Outcome of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Substance Use Disorders: A Review of Randomized Sham-Controlled Clinical Trials
Abstract
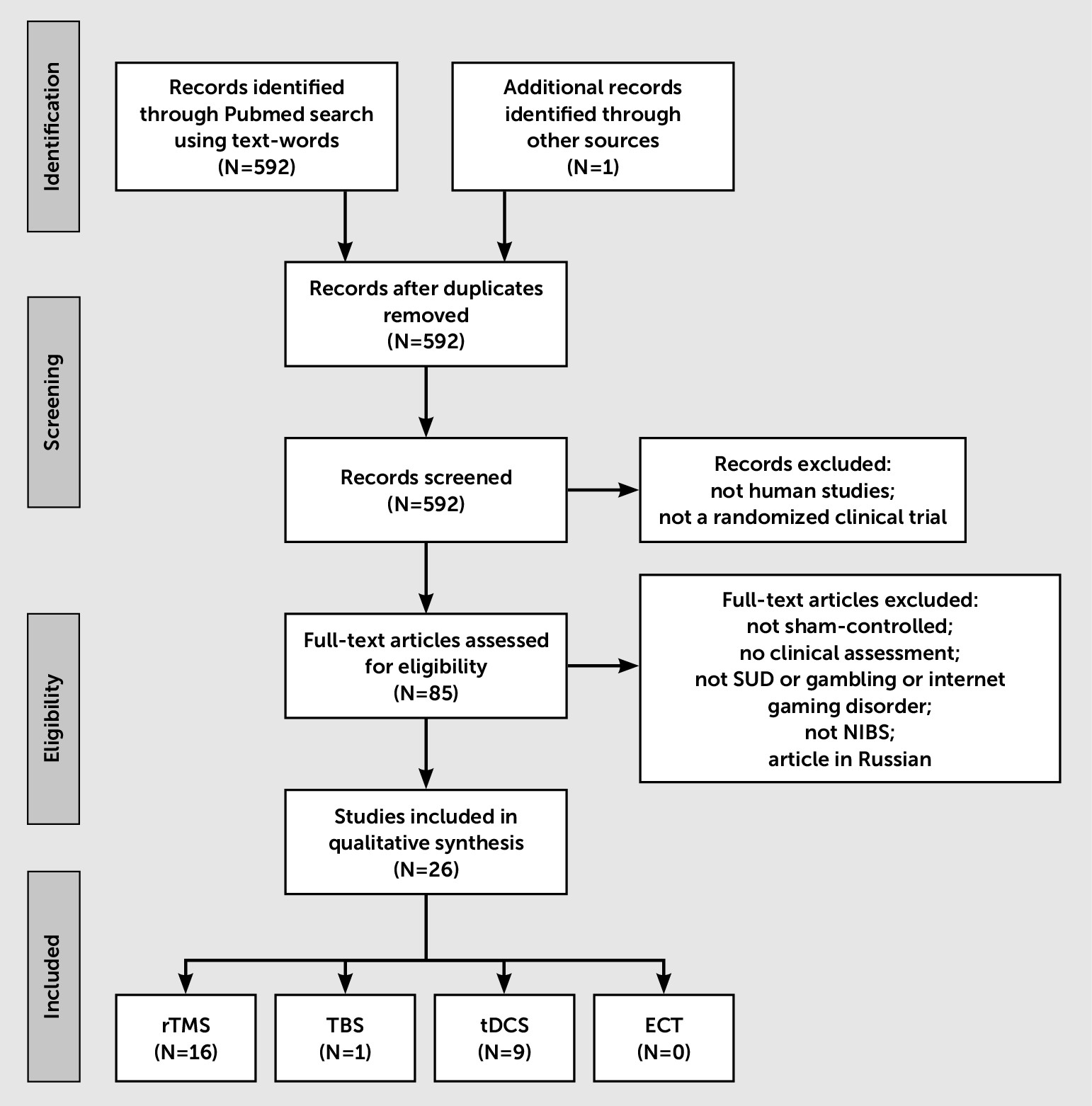
Methods
Search Strategy
Inclusion Criteria
Results
Sample Characteristics and Qualitative Findings
| Study | Clinical Trial Registry (Registration Number) | Study Design | Targeted Brain Region | Stimulation Frequency/Motor Threshold | Number of Sessions/Total Pulses | Number of Patients (+Healthy Controls) | Substances (Patients’ Status) | Target Symptom (Scales) | Follow-Up | Results (Compared With Sham) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trojak49 | NCT02812810* | Parallel | Right-DLPFC | 1 Hz | 10/3,600 | 37 | Tobacco (abstinent) | Relapse rates | 3 months | Reduction in the number of relapses (during stimulation period only) |
| 120% MT | Baseline craving (VAS, FTCQ–12, QSU) | Reduction in compulsivity | ||||||||
| Dieler50 | — | Parallel (add-on to CBT) | Right-DLPFC | 3 pulses/50 Hz every 200 ms 80% MT | 4/2,400 | 74 | Tobacco (abstinent) | Relapse rates | 12 months | Reduction in the number of relapses (up to 3 months) |
| Nicotine dependence (FTND) | ||||||||||
| Baseline craving (QSU) | ||||||||||
| Self-efficacy (SER) | ||||||||||
| Prikryl48 | — | Parallel | Left-DLPFC | 10 Hz | 21/42,000 | 35 | Tobacco (consumers) | Number of cigarettes smoked | 1 week | Reduction in cigarettes smoked |
| 110% MT | Schizophrenia symptoms (PANSS) | |||||||||
| Depression symptoms (MADRS, CDSS) | ||||||||||
| Dinur-Klein24 | NCT00951782* | Parallel | PFC (H-coil) bilaterally | 10 Hz or 1 Hz 120% MT | 13/12,870 or 7,800 | 115 | Tobacco (consumers) | Number of cigarettes smoked | 6 months | With 10 Hz-rTMS: |
| Response (–50%) and abstinence rates | Reduction in cigarettes smoked (up to 6 months) | |||||||||
| Nicotine dependence (FTND) | Reduction in nicotine dependence | |||||||||
| Baseline and cue-induced craving (sTCQ) | Reduction in urine cotinine levels | |||||||||
| Urine cotinine levels | Higher response and abstinence rates (up to 6 months) | |||||||||
| Pripfl35 | — | Crossover | Left-DLPFC | 10 Hz | 1/1,200 | 14 | Tobacco (consumers) | Cue-induced craving (VAS) | <1 day | Reduction in craving |
| 90% MT | Delta EEG activity (resting-state EEG) | Reduction in EEG delta power | ||||||||
| Sheffer21 | NCT00973622* | Crossover | Left-DLPFC | 10–20 Hz | 2/1,800 | 47 (+19) | Tobacco (consumers) | Decision making (DDT, RT) | 1 day (24 hours) | Decrease in delay discounting of monetary gains; increase in |
| 110% MT | Number of cigarettes smoked | discounting of monetary losses | ||||||||
| Li47 | NCT01690130* | Crossover | Left-DLPFC | 10 Hz | 1/3,000 | 16 | Tobacco (consumers) | Cue-provoked craving (adapted QSU-B) | No | Reduction in craving |
| 100% MT | ||||||||||
| Hayashi45 | — | Parallel | Left-DLPFC | 1 Hz | 1/1,800 | 10 | Tobacco (consumers) | Cue-provoked craving (VAS) | <1 day | Transient reduction in craving |
| 110% MT | ||||||||||
| Wing15 | NCT01523730* | Parallel | DLPFC bilaterally | 20 Hz | 20/30,000 | 15 schizophrenia patients | Tobacco (smokers) | Baseline cravingb (TQSU) | 9 weeks | Reduction in craving only at short-term (up to 1 week) |
| 90% MT | Withdrawal (MNWS) | |||||||||
| Abstinence (CO) | ||||||||||
| Psychiatric (PANSS) | ||||||||||
| Amiaz43 | — | Parallel | Left-DLPFC | 10 Hz | 10/20,000 | 48 | Tobacco (consumers) | Cue-induced craving (VAS, sTCQ) | 6 months | Reduction in craving during stimulation period |
| 100% MT | Nicotine dependence (FTND) | Reduction in cigarettes smoked (but not at 6 months) | ||||||||
| Number of cigarettes smoked | Reduction in nicotine dependence (but not at 6 months) | |||||||||
| Urine cotinine levels | Reduction in urine cotinine levels | |||||||||
| Johann41 | — | Crossover | Left-DLPFC | 20 Hz | 1/1,000 | 11 | Tobacco (consumer) | Baseline craving (VAS) | No | Reduction in craving |
| 90% MT | ||||||||||
| Eichhammer25 | — | Crossover | left-DLPFC | 20 Hz | 2/2,000 | 14 | Tobacco (consumer) | Number of cigarettes smoked | <1 day | Reduction in cigarettes smoked |
| 90% MT | Baseline craving (VAS) | |||||||||
| Herremans52 | — | Crossover | Right-DLPFC | 20 Hz, | 1/1,560 | 29 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Inhibitory control (Go-NoGo task) | <1 day | |
| 110% MT | Baseline craving (OCDS) | |||||||||
| Herremans66 | — | Parallel / Crossover | Right-DLPFC | 20 Hz | 1/1,560 | 36 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Baseline and habitual alcohol-related cue-induced craving (OCDS) | 1 week | |
| 110% MT | ||||||||||
| Höppner57 | — | Parallel | Left-DLPFC | 20 Hz | 10/10,000 | 19 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Baseline craving (OCDS); | No | Increase in the attentional blink effect |
| 90% MT | Depression (HAM-D, BDI) | |||||||||
| Attentional blink paradigm | ||||||||||
| Mishra42 | NCT01685463c | Parallel | Right-DLPFC | 10 Hz | 10/9,800 | 45 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Baseline craving (ACQ) | 4 weeks | Reduction in craving |
| 110% MT | ||||||||||
| Li47 | — | Crossover | Left-DLPFC | 1 Hz | 1/900 | 10 (+8) | Methamphetamine (consumers) | Cue-induced craving (VAS) | <1 day | Increase in craving |
| 100% MT |
| Study | Clinical Trial Registry (Registration Number) | Study Design | Parameters/Electrode Positioningb | Number of Active Sessions | Number of Patients | Substances (Patients’ Status) | Target Symptoms (Measurement Tools) | Follow-Up (Long-Term Effects) | Active tDCS (Compared With Sham) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smith40 | — | Parallel | 2 mA; 20 min Anode over F3 | 5 | 37 | Tobacco (consumers) | Number of cigarettes | 1 week | |
| Baseline and cue-induced craving (QSU, VAS) | |||||||||
| Carbon monoxide levels (CO) | |||||||||
| Fecteau26 | — | Cross-over | 2 mA; 30 min Anode over F4 | 5 | 20 | Tobacco (consumers) | Number of cigarettes (DC) | 4 days | Reduction in consumption |
| Carbon monoxide levels (CO) | Reduction in the item “desire to smoke” | ||||||||
| Cue-induced craving (QSU) | Modulation of decision-making process | ||||||||
| Decision making (UG, RT) | |||||||||
| Boggio37 | — | Parallel | 2 mA; 20 min; Anode over F3 | 5 | 27 | Tobacco (consumer) | Number of cigarettes (DC) | No | Reduction in consumption |
| Baseline and cue-induced craving (VAS) | Reduction in craving (both baseline and cue-induced) | ||||||||
| Mood (VAS) | |||||||||
| Fregni38 | — | Cross-over | 2 mA; 20 min; Anode over both F3 and F4 | 2 | 24 | Tobacco (consumer) | Baseline and cue-induced craving (VAS) | No | Reduction in craving (both baseline and cue-induced) |
| Mood (VAS) | |||||||||
| Klauss51 | NCT01330394b | Parallel | 2 mA; 2×13 min; Anode over F4 | 5 | 33 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Relapse rates | 6 months | Reduction in the number of relapses (up to 6 months) |
| Baseline craving (OCDS) | Improvement in quality of life (perception) | ||||||||
| Executive functions (FAB, MMSE) | |||||||||
| Mood (HAM-D) | |||||||||
| Anxiety (HAM-A) | |||||||||
| Quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) | |||||||||
| Da Silva44 | — | Parallel | 2 mA; 20 min Anode over F3 | 5 | 13 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Relapse rates | 4 weeks | Reduction in craving |
| Cue-induced craving (OCDS, AUQ) | Reduction in depressive symptoms | ||||||||
| Quality of life (WHOQOL-BREF) | Increase in relapse (trend) | ||||||||
| Mood (HAM-D) | |||||||||
| Anxiety (HAM-A) | |||||||||
| Executive functions (FAB) | |||||||||
| Cognitive functions (MMSE) | |||||||||
| Boggio16 | — | Cross-over | 2 mA; 20 min Anode over both F3 and F4 | 2 | 13 | Alcohol (abstinent) | Cue-induced craving (AUQ) | No | Reduction in craving |
| Mood (VAS) | |||||||||
| Boggio22 | — | Parallel | 2 mA; 10 min Anode over both F3 or F4 | 1 | 25 | Marijuana (24-hour of abstinence) | Baseline craving (VAS) | No | Modulation of decision-making process |
| Decision making (RT) | Reduction in craving (anode F4) | ||||||||
| Shahbabaie39 | IRCT2012102311234N1c | Cross-over | 2 mA; 20 min; Anode over F4 | 1 | 32 | Methamphetamine (1 week of abstinence) | Baseline craving (VAS) and cue-induced craving (CICT) | No | Reduction in baseline craving but increase in cue-induced craving |
| Mood (PANAS) |
Efficacy of NIBS to Decrease Craving
Efficacy of NIBS to Reduce Consumption or Prevent Relapse
Efficacy of NIBS to Improve Cognitive Function
Parameters That Seem to be Less Influenced by NIBS
Stimulation Parameters and Efficacy
Discussion
Assessment of the Performance of Craving Reduction
Alternative Outcome to Craving Reduction
How to Explain Convergent and Divergent Results?
Limitations
Conclusions
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Keywords
Authors
Competing Interests
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

