The Hotel Study: Multimorbidity in a Community Sample Living in Marginal Housing
Abstract
Objective
Method
Results
Conclusions
Method
Study Enrollment and Design
| Variable and Assessment Measure |
|---|
| Sociodemographic data |
| Standard interview incorporates questions from the Canadian Community Health Survey (20). (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Substance use |
| Initial interview records lifetime history of use, age of first exposure, and periods of heavy use for alcohol and illicit drugs. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence (21). (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Maudsley Addiction Profile (22): assesses drug use, related mental and physical symptoms, and risk behaviors for the past 30 days. Includes a rating of frequency of thoughts of ending life, scored on a scale of 0 to 4, with 2 representing “sometimes.” (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Time-Line Follow-Back (23): records alcohol and drug use (prescribed and illicit, types, amounts, and pattern) over the previous 4 weeks, as well as money spent on alcohol and illicit drugs. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Urine drug screen: detects amphetamines, methamphetamine, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cocaine (crack), marijuana, methadone, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy), opiates, and tricyclic antidepressants. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Mental illness |
| Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (24, 25): a semistructured clinical interview used to collect information allowing a diagnosis of DSM-IV axis I disorders, validated in substance-using and general medical samples. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| International Personality Disorder Examination, Screener (26): a screening instrument for DSM-IV personality disorders. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (27): a 30-item scale rated after an interview and mental status examination by a psychiatrist, used to assess the severity of a range of symptoms of psychosis and general mental health. (Administered by a psychiatrist.) |
| Beck Depression Inventory (28): a self-report measure of depression, including an assessment of suicidal ideation, scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with 1 representing thoughts of killing self, without intent. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Trauma History Questionnaire (29): measures exposure to traumatic life events and records frequency and age of exposure. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Best Estimate Clinical Evaluation and Diagnosis (30): information obtained from all assessments and from hospital records is used to make DSM-IV diagnoses of substance dependence and mental illness. (Psychiatrist assessment.) |
| Cognitive functioning |
| Wechsler Test of Adult Reading (31): provides an index of premorbid intellectual ability. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Stroop color and word test (32): measures the ability of the individual to separate word and color naming stimuli; this requires sustained attention and inhibition of a dominant response set. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Intradimensional-extradimensional shift task from the Cambridge Neuropsychological Automated Test Battery (33): evaluates attentional shifting to attributes of a complex stimulus array. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Rapid Visual Information Processing Task from the Cambridge Neuropsychological Automated Test Battery (34): a test that requires monitoring and responding to specific digit sequences and inhibiting responses to distracters. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Hopkins Verbal Learning Test, Revised (35): a brief assessment of memory, which includes many of the elements also found in detailed tests, such as the California Verbal Learning Test. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Iowa gambling task (36): assesses decision making in response to differential incentive conditions, sensitive to orbitofrontal functioning, and used to evaluate decision making. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Neurological illness |
| Traumatic brain injury: inquiry into serious head or facial injury, the event causing the injury, the extent of the injury, duration of loss of consciousness, need for hospitalization, duration of symptoms of dizziness, blurred vision, and confusion or memory loss. (Administered by a research assistant/neuropsychologist interpretation.) |
| Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale (37): rated after a movement disorders examination. (Administered by a psychiatrist or neurologist.) |
| Barnes Akathisia Rating Scale (38): rated after a movement disorders examination. (Administered by a psychiatrist or neurologist.) |
| Cambridge Neurological Inventory (39): a focused neurological examination for motor coordination and sensory integration soft signs, including anomia. (Administered by a psychiatrist or neurologist.) |
| Medical illness |
| Serology for HIV, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus, qualitative polymerase chain reaction for hepatitis C virus; blood samples were drawn for testing at the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control. |
| CBC and differential, platelet count, AST, ALT. |
| Psychosocial functioning |
| Role Functioning Scale (40): a rating of daily functioning in four domains (work productivity, independent living, and immediate and extended social network relationships; each rated on a scale of 1 to 7). Higher scores represent better function. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
| Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale (41): rated on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher scores representing better functioning. (Administered by a research assistant.) |
Assessment of Mortality
Assessment of Substance Dependence
Assessment and Diagnosis of Mental Illness
Assessment and Diagnosis of Physical Illness
Statistical Analysis
Results
Participants
| Characteristic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | Median | Interquartile Range | |
| Age (years) | 293 | 44.1 | 37.1–50.9 |
| Monthly income (Canadian dollars) | 286 | 870 | 610–1,100 |
| Months in current hotel at baseline | 292 | 16 | 2–52 |
| Months since last homeless | 195 | 38 | 8–93 |
| Total N | N | % | |
| Female | 293 | 68 | 23.2 |
| Current marital status | |||
| Married or common-law | 293 | 50 | 17.1 |
| Separated or divorced | 293 | 67 | 22.9 |
| Single | 293 | 176 | 60.1 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| White | 293 | 172 | 58.7 |
| Black | 293 | 7 | 2.4 |
| Asian | 293 | 8 | 2.7 |
| Aboriginal | 293 | 83 | 28.3 |
| Mixed/other | 293 | 23 | 7.8 |
| Education | |||
| Did not complete high school | 293 | 168 | 57.3 |
| Completed high school | 293 | 113 | 38.6 |
| Completed a college or university program | 293 | 12 | 4.1 |
| Earned income in addition to benefits | 291 | 23 | 7.6 |
| Homeless in the past | 293 | 195 | 66.6 |
| Jailed in the past | 293 | 71 | 24.2 |
Mortality
Substance Dependence and Mental Illness
| Clinical Characteristic | Total N | Baseline | Lifetime | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Substance dependence, any (nicotine excluded)a | 293 | 279 | 95.2 | 287 | 98.0 |
| Stimulant use (cocaine and/or methamphetamine) | 293 | 240 | 81.9 | 257 | 87.7 |
| Opioid use (heroin or other) | 293 | 115 | 39.2 | 179 | 61.9 |
| Alcohol dependence | 293 | 56 | 19.1 | 140 | 47.8 |
| Tobacco use (daily) | 289 | 240 | 83.0 | 260 | 90.0 |
| Mental illness, anyb | 293 | 218 | 74.4 | 250 | 85.3 |
| Psychotic illness, any | 293 | 139 | 47.4 | 172 | 58.7 |
| Mood disorder, any | 293 | 87 | 29.7 | 155 | 52.9 |
| Anxiety disorder, any | 293 | 70 | 23.5 | 92 | 31.4 |
| Neurological illness (active and/or current treatment)c | 273 | 125 | 45.8 | ||
| Movement disorderd | 269 | 52 | 19.3 | ||
| Brain infarction on MRI, any | 232 | 26 | 11.2 | ||
| Aneurysm on MR angiography | 232 | 20 | 8.6 | ||
| Traumatic brain injury (definite)e | 293 | 31 | 10.6 | ||
| Seizures in past year and/or current treatment | 292 | 26 | 8.9 | ||
| Clinical cognitive impairment (according to DSM-IV criteria) | 293 | 19 | 6.5 | ||
| Other neurological illnessf | 293 | 4 | 1.4 | ||
| Other MRI findingsg | 232 | 7 | 3.0 | ||
| Infection | |||||
| Anti-HIV positive | 283 | 52 | 18.4 | ||
| Anti-hepatitis C virus positive | 283 | 199 | 70.3 | ||
| Hepatitis C viremia (hepatitis C virus seropositive only) | 190 | 145 | 76.3 | ||
| AST:platelet ratio index (hepatitis C virus seropositive only)h | |||||
| 0–0.7 | 191 | 139 | 72.8 | ||
| >0.7 | 191 | 52 | 27.2 | ||
| >2 | 191 | 11 | 5.8 | ||
| Hepatitis B virus surface antigen positive | 283 | 3 | 1.1 | ||
Neurological Illness and Viral Exposure
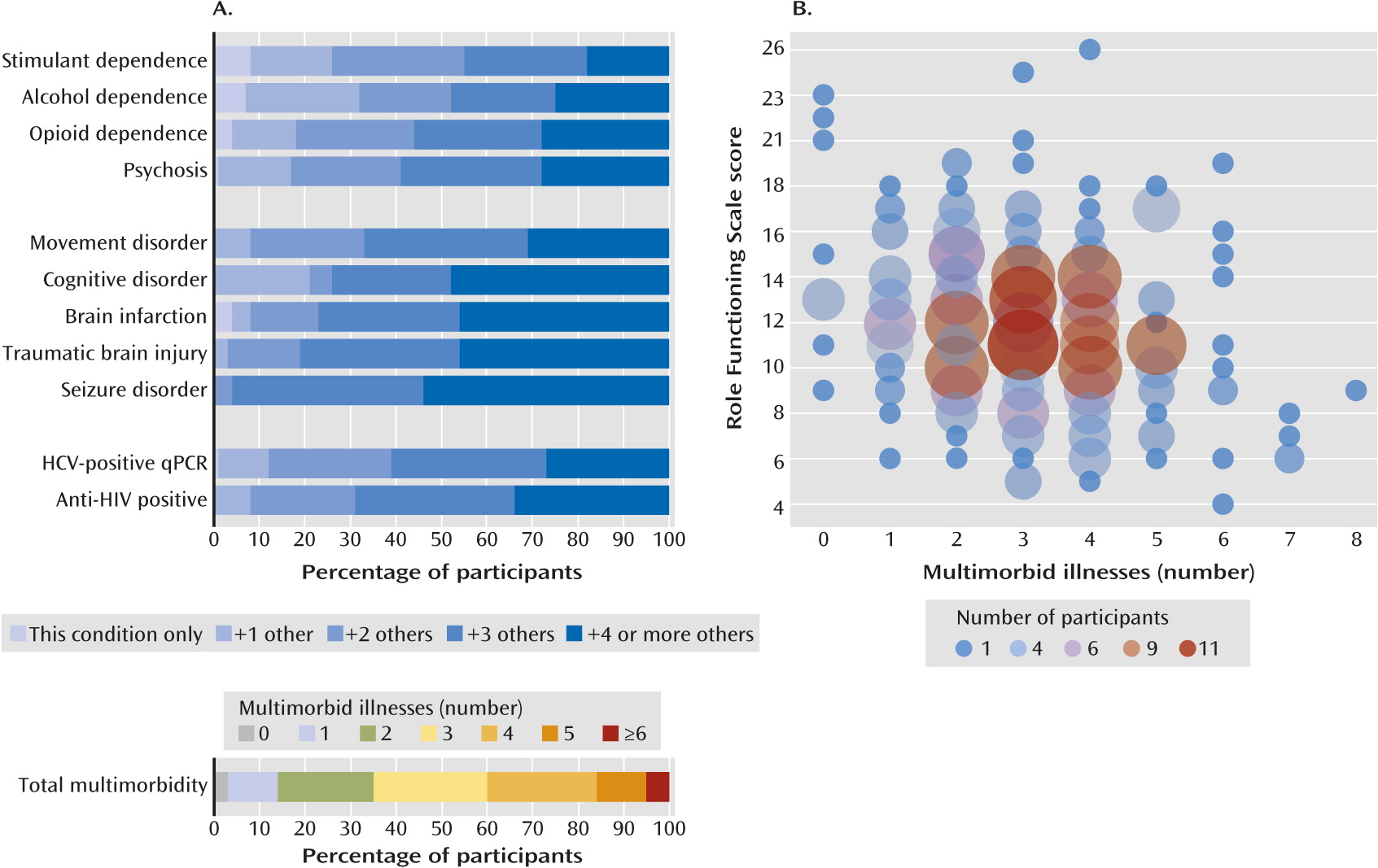
Multimorbidity
| Treatment Provided | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Antipsychotic medication | ||
| Of total number with psychosis (N=135) | 44 | 32.6 |
| Without opioid dependence or HIV/AIDS multimorbidity (N=64) | 29 | 45.3 |
| With opioid dependence or HIV/AIDS multimorbidity (N=71) | 15 | 21.1a |
| Methadone | ||
| Of total number with opioid dependence (N=113) | 56 | 49.6 |
| Without psychosis or HIV/AIDS multimorbidity (N=52) | 24 | 46.0 |
| With psychosis or HIV/AIDS multimorbidity (N=61) | 32 | 52.5 |
| Antiretroviral medication | ||
| Of total number with HIV/AIDS treatment indicated (N=52) | 32 | 61.5 |
| Without opioid dependence or psychosis multimorbidity (N=16) | 9 | 56.3 |
| With opioid dependence or psychosis multimorbidity (N=36) | 23 | 63.9 |
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 3.57 MB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

