Uncovering the Hidden Risk Architecture of the Schizophrenias: Confirmation in Three Independent Genome-Wide Association Studies
Abstract
Objective:
Method:
Results:
Conclusions:
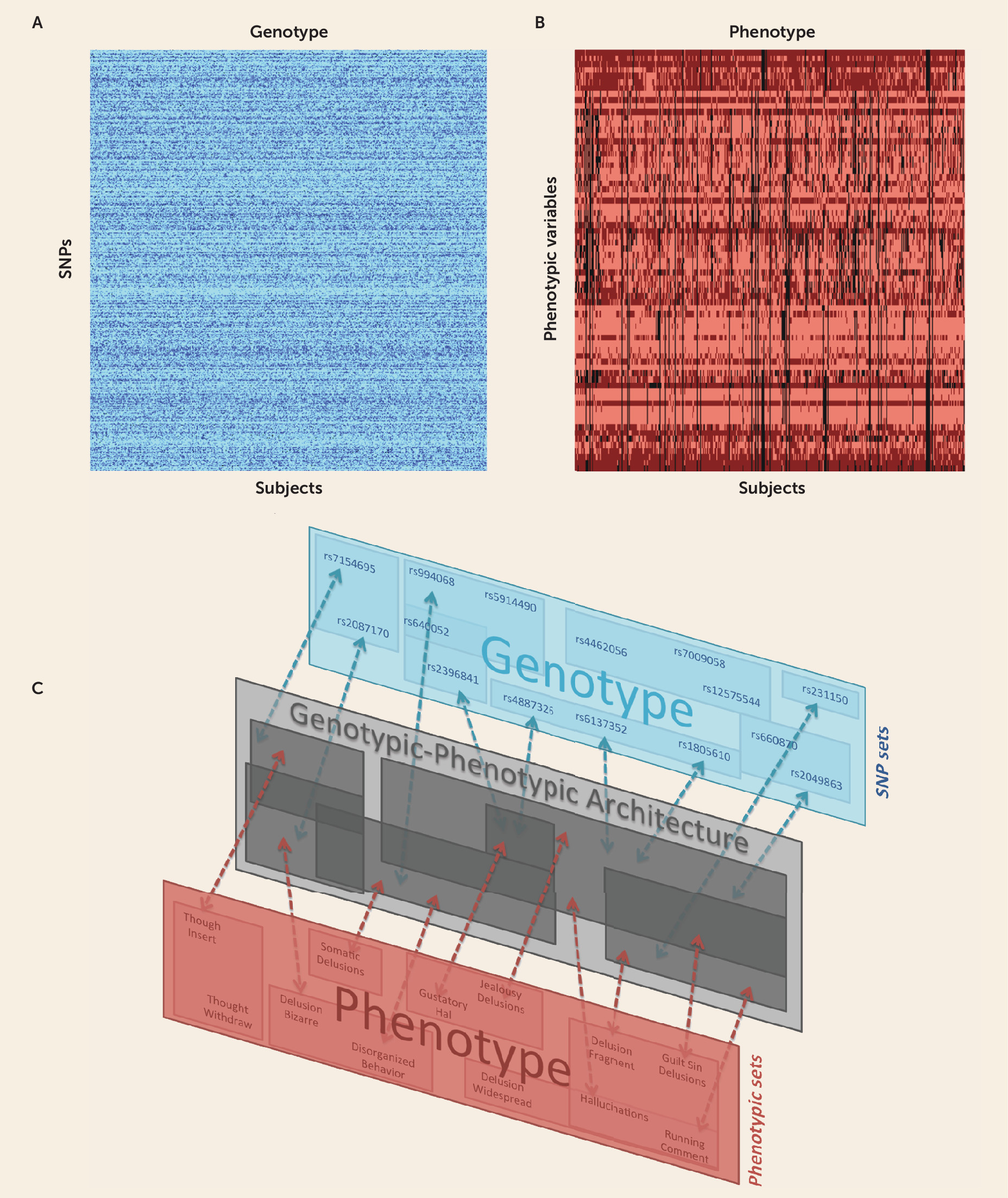
Method
| SKAT p Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP set | Group | Average SNP | Best SNP | Worst SNP | Subjects (N) | SNPs (N) | Risk (%) |
| 19_2 | 2.88E–05 | 3.43E–02 | 4.60E–04 | 1.38E–02 | 9 | 9 | 100 |
| 88_64 | 1.43E–11 | 2.06E–03 | 2.15E–07 | 1.79E–02 | 176 | 6 | 96 |
| 81_13 | 1.46E–10 | 5.44E–03 | 2.15E–07 | 3.70E–02 | 234 | 10 | 95 |
| 87_76 | 7.11E–07 | 1.05E–02 | 1.37E–05 | 3.13E–02 | 74 | 3 | 95 |
| 58_29 | 5.41E–04 | 6.52E–03 | 2.07E–04 | 2.83E–02 | 125 | 6 | 94 |
| 83_41 | 3.87E–05 | 1.56E–04 | 1.01E–04 | 2.68E–04 | 61 | 4 | 93 |
| 9_9 | 1.51E–06 | 2.52E–03 | 1.23E–04 | 1.18E–02 | 144 | 19 | 92 |
| 10_4 | 3.83E–05 | 1.72E–02 | 2.11E–04 | 1.05E–02 | 58 | 11 | 91 |
| 14_6 | 2.38E–06 | 1.85E–03 | 1.23E–04 | 5.87E–03 | 22 | 11 | 90 |
| 56_30 | 1.91E–10 | 4.33E–03 | 2.15E–07 | 2.10E–02 | 382 | 11 | 88 |
| 42_37 | 4.15E–06 | 2.35E–02 | 6.59E–05 | 1.38E–02 | 70 | 24 | 86 |
| 65_25 | 3.95E–05 | 1.99E–02 | 2.53E–04 | 8.83E–02 | 62 | 5 | 86 |
| 71_55 | 1.90E–05 | 3.99E–04 | 2.63E–05 | 1.08E–03 | 63 | 6 | 86 |
| 12_11 | 6.53E–04 | 2.28E–02 | 7.34E–03 | 1.05E–01 | 94 | 11 | 84 |
| 90_78 | 7.87E–04 | 2.99E–02 | 3.58E–02 | 9.53E–02 | 200 | 4 | 83 |
| 77_5 | 4.86E–05 | 5.01E–04 | 2.08E–05 | 1.49E–03 | 297 | 5 | 82 |
| 88_8 | 2.88E–04 | 2.95E–02 | 3.58E–02 | 8.36E–02 | 32 | 10 | 82 |
| 51_28 | 2.07E–04 | 2.25E–02 | 1.75E–02 | 3.13E–02 | 258 | 3 | 81 |
| 59_48 | 2.32E–09 | 9.48E–03 | 2.38E–05 | 2.96E–02 | 174 | 7 | 80 |
| 41_12 | 1.36E–03 | 1.62E–02 | 1.12E–01 | 2.17E–02 | 78 | 3 | 76 |
| 22_11 | 6.24E–05 | 4.29E–04 | 1.33E–04 | 1.08E–03 | 97 | 12 | 75 |
| 13_12 | 4.52E–05 | 3.61E–04 | 5.88E–05 | 1.45E–03 | 148 | 10 | 75 |
| 31_22 | 1.01E–04 | 2.37E–04 | 1.11E–04 | 4.03E–04 | 92 | 7 | 74 |
| 85_84 | 1.53E–05 | 1.01E–04 | 1.37E–05 | 1.81E–04 | 39 | 4 | 74 |
| 87_84 | 1.19E–04 | 1.40E–02 | 1.37E–05 | 1.30E–02 | 22 | 13 | 74 |
| 16_10 | 1.81E–03 | 1.59E–02 | 2.92E–03 | 5.92E–02 | 141 | 12 | 73 |
| 56_19 | 2.02E–04 | 6.69E–04 | 1.02E–04 | 1.76E–03 | 90 | 5 | 73 |
| 75_31 | 2.61E–05 | 1.37E–02 | 1.02E–04 | 9.53E–02 | 197 | 8 | 73 |
| 81_73 | 1.13E–05 | 2.99E–02 | 2.57E–04 | 1.29E–02 | 213 | 10 | 73 |
| 85_23 | 6.20E–03 | 9.46E–03 | 5.58E–03 | 1.16E–02 | 53 | 4 | 73 |
| 21_8 | 6.24E–05 | 4.29E–04 | 1.33E–04 | 1.08E–03 | 188 | 12 | 71 |
| 76_74 | 1.58E–17 | 1.33E–02 | 1.12E–05 | 1.17E–02 | 284 | 14 | 71 |
| 61_39 | 1.04E–03 | 2.43E–02 | 1.90E–03 | 5.45E–02 | 51 | 3 | 71 |
| 75_67 | 3.76E–18 | 7.16E–02 | 2.15E–07 | 1.00E–03 | 877 | 32 | 71 |
| 76_63 | 2.07E–02 | 2.25E–02 | 1.75E–02 | 3.13E–02 | 34 | 3 | 71 |
| 81_3 | 6.24E–05 | 4.29E–04 | 1.33E–04 | 1.08E–03 | 107 | 12 | 71 |
| 87_26 | 2.49E–03 | 6.03E–03 | 4.14E–03 | 1.12E–02 | 28 | 5 | 71 |
| 88_43 | 1.37E–04 | 1.85E–03 | 6.03E–04 | 4.82E–03 | 70 | 7 | 71 |
| 25_10 | 3.49E–06 | 1.67E–03 | 1.11E–04 | 1.53E–02 | 124 | 9 | 70 |
| 12_2 | 1.81E–03 | 1.59E–02 | 2.92E–04 | 5.92E–02 | 194 | 12 | 70 |
| 52_42 | 5.70E–05 | 5.06E–03 | 6.59E–05 | 3.60E–02 | 87 | 16 | 70 |
| 54_51 | 1.49E–05 | 5.01E–04 | 2.08E–04 | 1.49E–03 | 132 | 5 | 70 |
Results
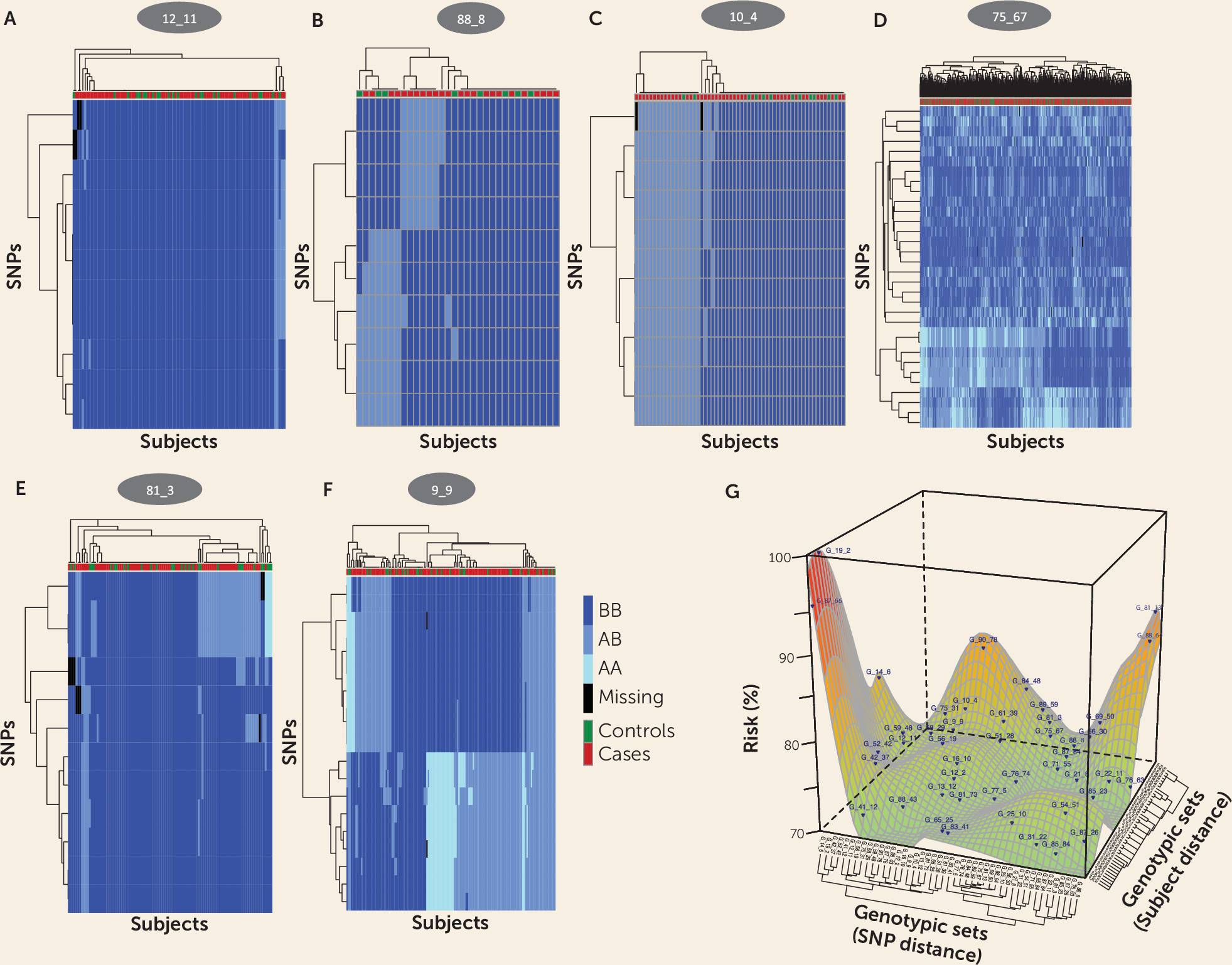
Identifying Many SNP Sets as Candidates for Schizophrenia Risk
SNP Sets Vary Greatly in Risk for Schizophrenia
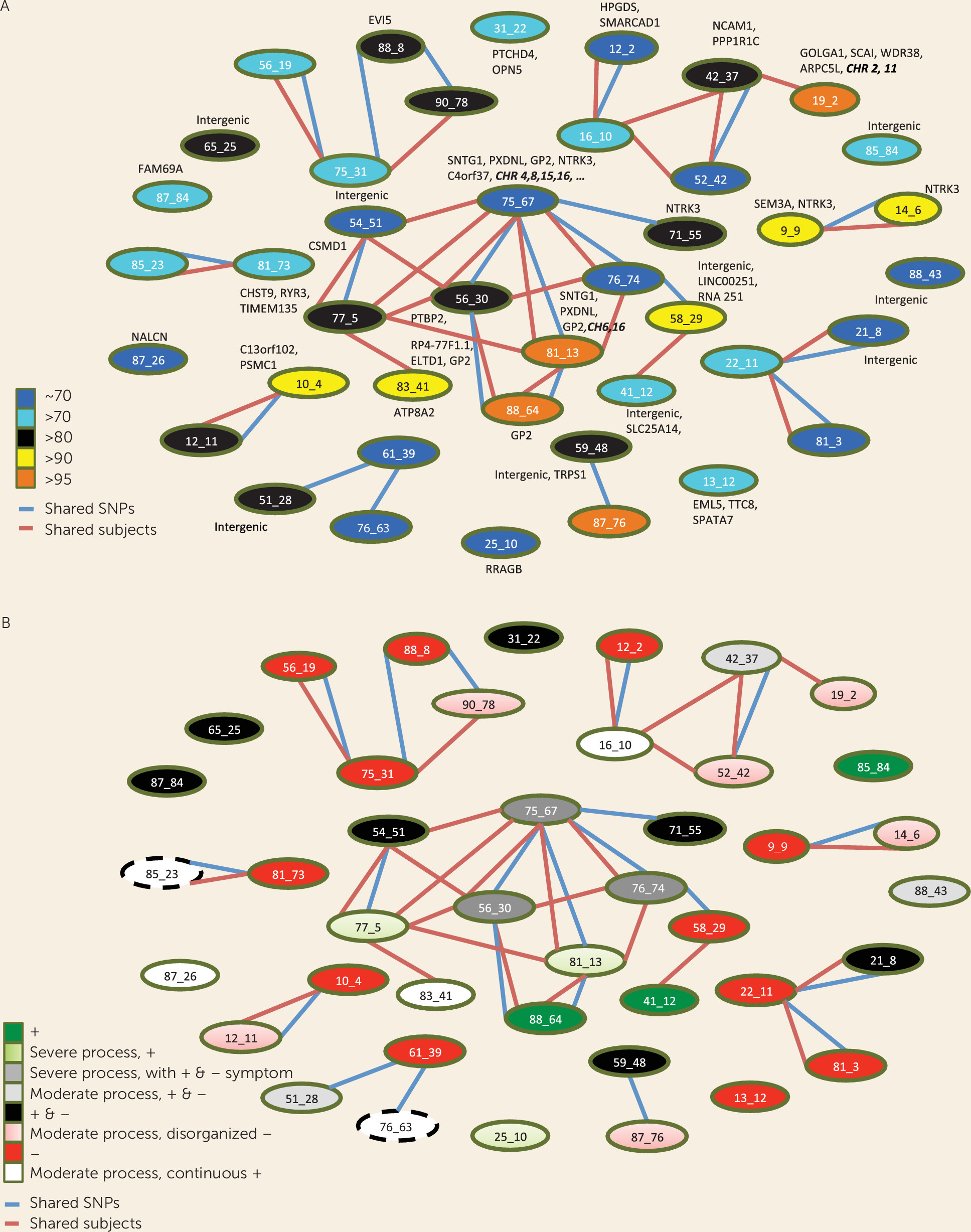
Relations Among SNP Sets to One Another and to Gene Products
| Signaling Pathways/Function | Genes | SNP Sets | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neural development | DKK4, STKY1, VANGL1 | 75_67 | Severe process, + and – |
| NCAM1 | 42_37 | Moderate process, + and – | |
| 52_42 | Moderate process, – | ||
| CHST9 | 81_73 | – | |
| EML5 | 13_12 | – | |
| SEM3A | 9_9 | Moderate process, – | |
| Neurotrophin function | NTRK3 | 75_67 | Severe process, + and – |
| Upstream region | 71_55 | + and – | |
| SNTG1 | 81_13 | Severe process, + | |
| MAGEH1 | 25_10 | Severe process, + | |
| Neurotransmission | NETO2 | 76_74, 75_67 | Severe process, with + and – |
| OPN5 | 31_22 | + | |
| NALCN | 87_26 | Moderate process, continuous + | |
| Neuronal function and neurodegenerative disorders | SPATA7, ZC3H14 | 13_12 | – |
| SLC20A2 | 41_12 | + |
Complex Genotypic-Phenotypic Relationships in Schizophrenia
| Schizophrenia Class, Symptomsb, and DSM Ratings | Phenotypic Sets | SNP Sets | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe process, with positive and negative symptom schizophrenia | |||
| Positive symptoms; moderate severity of impairment; unable to function since onset | 15_13 | 56_30 | 2.55E–05 |
| Auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries) | 12_11 | 1.79E–04 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries); thought echoing; withdrawal; insertion and broadcasting; delusions of mind reading | 21_1 | 3.66E–04 | |
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (ever; 2 or more voices); grossly disorganized behavior | 50_46 | 5.70E–04 | |
| Hallucinations (mood incongruent); auditory hallucinations; somatic hallucinations (olfactory; gustatory; tactile); religious delusions; delusions of mind reading; delusions of control; thought echoing; withdrawal; insertion and broadcasting | 9_6 | 4.45E–03 | |
| Hallucinations (mood incongruent); persecutory delusions; delusions of reference; jealousy delusions; bizarre delusions; disorganized odd behavior; disorganized odd speech; delusions, fragmented (unrelated themes); delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life); thought insertion; flat affect; avolition and apathy | 46_23 | 4.15E–03 | |
| Continuously positive symptoms; severe impairment; continuous course; no affective symptoms | 15_13 | 75_67 | 2.31E–13 |
| Grossly disorganized behavior; severe impairment; continuous course | 54_11 | 4.90E–06 | |
| Delusions of persecution and reference; disorganized speech; severe impairment; unable to function since onset | 30_17 | 2.56E–04 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (ever; 2 or more voices; running commentaries); jealousy delusions | 18_13 | 3.50E–04 | |
| Thought insertion and withdrawal | 27_6 | 3.62E–03 | |
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices); grossly disorganized behavior | 50_46 | 3.61E–03 | |
| Delusions, persecutory and reference; delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life) | 61_18 | 4.28E–03 | |
| Disorganized; odd speech | 64_11 | 1.45E–03 | |
| Delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life); continuous course | 65_64 | 1.21E–03 | |
| Continuously positive symptoms; severe impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 15_13 | 76_74 | 1.07E–07 |
| Delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life) | 65_64 | 1.47E–03 | |
| Positive and negative schizophrenia | |||
| Auditory hallucinations; delusions (any); bizarre delusions; disorganized speech and behavior; flat affect; alogia; avolition | 12_4 | 59_48 | 1.88E–04 |
| Auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries) | 42_9 | 71_55 | 1.98E–03 |
| Negative schizophrenia | |||
| Thought insertion and withdrawal | 52_28 | 58_29 | 1.44E–04 |
| Disorganized speech; odd speech | 7_3 | 9_9 | 1.97E–04 |
| Flat affect; persecutory delusions | 48_41 | 2.23E–03 | |
| Delusions of mind reading; guilt delusions; sin delusions; jealousy delusions | 26_8 | 4.20E–03 | |
| Flat affect; apathy; avolition | 69_41 | 22_11 | 5.52E–05 |
| Flat affect; apathy; avolition; alogia; continuous mixture of positive and negative symptoms | 10_5 | 4.62E–04 | |
| Disorganized and odd speech | 17_2 | 1.01E–04 | |
| Positive schizophrenia | |||
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (ever; 2 or more voices); no affective symptoms | 63_24 | 88_64 | 3.45E–04 |
| Delusions of jealousy; auditory hallucinations (running commentaries) | 69_66 | 4.49E–03 | |
| Severe process, positive schizophrenia | |||
| Continuously positive symptoms; severe impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 22_13 | 77_5 | 5.66E–05 |
| Auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries) | 18_13 | 3.25E–03 | |
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries); continuous course | 53_6 | 4.76E–03 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (ever; voices; noises; music) | 59_41 | 1.22E–03 | |
| Continuously positive symptoms; severe impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 20_19 | 81_13 | 2.83E–04 |
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (ever; 2 or more voices); bizarre delusions; delusions, fragmented (unrelated themes); delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life) | 55_7 | 8.57E–04 | |
| Delusions of reference; delusions of persecution | 34_17 | 2.40E–03 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (running commentaries); jealousy delusions | 69_66 | 1.30E–03 | |
| Severe impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 27_7 | 25_10 | 4.76E–06 |
| Auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries) | 18_13 | 9.50E–05 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (ever; voices; noises; music); auditory hallucinations (2 or more voices; running commentaries); thought echoing | 4_1 | 2.49E–03 | |
| Delusions of reference; delusions of persecution | 66_54 | 2.10E–03 | |
| Bizarre delusions; delusions of mind reading; delusions, widespread (intrude into most aspects of life) | 8_4 | 1.93E–03 | |
| Moderate process, disorganized negative schizophrenia | |||
| Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior; disorganized speech | 51_38 | 19_2 | 4.03E–04 |
| Moderate deterioration; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 42_7 | 14_6 | 4.96E–04 |
| Grossly disorganized and inappropriate behavior | 18_3 | 2.55E–03 | |
| Auditory hallucinations (running commentaries); thought echoing | 46_29 | 3.78E–03 | |
| Moderate process, positive and negative schizophrenia | |||
| Hallucinations (any); auditory hallucinations (ever; voices; noises; music); continuous mixture of positive and negative symptoms; continuous course; moderate impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 5_2 | 42_37 | 1.32E–04 |
| Bizarre delusions; delusions of reference | 57_39 | 4.70E–03 | |
| Continuous mixture of positive and negative symptoms; continuous course; moderate impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 11_5 | 88_43 | 6.88E–04 |
| Auditory hallucinations (ever); bizarre delusions; delusions, fragmented (unrelated to theme) | 24_4 | 51_28 | 9.58E–04 |
| Moderate process, continuous positive schizophrenia | |||
| No affective symptoms | 48_7 | 16_10 | 1.44E–03 |
| Continuously positive symptoms; severe impairment; unable to function since onset; no affective symptoms | 28_23 | 83_41 | 3.48E–03 |
| Continuously positive symptoms; no affective symptoms | 25_20 | 87_26 | 4.22E–03 |
Positive and Negative Symptoms Differentiate Classes of Schizophrenia
Replication of Results in Two Independent Samples
Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
Replication: A Lock and Key Combination of Genomics and Phenomics
Acknowledgments
Footnote
Supplementary Material
- View/Download
- 5.81 MB
- View/Download
- 1.83 MB
- Download
- 33.17 KB
- View/Download
- 238.05 KB
- Download
- 96.03 KB
- Download
- 37.50 KB
- Download
- 36.92 KB
- View/Download
- 72.10 KB
- Download
- 55.10 KB
- Download
- 51.82 KB
- Download
- 50.59 KB
- Download
- 12.02 KB
References
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
History
Authors
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
For more information or tips please see 'Downloading to a citation manager' in the Help menu.
View Options
View options
PDF/EPUB
View PDF/EPUBLogin options
Already a subscriber? Access your subscription through your login credentials or your institution for full access to this article.
Personal login Institutional Login Open Athens loginNot a subscriber?
PsychiatryOnline subscription options offer access to the DSM-5-TR® library, books, journals, CME, and patient resources. This all-in-one virtual library provides psychiatrists and mental health professionals with key resources for diagnosis, treatment, research, and professional development.
Need more help? PsychiatryOnline Customer Service may be reached by emailing [email protected] or by calling 800-368-5777 (in the U.S.) or 703-907-7322 (outside the U.S.).

