Efficacy of Pharmacotherapies for Bulimia Nervosa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
Background
Materials and Methods
Search Strategy
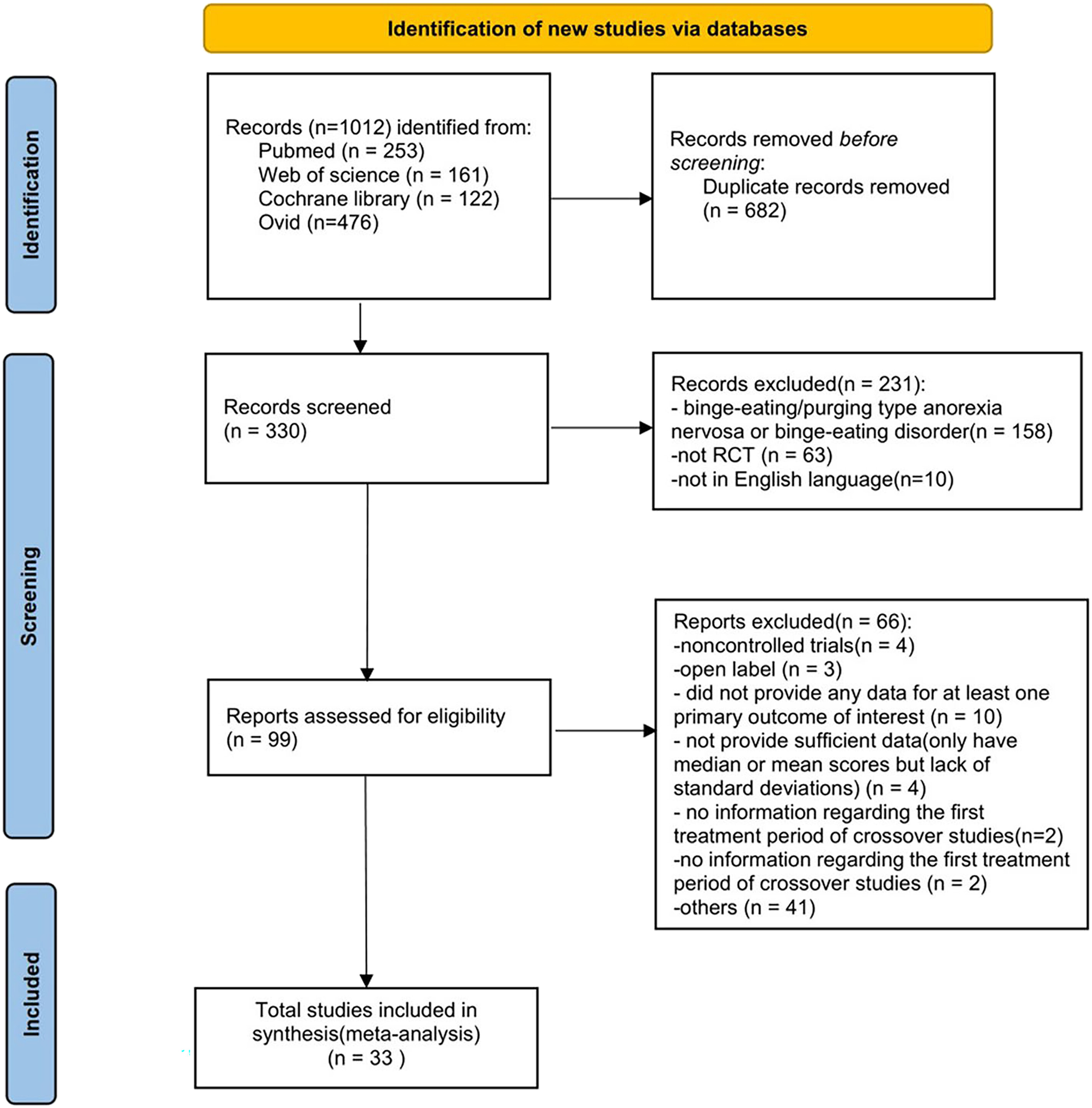
Eligibility Criteria
Data Extraction
| Study | Treatment | Outcome | Dose (mg/d) | Duration (weeks) | Number of patients | Age, years (SD) | Random | Allocation concealment | Double blindness | Outcome data integrity | Selective Reporting | Other bias | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Placebo | Drug | Placebo | |||||||||||
| Attia 1998 [43] | Fluoxetine | Weight, BDI, drop outs due to adverse events | 60 | 7 | 15 | 16 | 29.1 (7.2) | 23.4 (6.4) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Goldstein 1995 [44] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of vomiting and binge eating episodes, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 60 | 16 | 296 | 102 | 27 (17.6) | 26 (17.6) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Goldbloom 1997 [45] | Fluoxetine, CBT | Frequency of vomiting and binge eating episodes, BDI | 60 | 16 | 29 | 23 | 25.8 (5.5) | 25.8 (5.5) | L | U | H | L | L | L |
| Grilo 2005 [46] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of binge eating episodes, BDI, drop outs due to adverse events | 60 | 16 | 27 | 27 | 44.3 (9.5) | 43.6 (8.5) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 2000 [47] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of binge eating and purging episodes, BDI | 60 | NA | 13 | 9 | 32.0 (7.8) | 27.8 (5.2) | L | U | L | U | L | L |
| Romano 2002 [48] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of vomiting and binge eating episodes, drop outs due to adverse events | 60 | 8 | 76 | 74 | 29.5 (7.0) | 30.0 (9.3) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Fichter 1991 [49] | Fluoxetine | HAMD, weight | 60 | 7 | 20 | 20 | 26.5 (NA) | 24.6 (NA) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| FBNC 1992 [39] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of binge-eating and purging episodes, weight, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 20,60 | 8 | 129 | 129 | 26.4 (6.2) | 27.7 (8.0) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Beumont 1997[50] | Fluoxetine | Frequency of vomiting and binge eating episodes, HAMD | 60 | 8 | 34 | 33 | 24.2 (4.5) | 25.1 (5.8) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Jacobi 2002 [51] | Fluoxetine, CBT | Frequency of bing eaing and purging episode, BDI | 20–60 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 26.0 (5.8) | 26.0 (5.8) | L | U | H | L | L | L |
| Kanerva 1994 [52] | Fluoxetine | Weight, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 60 | 8 | 24 | 26 | 25.2 (9.9) | 25.2 (9.9) | L | U | L | U | L | L |
| Marcus 1990 [53] | Fluoxetine | Weight, BDI | 60 | 52 | 18 | 15 | 40.3 (9.5) | 40.9 (7.9) | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Sundblad 2005 [54] | Citalopram | Frequency of binge eating episodes | 20–40 | 12 | 18 | 14 | 26.0 (NA) | 28.0 (NA) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Fichter 1997 [28] | Fluvoxamine | Drop-outs due to adverse events, CGI,HAMD | 100–300 | 15 | 37 | 35 | 25.2 (NA) | 23.7 (NA) | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Safer 2020 [41] | Topiramate | Frequency of binge eating episodes, drop outs dueto adverse events | 3.75 /23; 15 /92 | 12 | 22 | 22 | 42.9 (10.1) | 42.9 (10.1) | L` | U | L | L | L | L |
| Nickel 2005 [55] | Topiramate | Frequency of bing eating episodes, weight | 25–250 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 21.5 (3.1) | 21.5 (3.1) | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Hoopes 2003 [56] | Topiramate | Frequency of binge and purge days, drop outs due to adverse events | 25–400 | 10 | 35 | 34 | 29.0 (9.7) | 29.6 (8.1) | L | L | L | L | L | L |
| Fahy 1993 [57] | Fenfluramine | Weight, frequency of binge eating and vomiting episodes | 45 | 8 | 20 | 23 | 23.0 (0.6) | 25.0 (1.4) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Carruba 2001 [58] | Moclobemide | Frequency of binge eating and vomiting episodes, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 600 | 6 | 38 | 39 | 25.6 (0.8) | 25.1 (0.9) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Pope 1983 [59] | Imipramine | Frequency of binge eating episodes, HAMD, dropout due to adverse events | 50 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 27.9 (6.2) | 27.6 (6.3) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Alger 1991 [60] | Imipramine | Weight, BDI, dropout due to adverse events | 50–150 | 8 | 12 | 11 | 40 (0.6) | 30 (0.8) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Agras 1987 [61] | Imipramine | Frequency of binge eating and purging episodes, BDI | 50–300 | 16 | 10 | 10 | 30.3 (NA) | 31.5 (NA) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Rothschild 1994 [62] | Imipramine | HAMD | 150 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 32.2 (47.2) | 29.7 (24.7) | L | U | L | U | L | L |
| McCann 1990 [63] | Desipramine | Frequency of binge eating episodes, BDI, weight | 25–300 | 12 | 15 | 15 | NA | NA | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Agras 1992 [64] | Desipramine, CBT | Frequency of binge eating and purging episodes | 50–350 | 24 | 12 | 23 | 29.6 (8.9) | 29.6 (8.9) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 1997 [65] | Desipramine, CBT,SPT | Frequency of binge eating and vomiting episodes, BDI, weight | 200–300 | 16 | 23 | 25 | 26.1 (5.7) | 25.8 (4.4) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 1991 [66] | Desipramine | HAMD, BDI, dropout due to adverse events | 200–300 | 6 | 40 | 38 | 25.7 (5.6) | 24.8 (4.5) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 1984 [67] | Phenelzine | Frequency of binge eating episodes, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 60–90 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 26.9 (5.1) | 26.0 (4.5) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 1988 [68] | Phenelzine | The frequency of binge eating episodes, BDI, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 60–90 | 8 | 31 | 31 | 26.9 (4.3) | 27.1 (5.2) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Walsh 1985 [69] | Phenelzine | The frequency of binge eating episodes, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 60–90 | 8 | 14 | 16 | 27.8 (4.7) | 27.2 (5.3) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Rothschild 1994 [62] | Phenelzine | HAMD | 45 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 37.1 (27.5) | 29.7 (24.7) | L | U | L | U | L | L |
| Hsu 1991 [70] | Lithium | The frequency of binge eating and vomiting episodes, HAMD, BDI, weight | 300 | 8 | 27 | 23 | 25.4 (7.0) | 25.4 (7.0) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
| Kennedy 1993 [71] | Brofaromine | The frequency of vomiting and binge eating episodes, HAMD, drop outs due to adverse events | 175 | 8 | 19 | 17 | 27.6 (6.7) | 25.9 (6.4) | L | U | L | L | L | L |
Outcome Measurement
Quality Assessment
Statistical Analysis
Results
Description of Studies
Risk of Bias Assessment
Effects of Treatment
Changes in the frequency of binge eating episodes.
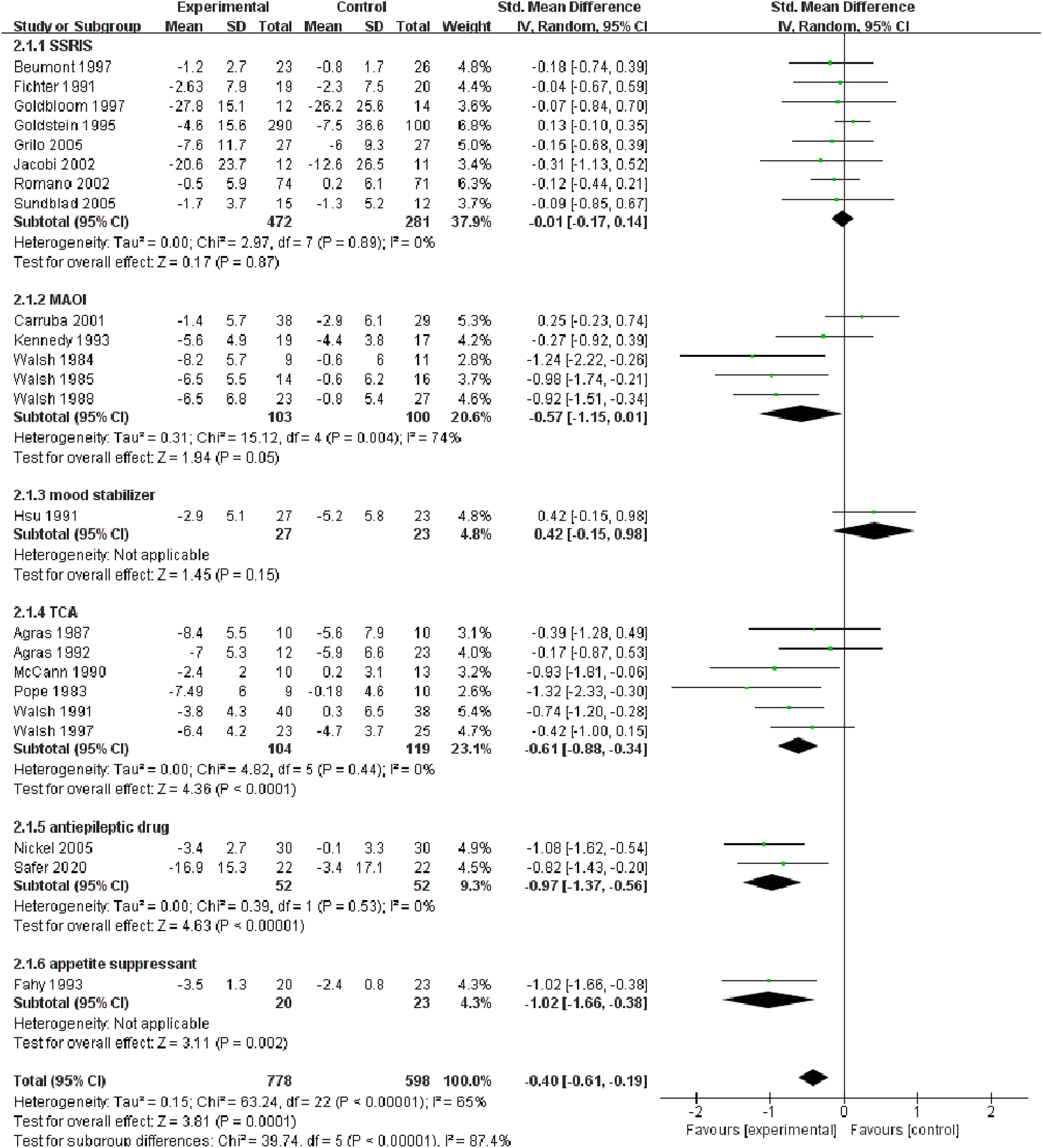
Changes in the frequency of vomiting episodes.

Weight
The Depression Scores.
Dropouts due to adverse events.
10-week duration of treatment.
Discussion
Conclusion
Footnotes
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

