] | [–1.10 to –0.62] | [–1.65 to –0.65] | [–62.08 to 62.10] | [–1.28 to –0.45] | [–1.10 to –0.27] | |||||
| Probable depression | 127 | 9,978 | 0.011 | –1.14 | –0.69 | –0.75 | –0.64 | –0.59 | –0.63 | –0.68 | p = 0.454 |
| [–1.49 to –0.78] | [–1.09 to –0.27] | [–0.91 to –0.59] [–0.92 to –0.34] | [–1.22 to –0.04] | [–1.08 to –0.19] | [–0.95 to –0.43] | ||||||
| Concealment of allocation | |||||||||||
| Adequate | 34 | 4,621 | 0.018 | –0.58 | –0.92 | –0.65 | –0.50 | 0.03 | –0.62 | –0.49 | 0.19 [–0.08 to 0.47] |
| [–1.97 to 0.77] | [–1.59 to –0.23] | [–0.89 to –0.41] | [–0.88 to –0.12] | [–62.07 to 62.74] | [–1.26 to 0.00] | [–1.03 to 0.04] | |||||
| Inadequate or not reported | 164 | 10,497 | 0.011 | –0.92 | –0.79 | –0.83 | –1.02 | –0.67 | –0.75 | –0.69 | p = 0.162 |
| [–1.18 to –0.67] | [–1.11 to –0.49] | [–1.00 to –0.68] | [–1.37 to –0.67] | [–1.23 to –0.14] | [–1.12 to –0.43] | [–0.94 to –0.45] | |||||
| Outcome assessment | |||||||||||
| Adequate | 169 | 13,913 | 0.011 | –0.90 | –0.73 | –0.74 | –0.69 | –0.62 | –0.68 | –0.59 | 0.38 [–0.06 to 0.87] |
| [–1.16 to –0.62] | [–1.08 to –0.36] | [–0.88 to –0.61] | [–0.94 to –0.44] | [–1.20 to –0.04] | [–0.99 to –0.38] | [–0.82 to –0.37] | |||||
| Inadequate or not reported | 29 | 1,205 | 0.024 | –1.15 | –1.16 | –1.11 | –1.08 | –0.85 | –0.92 | –0.75 | p = 0.100 |
| [–1.73 to –0.59] | [–1.76 to –0.56] | [–1.56 to –0.66] | [–2.15 to –0.04] | [–2.73 to 1.05] | [–1.96 to 0.06] | [–1.58 to 0.16] | |||||
| Adequate analysis [ITT] | |||||||||||
| Yes | 91 | 10,007 | 0.014 | –0.89 | –0.73 | –0.73 | –0.64 | 0.23 | –0.72 | –0.51 | 0.13 [–0.14 to 0.39] |
| [–1.19 to –0.58] | [–1.19 to –0.26] | [–0.90 to –0.55] | [–0.93 to –0.36] | [–61.92 to 61.92] | [–1.12 to –0.32] | [–0.79 to –0.22] | |||||
| No | 107 | 5,111 | 0.012 | –0.88 | –0.85 | –0.83 | –1.07 | –0.65 | –0.68 | –0.77 | p = 0.354 |
| [–1.29 to –0.46] | [–1.22 to –0.49] | [–1.05 to –0.63] | [–1.63 to –0.50] | [–1.18 to –0.09] | [–1.14 to –0.21] | [–1.13 to –0.39] | |||||
| Trial size | |||||||||||
| moderate to large [≥25] | 95 | 11,704 | 0.013 | –0.85 | –0.69 | –0.68 | –0.57 | –0.51 | –0.60 | –0.51 | 0.29 [–0.01 to 0.58] |
| [–1.12 to –0.58] | [–1.22 to –0.16] | [–0.84 to –0.53] | [–0.85 to –0.29] | [–62.04 to 61.30] | [–0.96 to –0.24] | [–0.78 to –0.26] | |||||
| small [< 25] | 103 | 3,414 | 0.013 | –0.99 | –0.92 | –0.95 | –1.23 | –0.72 | –0.90 | –0.79 | p = 0.063 |
| [–1.48 to –0.49] | [–1.27 to –0.56] | [–1.19 to –0.71] | [–1.76 to –0.71] | [–1.29 to –0.14] | [–1.38 to –0.37] | [–1.17 to –0.39] | |||||
| Trial size | |||||||||||
| large [≥50] | 36 | 7,229 | 0.025 | –0.73 | –0.14 | –0.57 | –0.46 | –0.25 | –0.12 | –0.29 | 0.33 [0.08 to 0.61] |
| [–1.14 to –0.32] | [–62.11 to 62.05] | [–0.80 to –0.35] | [–0.81 to –0.12] | [–62.44 to 61.74] | [–0.92 to 0.67] | [–0.67 to 0.09] | |||||
| small to moderate [< 50] | 162 | 7,889 | 0.009 | –1.00 | –0.92 | –0.90 | –1.09 | –0.72 | –0.89 | –0.80 | p = 0.012 |
| [–1.28 to –0.70] | [–1.23 to –0.60] | [–1.07 to –0.73] | [–1.52 to –0.67] | [–1.31 to –0.15] | [–1.23 to –0.55] | [–1.05 to –0.53] | |||||
| Publication year | |||||||||||
| Early [< 2000] | 115 | 3,686 | 0.012 | –0.79 | –0.86 | –0.83 | –1.16 | –0.63 | –0.61 | –0.81 | 0.14 [–0.15 to 0.42] |
| [–1.23 to –0.34] | [–1.26 to –0.46] | [–1.06 to –0.59] | [–1.73 to –0.65] | [–1.22 to –0.07] | [–1.09 to –0.15] | [–1.20 to –0.40] | |||||
| Recent [≥2000] | 83 | 11,432 | 0.013 | –0.95 | –0.74 | –0.73 | –0.61 | 0.10 | –0.76 | –0.51 | p = 0.363 |
| [–1.22 to –0.67] | [–1.17 to –0.29] | [–0.89 to –0.57] | [–0.89 to –0.33] | [–61.51 to 62.60] | [–1.14 to –0.39] | [–0.77 to –0.25] |
Stepwise Restriction of Network Meta-Analyses According to Sample Size
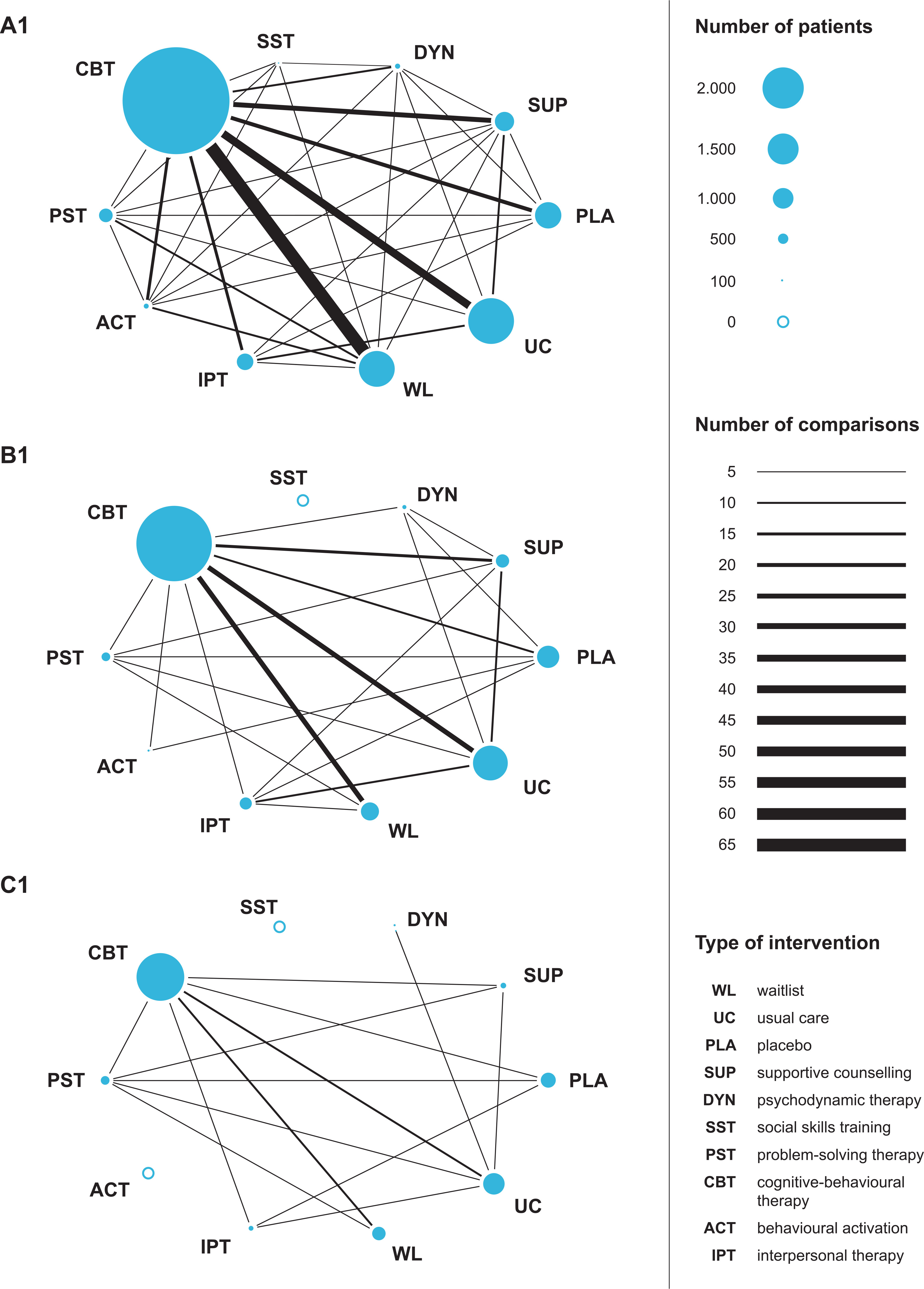
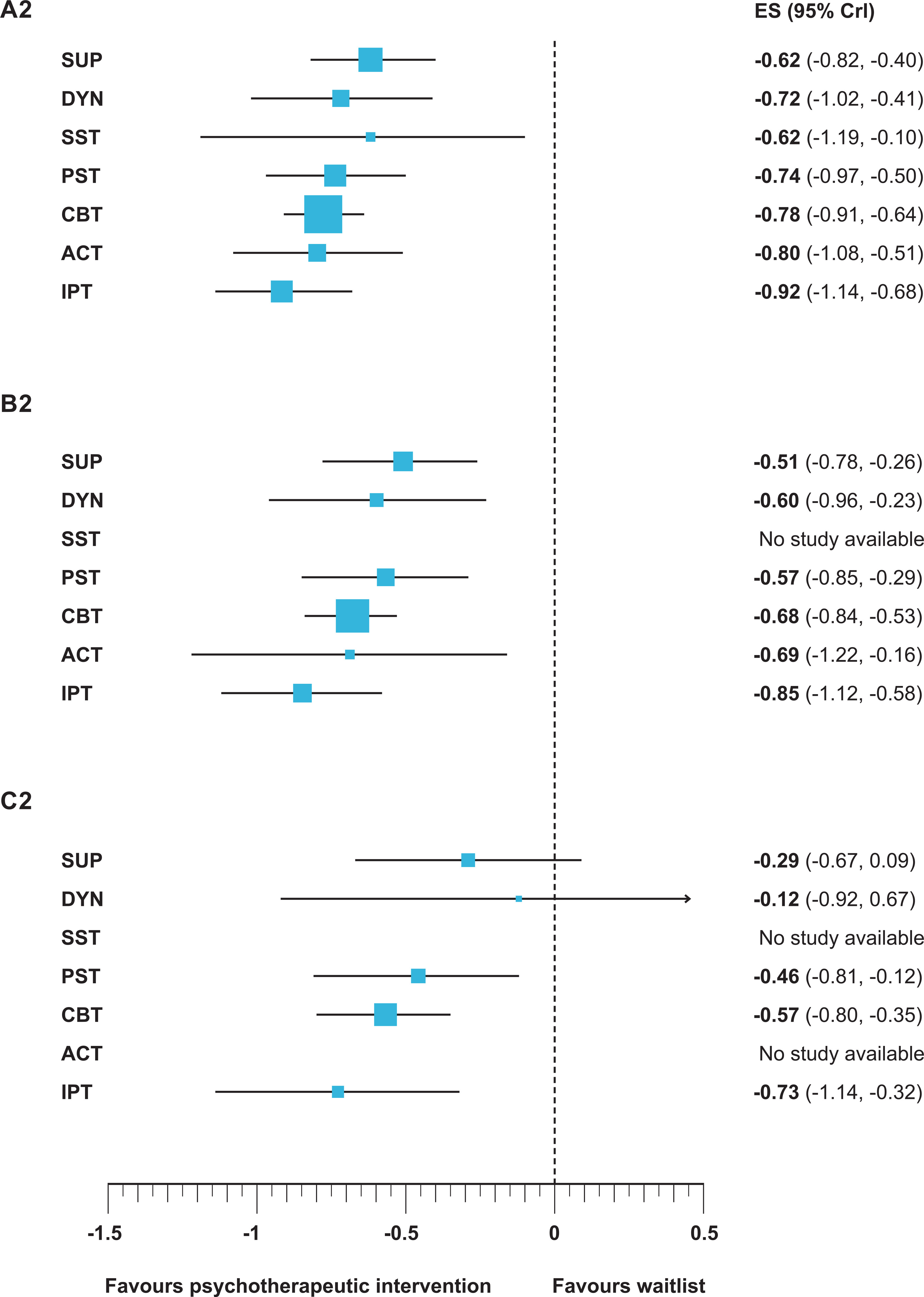
Discussion
Editors’ Summary
Conclusions
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBGet Access
Login options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

