Due to lower rates of extrapyramidal side effects
(1) and tardive dyskinesia
(2), as well as superior
(3) and potentially broader
(4) efficacy than conventional neuroleptics, second-generation antipsychotics are widely prescribed for psychotic and nonpsychotic disorders. However, reports of significant weight gain
(5–
9), dyslipidemia
(10,
11), and hyperglycemia
(10,
12) have caused considerable concern. These adverse effects associated with second-generation antipsychotics are also part of the metabolic syndrome, which has been associated with higher morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disorders than its individual components
(13,
14). This is of particular relevance to individuals with schizophrenia spectrum disorders because these conditions by themselves have also been associated with higher rates of cardiovascular disease
(15). Surprisingly, however, except for one small study in 35 patients with schizophrenia (20% of whom were treated with conventional antipsychotics)
(16), reports of anthropometric and metabolic effects related to second-generation antipsychotics have focused only on parts of this critical symptom constellation. Despite its relevance, little is known about the prevalence and correlates of the metabolic syndrome in patients receiving second-generation antipsychotics, and patients are not regularly screened for this condition.
The aim of this study was to 1) assess the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients treated with second-generation antipsychotics and 2) determine the most clinically useful and cost-effective screening method for the metabolic syndrome in these patients.
Method
As part of a Performance Improvement Project initiated by our hospital’s Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee, newly admitted patients receiving second-generation antipsychotics were assessed for the presence of obesity and metabolic abnormalities between August and November 2002. After completion of the project, data regarding presence of the metabolic syndrome as well as patient and treatment characteristics were collected as part of a chart review protocol approved by our institutional review board.
In a nearly consecutive group of 100 psychiatric inpatients treated with at least one second-generation antipsychotic (i.e., clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone), blood pressure and waist circumference at the level of the umbilicus were measured, as well as fasting blood glucose and lipid levels, which were routinely monitored on the morning after admission by the medical and nursing staff. Psychiatric diagnoses were determined by the admitting psychiatrist and reconfirmed by the attending inpatient psychiatrist using DSM-IV criteria. Except for waist circumference, where only presence or absence of abdominal obesity was recorded, individual data for the remaining criteria were documented.
The metabolic syndrome was defined according to Adult Treatment Panel III criteria
(17) by presence of three or more of the following: 1) high blood pressure, i.e., ≥130/85 mm Hg (or a history of hypertension); 2) abdominal obesity, i.e., waist circumference >102 cm (40 inches) in males and >88 cm (35 inches) in females; 3) fasting blood glucose ≥110 mg/dl (or a history of diabetes mellitus); 4) fasting HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dl in males and <50 mg/dl in females; 5) fasting triglycerides ≥150 mg/dl. Of five patients taking lipid-lowering agents, four still had abnormal lipid values; lipids were normal in the remaining patient. The fifth patient did not fulfill any other criteria for the metabolic syndrome; therefore, this potential confounder was irrelevant for assignment of the metabolic syndrome.
Associations between presence of the metabolic syndrome and demographic or treatment variables were assessed by using chi-square tests and analyses of variance for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Furthermore, sensitivity (correct prediction of cases), specificity (correct prediction of noncases), positive predictive value (probability of a condition being present if the test is positive), and positive likelihood ratio (sensitivity/[1–specificity])
(18) were calculated. Significance level was set at alpha=0.05, two-tailed (data were analyzed with JMP 5.0.1, 1989–2003, SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.).
Results
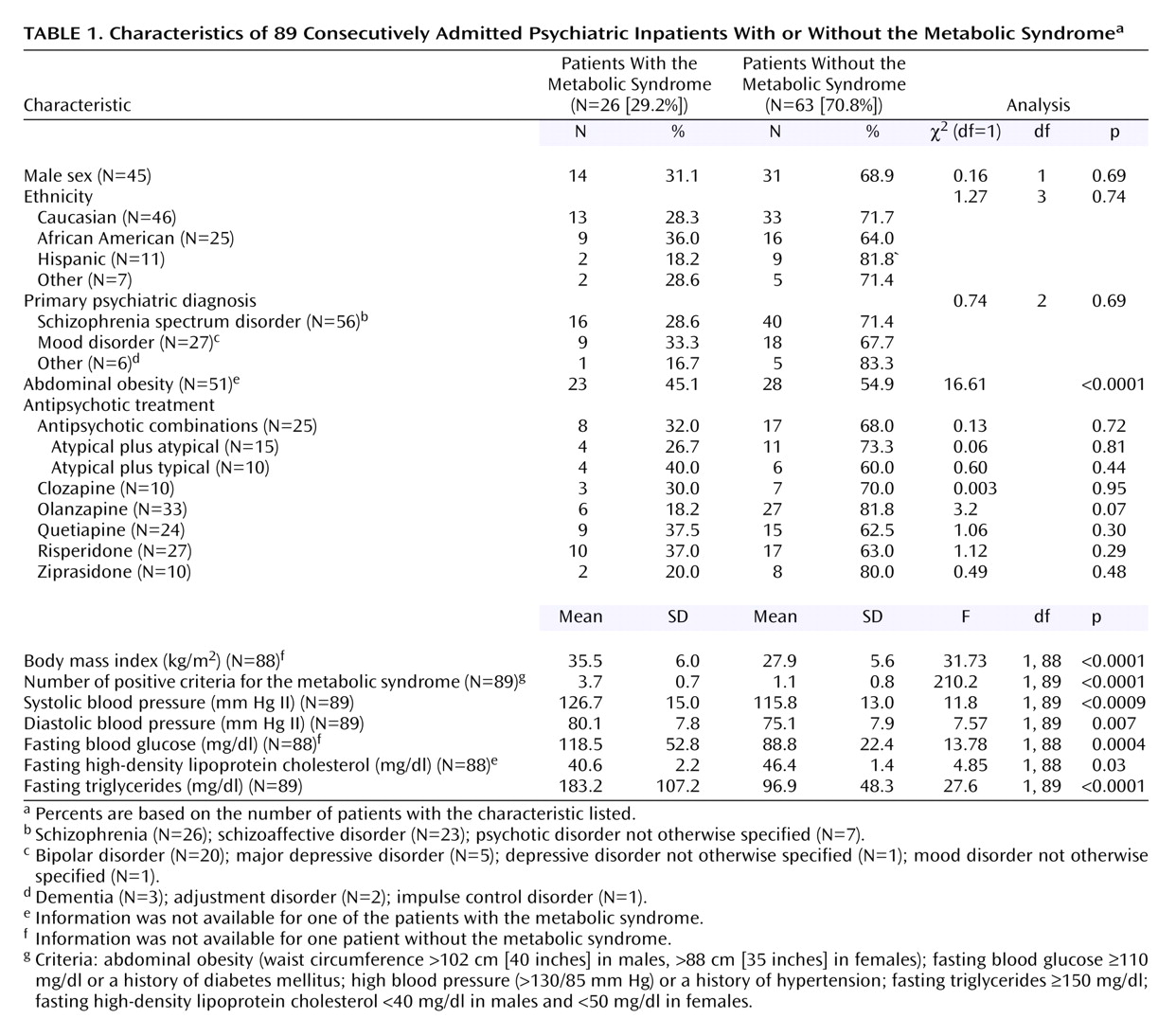
Eleven of the 100 patients initially included in the project were ultimately excluded from the analysis due to record duplication (N=1), treatment with a conventional antipsychotic only (N=3), or incomplete data (N=7). The final study group included 89 patients (mean age=39.8 years, SD=15.3, range=18–78, 50.6% male, 51.7% Caucasian) treated with at least one second-generation antipsychotic (mean number of antipsychotics=1.4, SD=0.5, range=1 [71.9%] to 2 [28.1%]). Twenty-six patients (29.2%) met criteria for the metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome was significantly associated with older age (χ
2=6.23, df=1, p<0.02), higher body mass index (
Table 1), and, as expected, higher values for each of the individual criteria for the metabolic syndrome (
Table 1).
Presence of the metabolic syndrome was not associated with gender, ethnicity, or primary psychiatric diagnosis (
Table 1). Similarly, current treatment with any specific second-generation antipsychotic, a combination of two second-generation antipsychotics, or one second-generation antipsychotic with a typical neuroleptic did not significantly increase the likelihood of metabolic syndrome (
Table 1). Finally, cotreatment with antidepressants (χ
2=0.002, df=1, N=38, p=0.96), lithium (χ
2=1.49, df=1, N=11, p=0.22), or valproic acid (χ
2=1.39, df=1, N=20, p=0.24) was not associated with the metabolic syndrome. Our investigation did not have sufficient power to determine the relative contribution of these factors on the risk for metabolic syndrome; this was not the aim of our study.
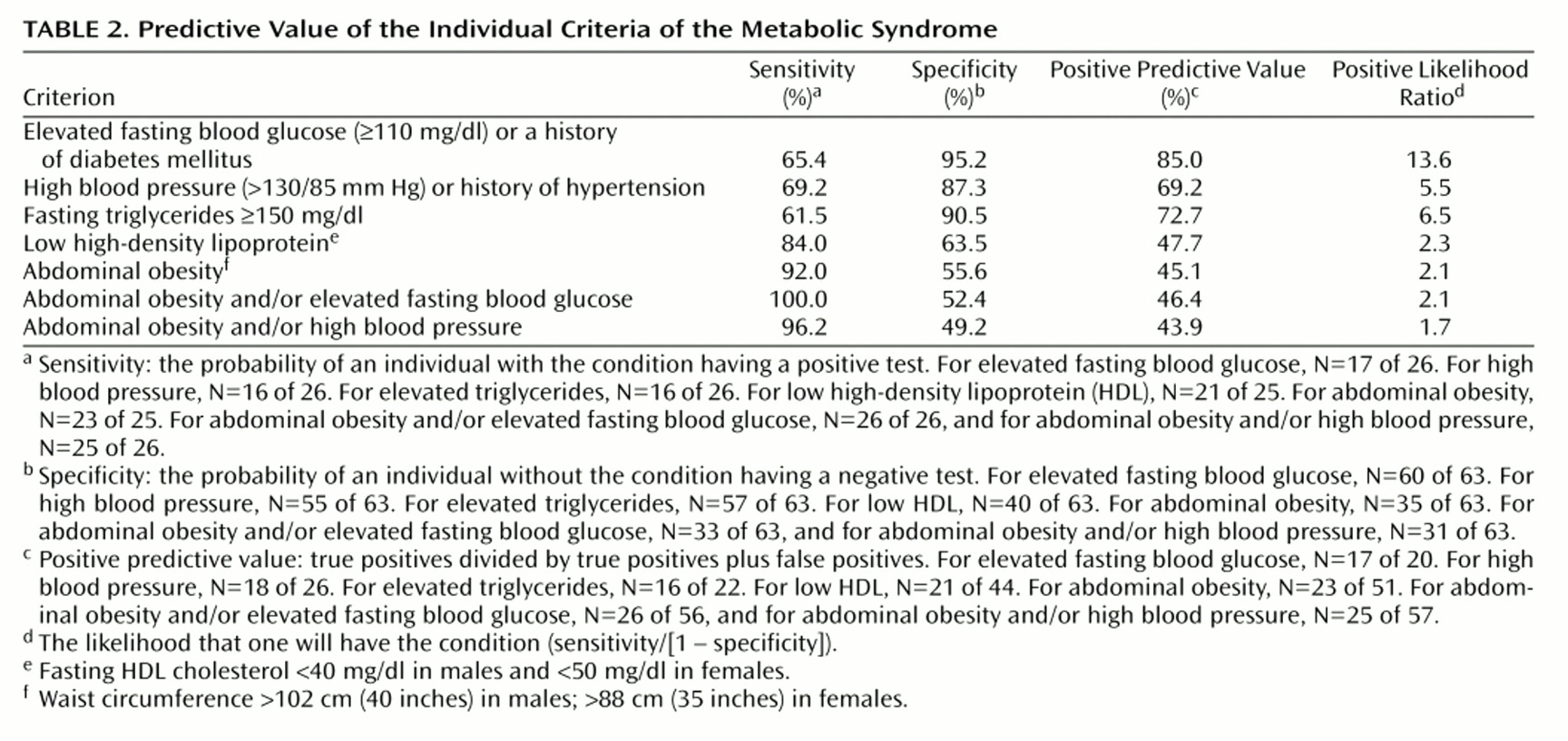
Among the five criteria, abdominal obesity had the highest sensitivity, correctly identifying 23 (92.0%) of 25 patients (
Table 2). Elevated fasting blood glucose was the most specific criterion, with normal values appropriately categorizing 60 (95.2%) of 63 patients without the metabolic syndrome, which translates into a positive likelihood ratio of 13.6. When elevated abdominal obesity and/or fasting blood glucose were combined, all 26 patients with the metabolic syndrome were correctly identified, while combining abdominal obesity and/or elevated blood pressure resulted in the correct identification of 25 (96.2%) of 26 subjects.
Discussion
In our group of patients treated with second-generation antipsychotics, the overall prevalence of the metabolic syndrome was 29.2%. The higher rate of 37% (despite a lower mean body mass index) found in the only other study investigating this issue in 35 patients with schizophrenia
(16) could be explained by the high proportion of patients treated with clozapine in that study (60%). Clozapine is among those medications most likely to be associated with diabetes and hyperlipidemia
(19). Alternatively, a diagnosis of schizophrenia itself might be associated with a higher risk
(15). However, in our study, a diagnosis of schizophrenia spectrum disorders, present in 62.9%, was not associated with the metabolic syndrome. The prevalence rates of 29.2% and 37.0% in antipsychotic-treated patients are higher than the prevalence rates of 21.8% (age-unadjusted)
(20) and 22.8% in men and 22.6% in women
(21) found in the U.S. population. Potential reasons include effects of the underlying psychiatric disorders, associated lifestyle differences, and treatment factors. In our patients, the metabolic syndrome was associated with older age and higher body mass index, which are two well-known risk factors
(22,
23). Like Heiskanen et al.
(16), we found no relationship between specific antipsychotic medications and the metabolic syndrome, although the number of subjects in their study and ours was not necessarily sufficient to detect differences.
Using presence of abdominal obesity and/or elevated fasting blood glucose identified 100% of the patients with the metabolic syndrome. This suggests an easy and cost-effective screening method for clinicians to detect patients at high risk for cardiovascular morbidity. The positive predictive value of 46.4% compares favorably with some frequently used screening tests, e.g., the fecal occult blood test for detecting colon cancer (14%)
(24), mammography for detecting breast cancer in women ages 50–59 with a positive family history (22%)
(25), and digital rectal examination or prostate-specific antigen for detecting prostate cancer (21% and 32%, respectively)
(26). In situations where it may be difficult to obtain fasting blood work, adding blood pressure measurements to the assessment of waist circumference still correctly identifies up to 96% of patients with the metabolic syndrome.
Limitations of this study include its cross-sectional design and relatively small number of subjects, which may have masked potential differences among antipsychotic agents, comedications, and underlying disorders. Moreover, the lack of a comparable psychiatric control group without second-generation antipsychotic treatment makes it impossible to determine the contributions of medications or diagnosis for the higher prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in our patients
(15). A further limitation is that we did not determine the duration of psychotropic treatment, reasons for medication choice, switching, etc. Nevertheless, to our knowledge this remains the largest study to date assessing the relationship between antipsychotic treatment and all of the components of the metabolic syndrome. Although patients received additional psychotropic medications and had heterogeneous psychiatric diagnoses, this reflects clinical reality. To our knowledge this is the first study to report the sensitivity, specificity, predictive value, and potential clinical utility of individual criteria of the metabolic syndrome, providing a helpful tool to clinicians to identify patients who are in greatest need for interventions to reduce cardiovascular morbidity.
In summary, our data suggest that patients treated with antipsychotics are at higher risk for the development of the metabolic syndrome than the general population. Larger, longitudinal studies, ideally in randomized and antipsychotic-naive subjects, are needed to determine the relative contributions of underlying psychiatric disorders, lifestyle-related factors, and specific psychotropic treatments. Concordant with studies in nonpsychiatric populations, waist circumference was the best single anthropometric measure to identify individuals at high risk for cardiovascular disease
(27,
28). The combined measurement of waist circumference and fasting blood glucose is a simple and inexpensive test to identify such patients. Although less sensitive, combining the measurement of blood pressure and abdominal circumference may be an alternative screening tool because it avoids the need for fasting blood work and is practical in outpatient settings. In cases where fasting blood glucose levels are ≥100 mg/dl
(29), in the presence of obesity, and, particularly, when the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is confirmed by an abnormal fasting lipid profile, appropriate treatment and/or referrals should be initiated.