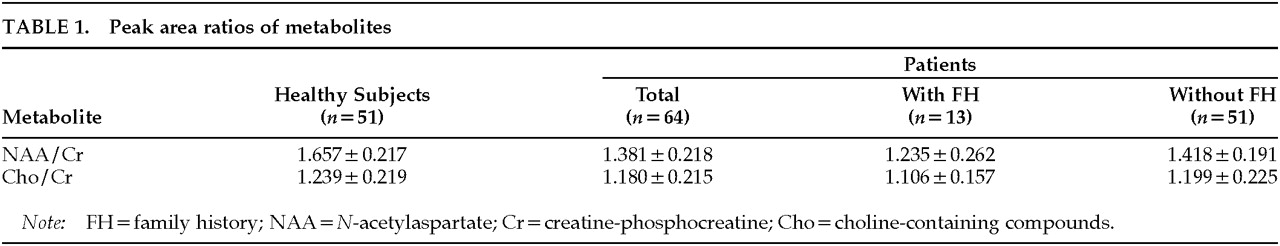
Sixty-four Japanese patients (34 men and 30 women, mean age 36.5±7.2 years; means±SD are reported) who met DSM-III-R
5 criteria for schizophrenia were recruited from the psychiatric wards in Fujimoto and Kagoshima University hospitals. None of the patients had a history of neurologic disorders, metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism), severe head trauma, or electroconvulsive therapy. No patients had been diagnosed with alcoholism, and none had access to alcohol or nonprescribed drugs for the more than 6 months that followed their admission. All patients were receiving typical neuroleptics such as haloperidol, perphenazine, propericiazine, nemonapride, and chlorpromazine at the time of MRS examination (mean chlorpromazine equivalent, 617±399 mg/day),
6 and 33 patients also were receiving anticholinergic agents such as biperiden or trihexyphenidyl. They had been ill for 14.9±7.8 years. A comparison group of 51 healthy subjects included hospital staff and university students (25 men and 26 women, mean age 35.5±7.9 years). None had a history of psychiatric or neurologic illness. All subjects were right-handed, as determined by the Edinburgh Inventory;
7 a laterality score greater than 80 qualified them as right-handed.
8 The Edinburgh Inventory score did not differ significantly between the patient and control groups (patient vs. control: 91.8±6.5 vs. 93.1±7.5;
t=1.027, df=113,
P=0.307). Nutritional condition was not systematically matched between groups. Subjects with total cholesterol greater than 240 mg/dl or abnormal electrolyte concentrations in routine blood chemistry screening were excluded. The definition of a positive FH was determined in accordance with the Family History Research Diagnostic Criteria.
9 Patients whose first- or second-degree relatives had histories of schizophrenia, delusional disorder, schizophreniform disorder, or schizoaffective disorder were defined as having a positive FH. Diagnoses in these relatives were made on the basis of information from their treating psychiatrists or physicians. Age and gender were not significantly different between patients with and without FH (with FH vs. without FH: mean age, 38.4±5.7 vs. 36.0±7.5 years;
t=1.112, df=62,
P=0.271; gender, 7 men and 6 women vs. 27 men and 24 women; χ
2=0.003, df=1,
P=0.999). The Edinburgh Inventory score was similar between the groups (with FH vs. without FH: mean score 91.6±6.3 vs. 91.9±6.6,
t=0.159, df=62,
P=0.874). All subjects gave written informed consent for their participation in the study.
The method of MRS data acquisition was similar to that in the previous study by Fukuzako and colleagues;
10 however, some parameters were different and the method of peak area measurement was improved. Investigations were conducted by using an MR system (Siemens-Asahi Meditec; Erlangen, Germany) with a magnetic field strength of 2.0 tesla. A quadrature detection head coil with a diameter of 29 cm was used. The head coil was tuned to 84.5 MHz for proton imaging and MRS. The volume of interest (VOI) was localized on the basis of series of T
1-weighted images (fast low-angle shot sequence, TR 23 ms, TE 10 ms, flip angle 35 degrees, slice thickness 5 mm, matrix size 192×256). Voxel placement was performed by a single expert (T. Matsumoto) who located the anterior hippocampus in the center of the VOI. The VOI (2×2×2 cm
3) included mainly the left medial temporal lobe (hippocampal formation, entorhinal cortex, and amygdala). Water-suppressed
1H MR spectra were obtained by using stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) pulse sequences. MR parameters were as follows: TR, 2,000 ms; TE, 60 ms; dwell time per point, 1,000 μs for 1,024 points; and filter band width, 500 Hz. After optimizing magnetic field homogeneity by shimming on the water signal, we obtained 256 measurements. Water-line widths below 4 Hz were achieved. Spectra were obtained through Fourier transformation of the raw data without line broadening. Chemical shifts were noted at NAA resonance (–CH
3) for 2.0 parts per million. Spectra of NAA (–CH
3), Cho, and Cr (–CH
3) were quantified by measurement of peak area. After automatic baseline correction (spline approximation), peak parameters such as height, position, and width were obtained by means of the standard software provided with the MAGNETOM Vision (Siemens, Germany; Lorentzian curve-fitting procedure). For each spectrum, integrated areas of the three metabolites were measured and ratios of NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr were calculated.
1H-MRS was performed twice, 1 to 2 weeks apart, in 9 patients for the assessment of test-retest reliability. Coefficients of variation for the metabolite ratios were 9.2% and 10.4% for NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr, respectively.
Statistical analysis was performed by using StatView 4.5 software. Two-tailed t-tests were used to assess differences between groups. The relationships between the two kinds of values were tested by using Pearson's product-moment correlation coefficient (r).