Functional Neuroimaging of Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-Analysis and New Integration of Baseline Activation and Neural Response Data
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
Method
Overview
Study Selection
Computing the Meta-Analytic Statistic
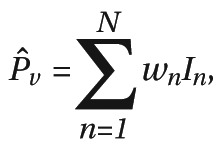
Comparing Meta-Analytic Maps
Results
Characteristics of Included Studies
| Number of Subjects in Group | Characteristics of Depressed Subjects | Imaging Technique | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Major Depressive Disorder | Comparison | Medicated (%) | Female (%) | Method | Tracer |
| Aihara et al. (17) | 24 | 23 | 0 | 63 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Bench et al. (18) | 33 | 23 | 58 | 36 | PET | [15O]H2O |
| Brody et al. (19) | 24 | 16 | 0 | 54 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Drevets et al. (20) | 13 | 33 | 0 | 54 | PET | [15O]H2O |
| Germain et al. (21) | 12 | 13 | 0 | 83 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Kennedy et al. (22) | 13 | 24 | 0 | 0 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Kimbrell et al. (23) | 38 | 37 | 0 | 66 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Kohn et al. (24) | 33 | 25 | 0 | 58 | SPECT | [99mTc]ECD |
| Krausz et al. (25) | 10 | 10 | 0 | 90 | SPECT | [99mTc]ECD |
| Mayberg et al. (6) | 6 | 5 | 100 | 50 | PET | [15O]H2O |
| Périco et al. (26) | 15 | 15 | 0 | 80 | SPECT | [99mTc]ECD |
| Saxena et al. (27) | 27 | 17 | 0 | 52 | PET | [18F]FDG |
| Skaf et al. (28) | 9 | 12 | 0 | 44 | SPECT | [99mTc]ECD |
| Videbech et al. (29) | 42 | 47 | 95 | 71 | PET | [15O]H2O |
| Number of Subjects in Group | Characteristics of Depressed Subjects | Included Contrasts | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Major Depressive Disorder | Comparison | Medicated (%) | Female (%) | Affective Challenge | Negative Valence | Positive Valence |
| Abler et al. (30) | 12 | 12 | 100 | 100 | Anticipating and viewing negative, neutral, and positive pictures | Anticipating negative versus neutral; viewing negative versus neutral | Viewing positive versus neutral |
| Bär et al. (31) | 13 | 13 | 0 | 100 | Experiencing variable-intensity thermal pain | Parametric thermal pain response | None |
| Canli et al. (32) | 15 | 15 | 47 | 80 | Performing lexical decision task for neutral, happy, sad, and threat-related words | Sad versus neutral; physical threat versus neutral; social threat versus neutral | Happy versus neutral |
| Cooney et al. (33) | 14 | 14 | 43 | 57 | Thinking about personal traits, abstract ideas, and physical objects | Personal traits versus abstract ideas | None |
| Frodl et al. (34) | 12 | 12 | 67 | 58 | Emotion (explicit) or gender (implicit) matching of negative faces to target; shape-matching control | Explicit versus control; implicit versus control | None |
| Fu et al., 2004 (36) | 19 | 19 | 0 | 68 | Gender identification of variable-intensity sad faces | Parametric sad face response | None |
| Fu et al., 2007 (35) | 19 | 19 | 0 | 68 | Gender identification of variable-intensity happy faces | None | Parametric happy face response |
| Fu et al., 2008 (7) | 16 | 16 | 0 | 81 | Gender identification of variable-intensity sad faces | Parametric sad face response | None |
| Gotlib et al. (37) | 18 | 18 | 50 | 72 | Viewing happy, sad, and neutral faces | Sad versus neutral | Happy versus neutral |
| Herwig et al. (38) | 14 | 14 | 100 | 57 | Viewing negative and neutral pictures | Negative versus neutral | None |
| Keedwell et al. (8) | 12 | 12 | 92 | 67 | Remembering happy, sad, and neutral experiences | Sad versus neutral | Happy versus neutral |
| Knutson et al. (39) | 14 | 12 | 0 | 64 | Anticipating and experiencing monetary gains, losses, and neutral outcomes | None | Anticipating gain versus neutral outcome; experiencing gain versus neutral outcome |
| Kumari et al. (40) | 6 | 6 | 100 | 100 | Viewing positive, negative, and neutral picture-caption pairs | Negative versus neutral | Positive versus neutral |
| Lawrence et al. (41) | 9 | 11 | 100 | 44 | Viewing high- and low-intensity happy, sad, and fearful faces; neutral-face control | High-intensity fearful versus neutral; high-intensity sad versus neutral | High-intensity happy versus neutral |
| Mitterschiffthaler et al., 2003 (42) | 7 | 7 | 100 | 100 | Viewing positive and neutral images | None | Positive versus neutral |
| Mitterschiffthaler et al., 2008 (43) | 17 | 17 | 0 | 82 | Identifying colors of sad and neutral words | Sad versus neutral | None |
| Osuch et al. (44) | 16 | 17 | 6 | 69 | Listening to endorsed favorite and neutral music | None | Favorite versus neutral |
| Pizzagalli et al. (45) | 30 | 31 | 0 | 50 | Anticipating and experiencing monetary gains, losses, and neutral outcomes | Anticipating loss versus neutral outcome; experiencing loss versus neutral outcome | Anticipating gain versus neutral outcome; experiencing gain versus neutral outcome |
| Scheuerecker et al. (46) | 13 | 15 | 0 | 77 | Emotion (explicit) or gender (implicit) matching of negative faces to target; shape-matching control | Explicit plus implicit versus control | None |
| Strigo et al. (47) | 15 | 15 | 0 | 80 | Anticipating and experiencing painful and nonpainful thermal stimuli | Anticipating pain versus nonpain; experiencing pain versus nonpain | None |
| Surguladze et al. (48) | 16 | 14 | 100 | 38 | Viewing variable-intensity happy and sad faces | Parametric sad face response | Parametric happy face response |
| Townsend et al. (49) | 15 | 15 | 0 | 40 | Matching negative faces to facial emotion or word target; shape-matching control | Face matching versus control | None |
| Wang et al. (50) | 19 | 20 | 58 | 63 | Oddball target detection with sad or neutral picture as background | Sad versus neutral | None |
| Yang (51) | 10 | 10 | 0 | 100 | Viewing erotic and neutral film clips | None | Erotic versus neutral |
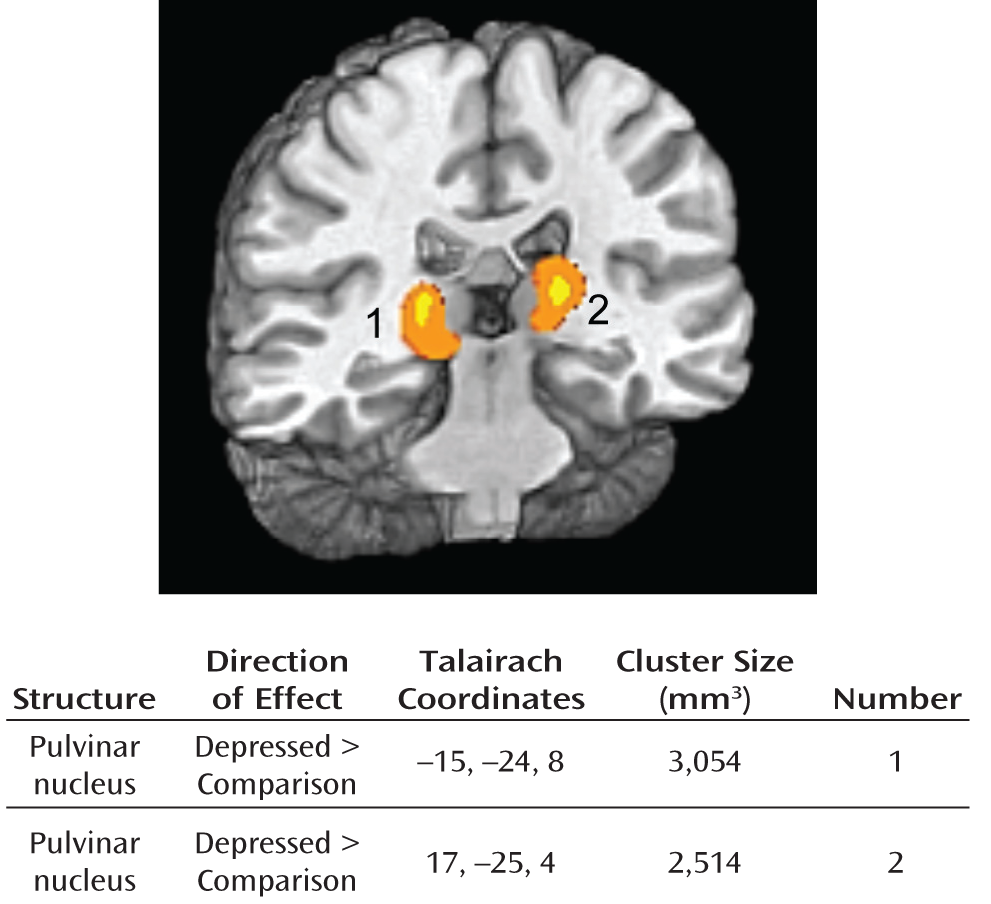
rCBF Meta-Analysis
fMRI Meta-Analysis
Negative stimuli.
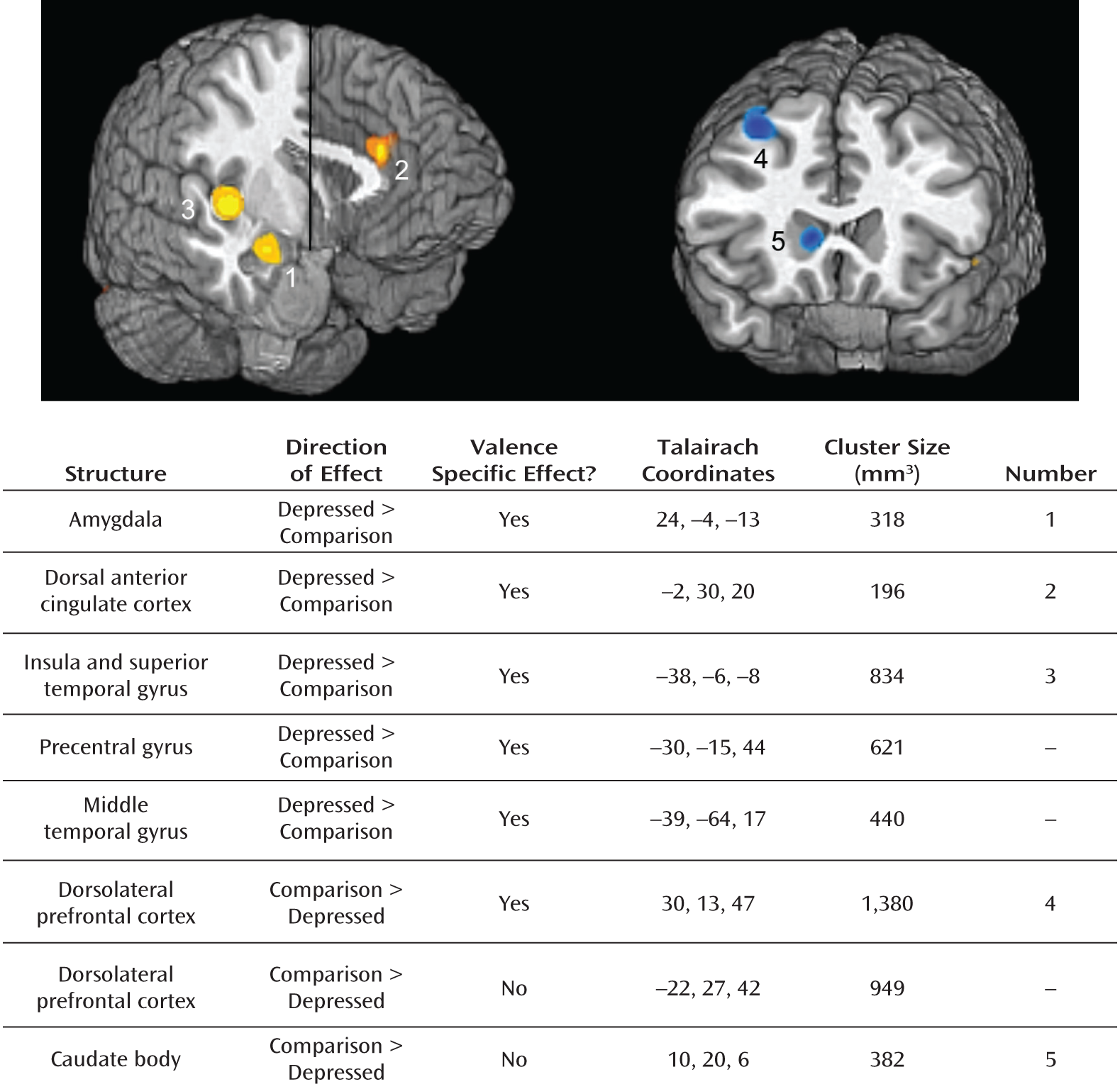
Positive stimuli.
Discussion
High Baseline Activity of Pulvinar Nucleus in Depression
Overreactive Salience Network and Low Response of Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex and Dorsal Striatum to Negative Information in Depression
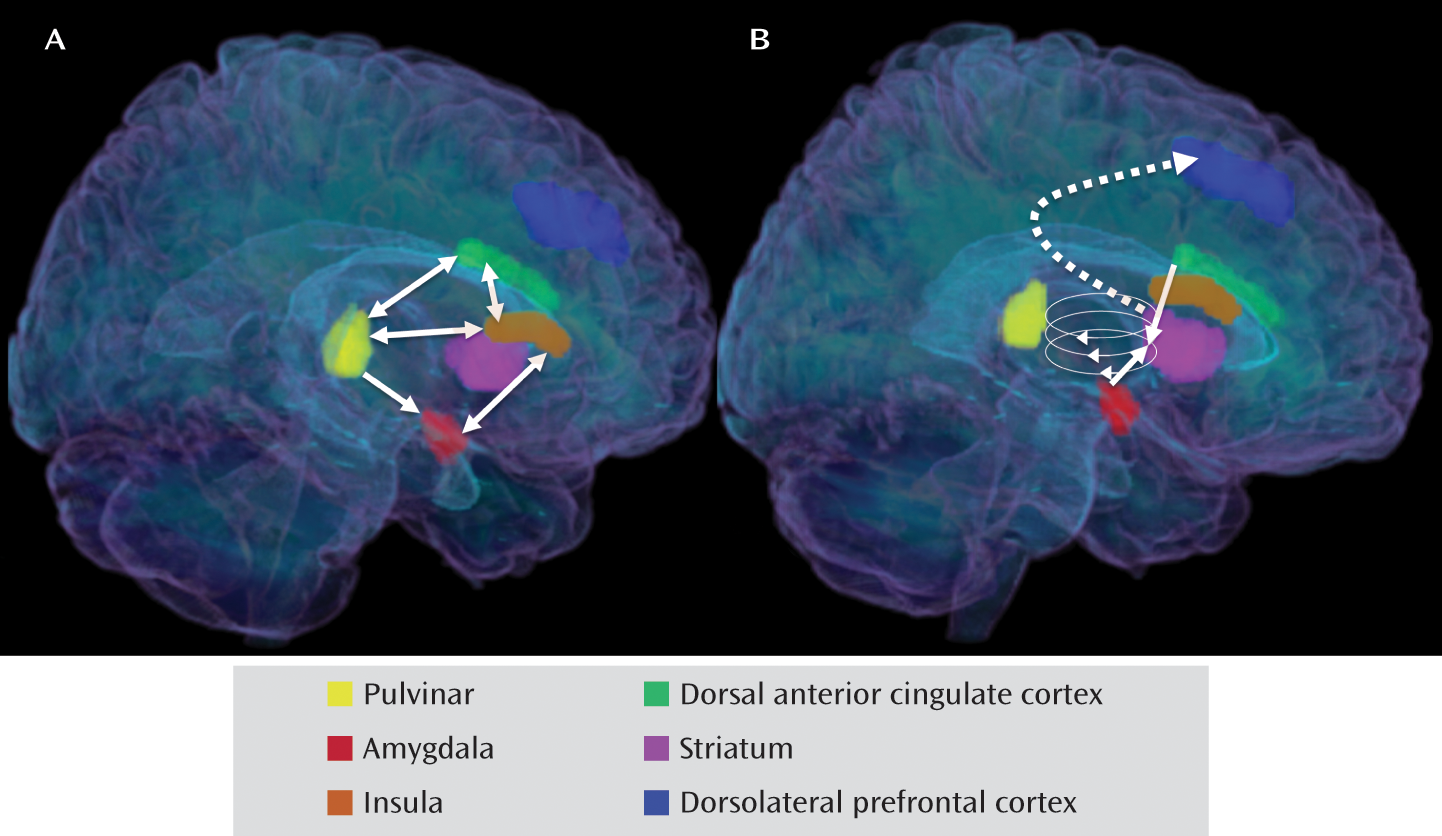
Patterns of Abnormal Neural Responding to Negative Stimuli in Depression: The Ascending Spiral Model of the Cortical-Striatal-Pallidal-Thalamic Circuit
Integrative Neural Model of Heightened Salience of Negative Stimuli in Depression
Limitations
Summary and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 266.54 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

