Intellectual Disability and Psychotic Disorders in Children: Association With Maternal Severe Mental Illness and Exposure to Obstetric Complications in a Whole-Population Cohort
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
Method
Study Population
Outcome Variable: Intellectual Disability
Psychotic Disorders in Children
Exposure Variables
Maternal severe mental illness.
Obstetric complications.
Other covariates.
Data Analyses
Results
Sample Characteristics
| Children With Intellectual Disability | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cohort (N=464,580) | Maternal Severe Mental Illness (N=15,351) | Maternal Schizophrenia (N=1,653) | Any (N=6,217) | Genetic Basis (N=860) | ||||||
| Characteristic | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % |
| Child with intellectual disability | 6,217 | 1.3 | 510 | 3.3 | 77 | 4.7 | ||||
| Child with intellectual disability and information on the cause | 3,179 | 262 | 43 | |||||||
| Child with intellectual disability of a genetic basis | 860 | 0.2 | 54 | 0.4 | 7 | 0.4 | ||||
| Exposure to obstetric complications of critical severity | ||||||||||
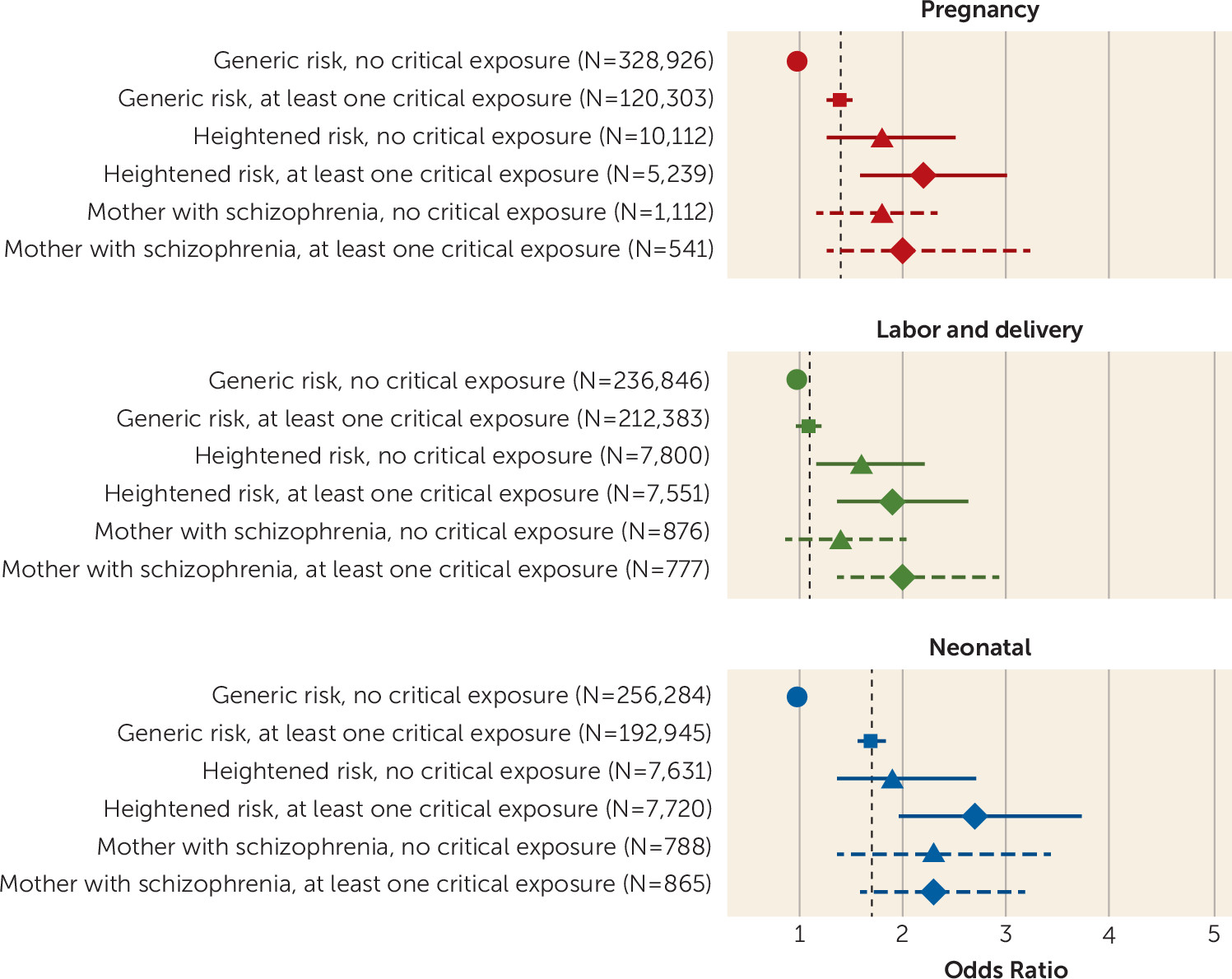
| During pregnancy | 125,542 | 27.0 | 5,239 | 34.1 | 541 | 32.7 | 2,380 | 38.3 | 406 | 47.2 |
| During labor and delivery | 219,934 | 47.3 | 7,551 | 49.2 | 777 | 47.0 | 3,311 | 53.3 | 439 | 51.0 |
| During the neonatal period | 200,665 | 43.2 | 7,720 | 50.3 | 865 | 52.3 | 3,768 | 60.6 | 636 | 74.0 |
| During pregnancy, labor and delivery, or the neonatal period | 327,452 | 70.5 | 11,552 | 75.3 | 1,232 | 74.5 | 5,013 | 80.6 | 749 | 87.1 |
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Male | 238,381 | 51.3 | 7,962 | 51.9 | 875 | 52.9 | 3,937 | 63.3 | 486 | 56.5 |
| Female | 226,199 | 48.7 | 7,389 | 48.1 | 778 | 47.1 | 2,280 | 36.7 | 374 | 43.5 |
| Maternal age (years) | ||||||||||
| ≤19 | 25,979 | 5.6 | 1,557 | 10.1 | 198 | 12.0 | 574 | 9.2 | 36 | 4.2 |
| 20–34 | 389,483 | 83.8 | 12,341 | 80.4 | 1,249 | 75.6 | 4,957 | 79.7 | 663 | 77.1 |
| ≥35 | 49,102 | 10.6 | 1,453 | 9.5 | 206 | 12.5 | 686 | 11.0 | 161 | 18.7 |
| Unknown | 16 | 0.6 | ||||||||
| Maternal place of birth | ||||||||||
| Outside Australia | 136,016 | 29.3 | 3,632 | 23.7 | 382 | 23.1 | 1,551 | 24.9 | 284 | 33.0 |
| Australia | 327,560 | 70.5 | 11,679 | 76.1 | 1,267 | 76.6 | 4,650 | 74.8 | 576 | 67.0 |
| Unknown | 1,004 | 0.2 | 40 | 0.3 | 4 | 0.2 | 16 | 0.3 | ||
| Father’s age (years) | ||||||||||
| ≤19 | 6,553 | 1.4 | 363 | 2.4 | 45 | 2.7 | 155 | 2.5 | 10 | 1.2 |
| 20–54 | 435,934 | 93.8 | 13,174 | 85.8 | 1,211 | 73.3 | 5,437 | 87.5 | 813 | 94.5 |
| ≥55 | 1,034 | 0.2 | 43 | 0.3 | 3 | 0.2 | 27 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.6 |
| Unknown | 17,795 | 3.8 | 1,577 | 10.3 | 356 | 21.5 | 532 | 8.6 | 29 | 3.4 |
| Father unknown | 3,264 | 0.7 | 194 | 1.3 | 38 | 2.3 | 66 | 1.1 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Father’s place of birth (if the father is known) | ||||||||||
| Outside Australia | 140,099 | 30.2 | 3,741 | 24.4 | 423 | 25.6 | 1,615 | 26.0 | 285 | 33.1 |
| Australia | 303,189 | 65.3 | 9,837 | 64.1 | 835 | 50.5 | 4,004 | 64.4 | 543 | 63.1 |
| Unknown | 18,028 | 3.9 | 1,579 | 10.3 | 357 | 21.6 | 532 | 8.6 | 29 | 3.4 |
| Birth cohort | ||||||||||
| 1980–1982 | 56,062 | 12.1 | 1,938 | 12.6 | 266 | 16.1 | 395 | 6.4 | 109 | 12.7 |
| 1983–1986 | 80,197 | 17.3 | 2,744 | 17.9 | 327 | 19.8 | 1,099 | 17.7 | 177 | 20.6 |
| 1987–1992 | 130,685 | 28.1 | 4,478 | 29.2 | 511 | 30.9 | 2,469 | 39.7 | 261 | 30.3 |
| 1993–1996 | 87,708 | 18.9 | 2,917 | 19.0 | 277 | 16.8 | 1,346 | 21.7 | 152 | 17.7 |
| 1997–2001 | 109,928 | 23.7 | 3,274 | 21.3 | 272 | 16.5 | 908 | 14.6 | 161 | 18.7 |
| Birth order | ||||||||||
| 1 | 180,960 | 39.0 | 5,449 | 35.5 | 628 | 38.0 | 2,241 | 36.0 | 297 | 34.5 |
| 2 | 156,878 | 33.8 | 4,795 | 31.2 | 496 | 30.0 | 1,853 | 29.8 | 256 | 29.8 |
| 3 | 80,423 | 17.3 | 2,842 | 18.5 | 281 | 17.0 | 1,151 | 18.5 | 166 | 19.3 |
| ≥4 | 46,319 | 10.0 | 2,265 | 14.8 | 248 | 15.0 | 972 | 15.6 | 141 | 16.4 |
| Mother’s marital status at time of child’s birth | ||||||||||
| Married or de facto marriage | 422,622 | 91.0 | 12,321 | 80.3 | 1,110 | 67.2 | 5,190 | 83.5 | 787 | 91.5 |
| Single or other | 41,697 | 9.0 | 3,006 | 19.6 | 539 | 32.6 | 1,023 | 16.5 | 73 | 8.5 |
| Unknown | 261 | 0.1 | 24 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.1 | ||
| Socioeconomic index of mother’s residence at time of child’s birth | ||||||||||
| Lowest quintile (most disadvantaged) | 90,433 | 19.5 | 4,322 | 28.2 | 581 | 35.1 | 1,854 | 29.8 | 161 | 18.7 |
| Second quintile | 102,855 | 22.1 | 3,801 | 24.8 | 399 | 24.1 | 1,479 | 23.8 | 202 | 23.5 |
| Third quintile | 90,257 | 19.4 | 2,869 | 18.7 | 274 | 16.6 | 1,139 | 18.3 | 167 | 19.4 |
| Fourth quintile | 83,589 | 18.0 | 2,315 | 15.1 | 208 | 12.6 | 884 | 14.2 | 145 | 16.9 |
| Highest quintile (least disadvantaged) | 94,502 | 20.3 | 1,968 | 12.8 | 184 | 11.1 | 823 | 13.2 | 179 | 20.8 |
| Missing data | 2,944 | 0.6 | 76 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.4 | 38 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.7 |
| Remoteness of mother’s residence at time of child’s birth | ||||||||||
| Major city | 308,520 | 66.4 | 8,991 | 58.6 | 1,086 | 65.7 | 4,087 | 65.7 | 588 | 68.4 |
| Inner regional | 45,047 | 9.7 | 1,625 | 10.6 | 122 | 7.4 | 590 | 9.5 | 85 | 9.9 |
| Outer regional | 56,136 | 12.1 | 2,564 | 16.7 | 222 | 13.4 | 772 | 12.4 | 104 | 12.1 |
| Remote | 35,842 | 7.7 | 1,466 | 9.5 | 140 | 8.5 | 495 | 8.0 | 61 | 7.1 |
| Very remote | 18,853 | 4.1 | 704 | 4.6 | 82 | 5.0 | 272 | 4.4 | 22 | 2.6 |
| Missing data | 182 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.0 | ||||
| Indigenous status: of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander descent | 30,551 | 6.6 | 2,056 | 13.4 | 354 | 21.4 | 871 | 14.0 | 42 | 4.9 |
| Mother with an intellectual disability | 712 | 0.2 | 273 | 1.8 | 97 | 5.9 | 153 | 2.5 | 10 | 1.2 |
| Father with an intellectual disability | 532 | 0.1 | 46 | 0.3 | 7 | 0.4 | 99 | 1.6 | 7 | 0.8 |
| Father with any mental health contact other than for a psychotic disorder | 45,538 | 9.8 | 2,801 | 18.2 | 305 | 18.5 | 1,066 | 17.1 | 111 | 12.9 |
| Father with any diagnosis of a psychotic disorder | 7,779 | 1.7 | 769 | 5.0 | 103 | 6.2 | 187 | 3.0 | 19 | 2.2 |
| Child’s conception after the mother’s diagnosis of severe mental illness | 3,161 | 20.6 | 676 | 40.9 | 2,380 | 38.3 | 13 | 1.5 | ||
Child Intellectual Disability by Maternal Severe Mental Illness
| Intellectual Disability and Maternal Severe Mental Illness | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | |
| Any intellectual disability | ||||||
| Child with heightened risk | ||||||
| Any maternal severe mental illness | 2.7 | 2.4, 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.8, 2.3 | 1.7 | 1.5, 1.9 |
| Schizophrenia | 3.8 | 3.0, 4.9 | 2.4 | 1.9, 3.2 | 1.7 | 1.3, 2.3 |
| Bipolar disorder | 2.0 | 1.6, 2.5 | 1.6 | 1.3, 2.1 | 1.3b | 1.0, 1.7 |
| Unipolar major depression | 2.6 | 2.3, 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.8, 2.4 | 1.9 | 1.6, 2.1 |
| Other psychoses | 3.4 | 2.5, 4.6 | 2.3 | 1.7, 3.1 | 1.8 | 1.3, 2.4 |
| Child with generic risk | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| Intellectual disability of genetic basis | ||||||
| Child with heightened risk | ||||||
| Any maternal severe mental illness | 2.0 | 1.5, 2.7 | 1.8 | 1.3, 2.4 | 1.6 | 1.2, 2.2 |
| Schizophrenia | 2.4 | 1.2, 5.1 | 2.1b | 1.0, 4.4 | 1.6 | 0.7, 3.6 |
| Bipolar disorder | 1.5 | 0.8, 2.9 | 1.3 | 0.7, 2.6 | 1.2 | 0.6, 2.3 |
| Unipolar major depression | 2.3 | 1.5, 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.4, 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.3, 2.9 |
| Other psychoses | 1.1 | 0.4, 3.4 | 0.9 | 0.3, 2.9 | 0.8 | 0.3, 2.5 |
| Child with generic risk | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
Child Intellectual Disability by Maternal-Specific Diagnosis
Combined Effect of Exposure to Maternal Severe Mental Illness and Obstetric Complications
| Intellectual Disability and Exposure to Obstetric Complications | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% CI | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | |
| Any intellectual disability | ||||||
| Obstetric complications | ||||||
| Pregnancy | 1.7 | 1.6, 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.3, 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3, 1.5 |
| Labor and delivery | 1.3 | 1.2, 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.1, 1.2 | 1.1b | 1.0, 1.2 |
| Neonatal | 2.0 | 1.9, 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.6, 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6, 1.8 |
| Any | 1.8 | 1.6, 1.9 | 1.7 | 1.6, 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6, 1.8 |
| No exposure of critical severity | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| Intellectual disability of genetic basis | ||||||
| Obstetric complications | ||||||
| Pregnancy | 2.4 | 2.1, 2.8 | 1.9 | 1.6, 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.6, 2.1 |
| Labor and delivery | 1.2b | 1.0, 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.8, 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8, 1.0 |
| Neonatal | 3.8 | 3.2, 4.4 | 3.4 | 2.9, 4.0 | 3.4 | 2.9, 3.9 |
| Any | 2.8 | 2.3, 3.5 | 2.9 | 2.3, 3.5 | 2.9 | 2.3, 3.5 |
| No exposure of critical severity | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
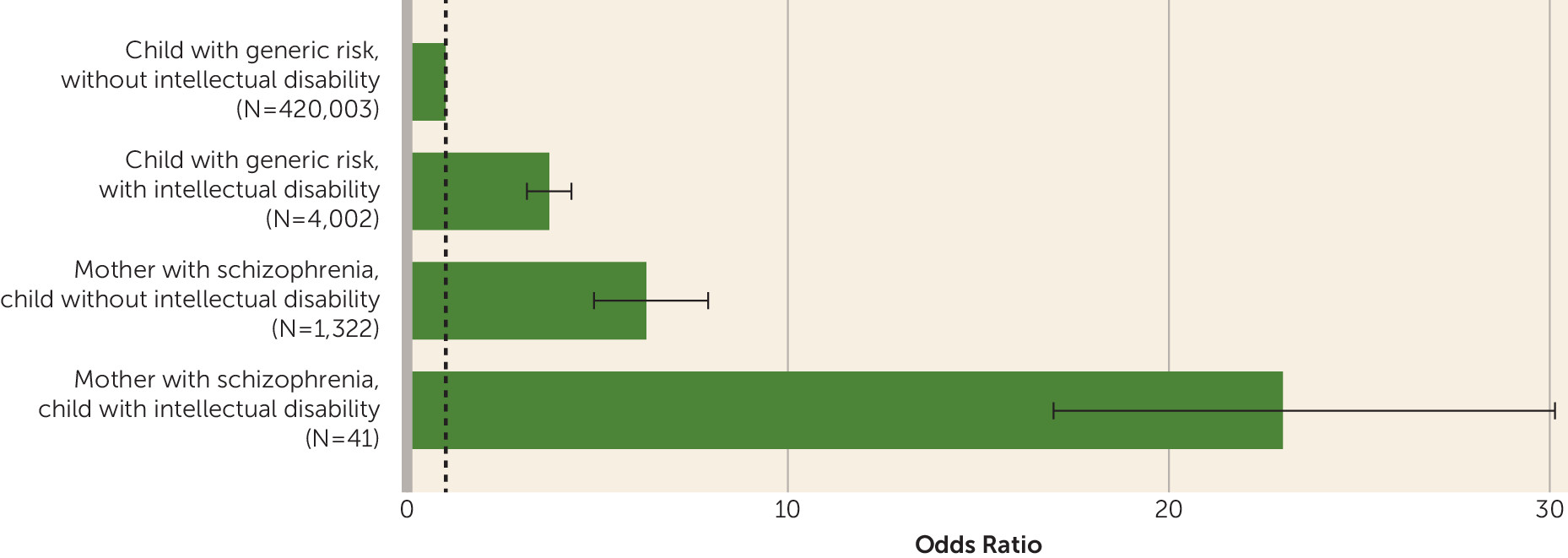
Intellectual Disability of Genetic Basis
Psychotic Disorders in Children
| Outcome | Mother With Schizophrenia | Children With Generic Risk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children With Intellectual Disability | Children Without Intellectual Disability | Children With Intellectual Disability | Children Without Intellectual Disability | |||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| Child with psychotic disorder | 10 | 24.4 | 86 | 6.5 | 159 | 4.0 | 4,717 | 1.1 |
| Child with no mental illness | 31 | 75.6 | 1,236 | 93.5 | 3,843 | 96.0 | 415,286 | 98.9 |
| Total | 41 | 100.0 | 1,322 | 100.0 | 4,002 | 100.0 | 420,003 | 100.0 |
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 400.67 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

