T
o the E
ditor: In the December 2011 issue, Veling et al. (
1) report on a study from the Netherlands that the risk of psychotic disorders in immigrants decreased with age at the time of immigration. The authors suggest that early life is an important risk period for the development of psychosis in immigrants. We sought to replicate their findings using data from the Danish nationwide population-based registers.
Data on persons who were born between 1971 and 1995 and who resided in Denmark by the age of 15 were followed for the development of schizophrenia (ICD-10:F20, ICD-8:295) from age 15 until December 31, 2010, using survival analysis techniques. Immigrants were identified as persons born abroad; developmental level of country of origin was categorized as “developing” or “developed” (
2). Age at migration was identified as age at the time of first permanent residence in Denmark.
During the study period, 809 immigrants from developing countries, 248 immigrants from developed countries, and 8,767 Danes developed schizophrenia. After adjusting for age, sex, and calendar year, immigrants from developing countries had a 2.34-fold greater risk for schizophrenia (95% confidence interval [CI]=2.17–2.51); immigrants from developed countries had a 1.90-fold greater risk (95% CI=1.67–2.15).
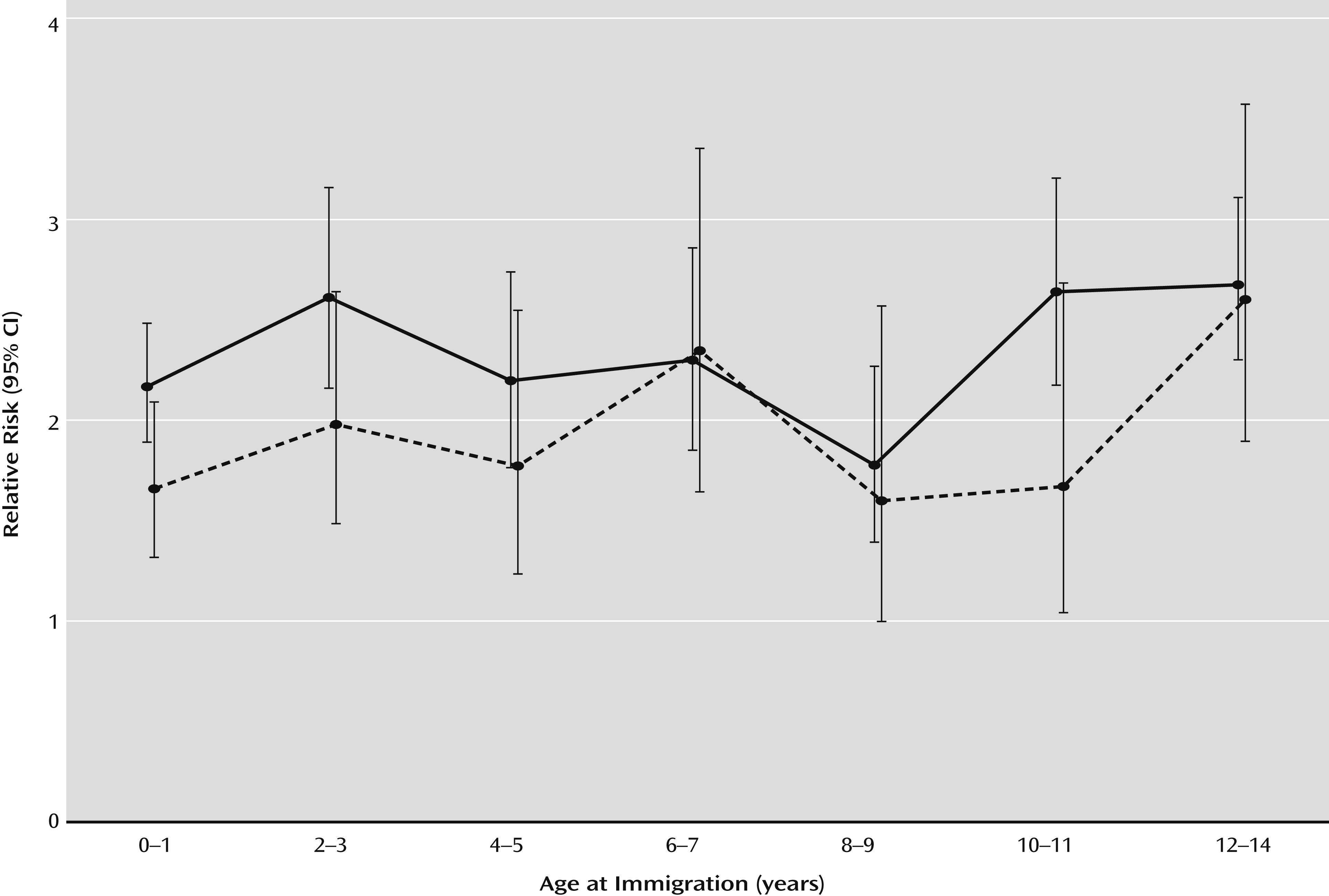
The incidence rate ratio of schizophrenia, by country of origin as well as by age at the time of immigration to Denmark, compared with Danish-born individuals, is depicted graphically in
Figure 1. For example, individuals from developed countries who immigrated to Denmark before their second birthday had a 1.66-fold significantly greater risk of schizophrenia (95% CI=1.30–2.07), and individuals from developing countries who immigrated to Denmark before their second birthday had a 2.16-fold significantly greater risk of schizophrenia (95% CI=1.88–2.48). When including age at migration as a trend in the model, the incidence rate ratio of schizophrenia increased by 1.02 (95% CI=1.00–1.05) for every 1-year increase in the age at migration from developed countries and increased by 1.01 (95% CI=1.00–1.03) for every 1-year increase in the age at migration from developing countries.
Although the majority of immigrants in our sample originated from developing countries, subdividing the developmental status of country of origin yielded no differences in the impact of age at immigration. Thus, the differences observed between the two studies are not due to any differential impact of age at migration in relation to degree of “Westernization” of the country of origin, a factor that Veling et al. (
1) suggest may be important. We found no evidence that risk of schizophrenia decreases with age at the time of immigration to Denmark. Our Danish study investigated the potential effect of age at immigration before the 15th birthday, while the Veling et al. Dutch study investigated the potential effect up until approximately age 30. However, because the greatest impact in the Dutch study was observed in individuals migrating early in life, this cannot explain the differences in the observed results.