Shared decision making is being promoted as a promising approach for engaging patients with schizophrenia in medical decisions and improving satisfaction with and adherence to treatment (
1,
2). To implement shared decision making, both physicians and patients must commit to it and engage in a mutual decision process (
3). Most research, however, has addressed interventions that either focus on the physician's side (in regard to the physician's communication skills) or on informing patients about treatment options (known as decision aids) (
4). These approaches have been shown to be feasible in clinical practice but have had no strong effects on treatment patterns or adherence (
4), possibly because they are insufficient to motivate and enable patients to engage actively in decision making (
5). Moreover, these interventions rely on the physician's willingness to share responsibility in making treatment decisions, which has been shown to vary considerably (
6).
To overcome these limitations and because many patients do not feel competent to participate in decision making (
7), we developed an intervention that focuses on patients' communicative competencies. In somatic medicine similar programs have been shown to be effective in engaging patients in medical decisions and improving long-term compliance (
8–
10).
Methods
The training consisted of five one-hour sessions for a group of five to eight patients. The content of the training was derived from theoretical considerations about patients' contributions to the shared decision-making process (
3), from an adaptation of related approaches from somatic medicine (
10), and from pilot testing the training. The training sessions included motivational aspects (such as prospects of participation) and behavioral aspects (including role-play exercises). The training emphasized interaction between moderators and patients as well as mutual support. All sessions were led by a psychiatrist and a psychologist, neither of whom was in charge of the specific care of these patients. Patients in the control condition participated in a five-session cognitive training group.
Patients were recruited from a university psychiatric hospital in Munich, Germany, from May 2009 to February 2010. Male and female inpatients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder according to the ICD-10 who were 18–60 years of age were eligible for the study provided they were capable of tolerating a 60-minute interactive patient group. Patients were recruited until group size was reached and then randomly assigned to the intervention or control condition. A randomization list and numbered closed-allocation concealment envelopes were prepared before the study. Institutional review board approval was obtained for the study, and patients gave written informed consent before participating.
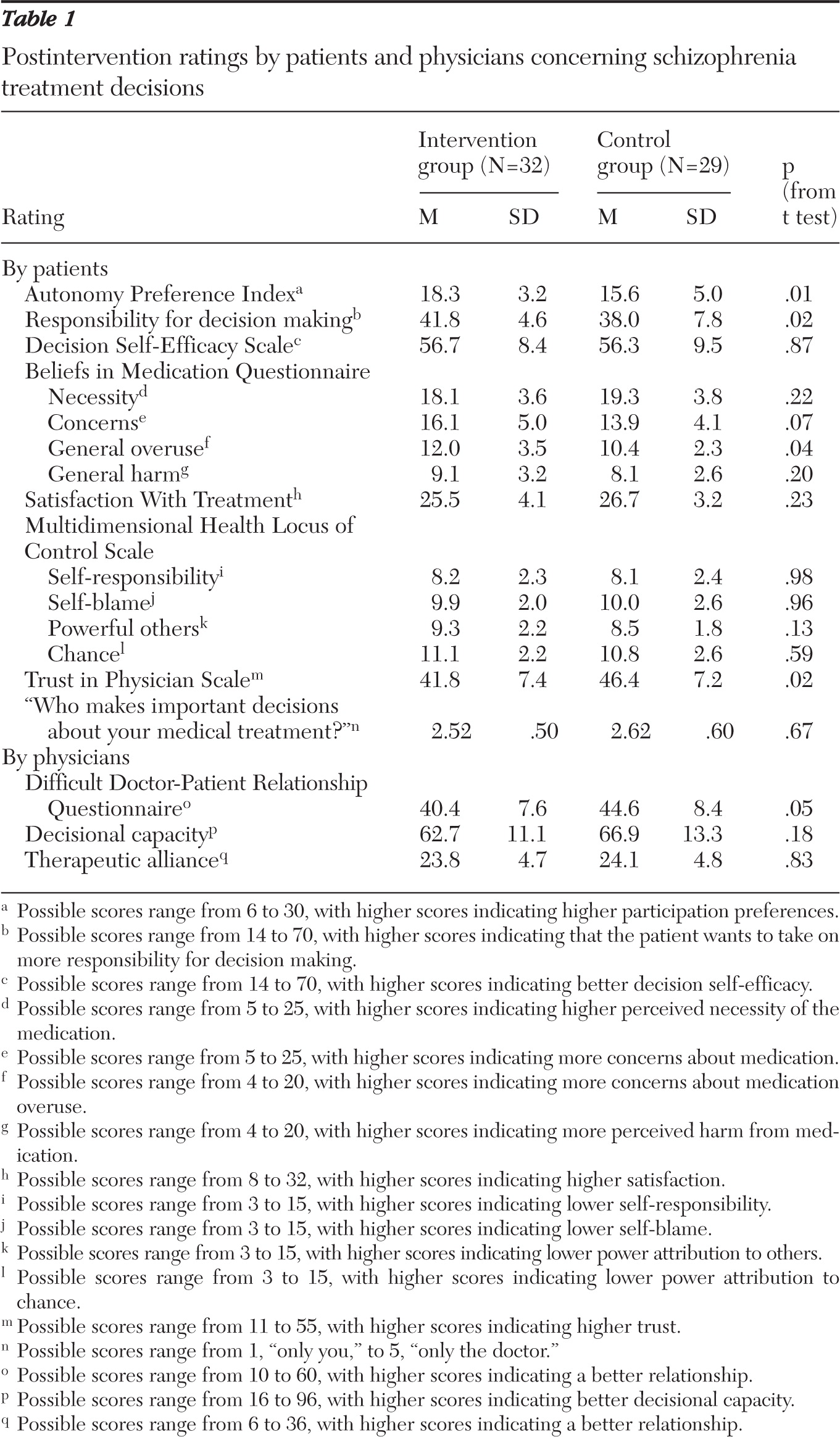
Before the intervention, patients' sociodemographic characteristics, participation preferences (based on the Autonomy Preference Index), decision self-efficacy (based on the Decision Self-Efficacy Scale), attitudes toward medication (based on the Beliefs in Medication Questionnaire), and satisfaction with treatment (satisfaction with treatment scale of the ZUF8) were obtained. Psychiatrists provided Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) scores.
After the intervention, patients' participation preferences, decision self-efficacy, attitudes toward medication, and treatment satisfaction were surveyed. In addition, the Trust in Physician Scale, the Multidimensional Health Locus of Control Scales, and a rating of the groups were administered. Finally, we administered a questionnaire on who should take responsibility for decision making. Here, patients answered 14 questions on different aspects of the treatment process (“Who is responsible [for ensuring] that there is a discussion about your treatment if you are suffering from side effects?”). Because internal consistency was high (α=.82), we used the sum score of all 14 items (“responsibility for decision making”) for further analyses.
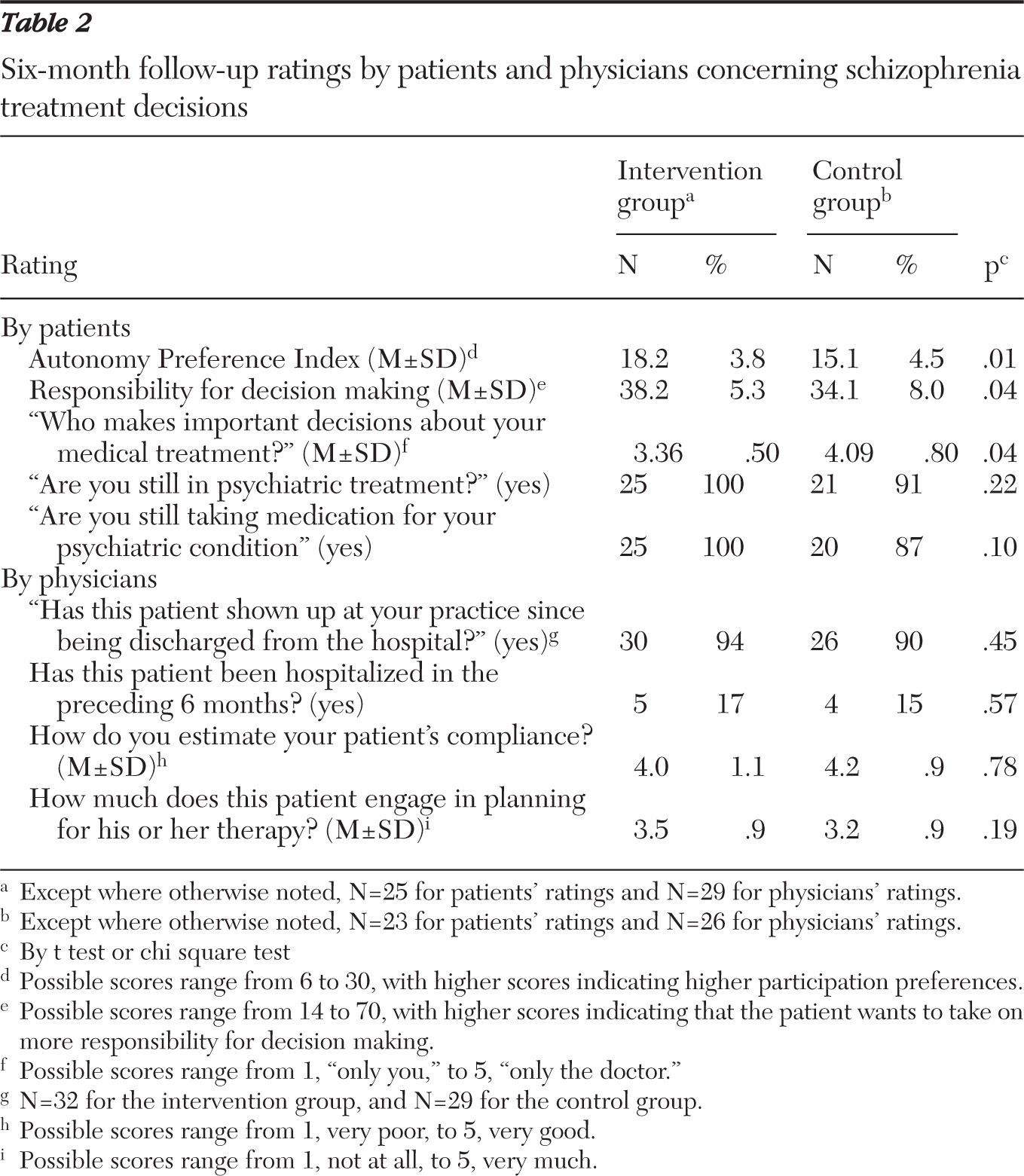
Psychiatrists provided ratings of their patients' decisional capacity (10-point rating scale) and the therapeutic alliance, and they filled out the Difficult Doctor-Patient Relationship Questionnaire. Six months after discharge from the hospital, patients completed the Autonomy Preference Index and our questionnaire on “responsibility for decision making.” They were asked who was making important medical decisions concerning their health and whether they were still taking medication. The outpatient psychiatrists were surveyed independently regarding their patients' compliance and rehospitalizations during the preceding six-month period.
The intervention and control group outcomes were compared with t tests and chi square tests. A p value less than .05 was considered significant.
[An appendix includes additional references concerning the instruments, information on the training sessions, and a CONSORT diagram of participation and is available online as a supplement to this brief report at
ps.psychiatryonline.org.]
Results
A total of 61 patients participated in the study (32 in the intervention and 29 in the control group). There were more female (N=38, 62%) than male (N=23, 38%) patients, and the mean±SD age was 40.7±11.7. Duration of illness was 11.1±9.6 years; patients had a mean of five previous hospitalizations. At study entry patients had been hospitalized for a mean of four weeks, and their illness was considered moderate (PANSS score 75.5±19.0, range 30–210). There were more women in the control group, and patients in the intervention group had higher PANSS scores. However, there were no significant differences between the intervention and control groups for any baseline measure.
After the group sessions, patients in the intervention group compared with patients in the control group showed higher participation preferences and wanted to take on more responsibility in decision making (
Table 1). This effect was still present six months after discharge from the hospital (
Table 2).
Intervention group patients expressed lower trust in their physicians, and psychiatrists perceived intervention group patients as more difficult than control group patients. Finally, intervention group patients became more skeptical about their treatment. There were no differences in patients' satisfaction with treatment, self-esteem about decision making, or perceived necessity of treatment. Physicians did not rate intervention and control group patients differently with respect to their decisional capacity or therapeutic alliance (
Table 1).
Overall, patients rated the training as very positive and helpful. Most patients (N=28, 88%) indicated that they would aim to play a more active role in future consultations. At follow-up, intervention group patients felt more involved in decision making than did control group patients, and there was a trend, according to self-ratings, that a higher proportion of intervention group patients continued their medication (
Table 2). Among the physicians' ratings, there were no differences between the groups with regard to rehospitalizations, engagement in decision making, or patients' compliance. For the three control group patients who stated that they no longer took medication, the psychiatrists estimated compliance to be good.
Discussion and conclusions
Our study had several limitations. It was conducted at a single center and involved the same moderators for all group sessions. Results may thus not be generalizable to other settings and should be judged as generating rather than confirming hypotheses. Finally, there were some baseline differences between the intervention and control groups that may have affected the results.
Patients who participated in the shared decision-making training were more interested and also more motivated to engage in decision making. This effect was still present six months after the intervention. Moreover, our intervention also changed patients' behavior, in that psychiatrists perceived patients in the intervention group as more difficult to treat (stressful) than control group patients. There were no effects on patients' decisional self-efficacy, which might be explained by a ceiling effect. With respect to locus of control, there was only a trend that intervention group patients gave slightly higher ratings on the “powerful others” subscale, indicating that they attributed less power to their physicians. In addition there was a trend for intervention patients to feel more involved in the decision-making process and to be more persistent about taking medication (self-rating) at follow-up. The latter finding, however, was not replicated by physicians' ratings.
Alongside these encouraging findings, we also found a drop in patients' trust in physicians and more skepticism toward psychiatric treatment. On the one hand one could argue that the training brought unnecessary discord into the doctor-patient relationship by making patients skeptical and less cooperative. This fits the traditional model of compliance, in which patients are expected to follow their physician's advice without disagreeing (
11). Accordingly, our intervention may have worsened some mediators of patients' compliance. Apparently, some psychiatrists might have felt this way and rated intervention patients as more difficult. Simultaneous shared decision-making training for physicians (including skills to deal with assertive patients) might have quelled some of the irritations shown in our study.
On the other hand, from the mental health care consumers' perspective, patients have a right to disagree with their physicians and to argue for treatment they believe to be best. Here, the concept of “adherence” might suit better, whereby patients actively influence treatment decisions and decide whether they want to consent to them (
12). Thus our results might be interpreted as patients who no longer follow their doctors blindly but ask for explanations or challenge doctors' recommendations when they go against the patient's preferences (
13). Therefore, our intervention might have boosted patients' behavior in the direction of adherence, even if some psychiatrists were unhappy with the results. This interpretation may be supported by our follow-up findings, in which a greater proportion of intervention group patients than control group patients indicated that they were still taking medication.
Acknowledgments and disclosures
This work was supported by research project grant 2168-1746.1/2007 from the German-Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development to Dr. Hamann and is registered as NCT00885716 at clinicaltrials.gov. The follow-up of the patients was made possible through a Young Minds in Psychiatry Award to Dr. Hamann from the American Psychiatric Association.
The authors report no competing interests.